Top 10 Best Foods and Drinks for Muscle Recovery
If you enjoy working out or strenuous physical activities such as long-distance bicycling or trail running, you are likely to experience muscle soreness. ... read more...Muscle soreness is not only unpleasant, but it may also interfere with your exercises and daily activities. Many recovery strategies, fortunately, can help reduce muscle soreness, minimize exercise-induced muscle damage, and promote muscle recovery. Below are some of the Best Foods and Drinks for Muscle Recovery you can refer to!
-
Both experienced athletes and novice gym-goers may benefit from drinking tart cherry juice. Tart cherry juice and tart cherry juice extract have been shown in studies to help muscle recovery and lessen delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS). DOMS is a muscle injury that happens as a result of unfamiliar or intensive activity. It causes symptoms such as severe mobility restrictions, swelling, and stiffness.
Exercise increases oxidative stress, cellular damage, and inflammation in addition to DOMS. Antioxidant-rich foods and beverages, on the other hand, may help to mitigate these negative effects and accelerate healing. The plant compounds anthocyanins are abundant in tart cherry juice. Drinking tart cherry juice accelerated muscle recovery, decreased DOMS, and lowered markers of inflammation after exercise, according to a 2021 review of 25 research. They have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which may help to minimize perceived soreness and exercise-induced muscle damage (EIMD).

Tart cherry juice 
Tart cherry juice -
Watermelon is nutrient-dense, sweet, and hydrating. Furthermore, eating watermelon or drinking watermelon juice may help enhance muscle recovery after exercise. The amino acid L-citrulline is abundant in watermelon. This amino acid, in addition to being a protein building block, may have antioxidant properties and boost nitric oxide production (NO). NO boosts cellular energy and improves blood circulation to muscles. This might explain why some research suggests that watermelon juice can help minimize muscle soreness and damage after exercise.
A small 2013 research involving 7 athletes found that drinking 16.9 ounces (500 mL) of either natural watermelon juice or watermelon juice enhanced with L-citrulline reduced muscle soreness 24 hours after exercise more than a placebo. Watermelon provides key nutrients including carbohydrates, amino acids, and antioxidants that help with workout performance and recovery. As a consequence, besides its possible advantages for muscle soreness, it remains a healthy choice for exercise enthusiasts.

Watermelon and watermelon juice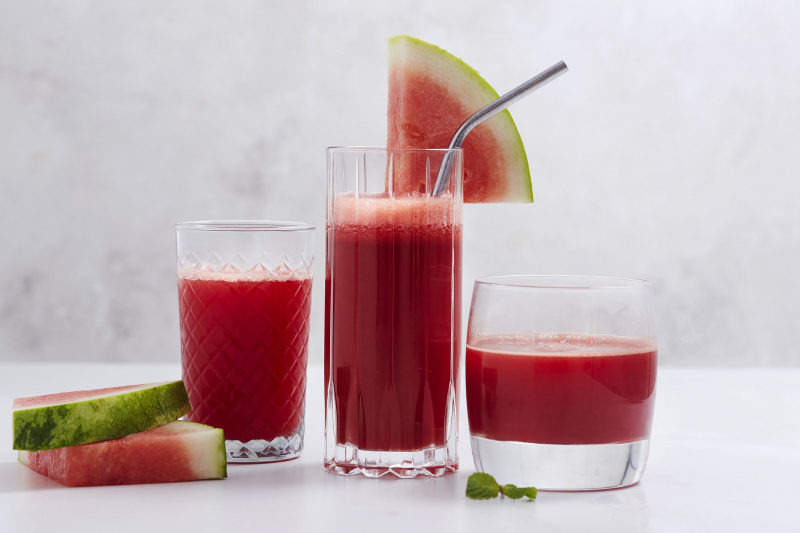 
Watermelon and watermelon juice -
Sardines, salmon, and trout are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which your body needs for muscle recovery. Fish is primarily a highly bioavailable source of protein, a macronutrient that helps muscle repair, which is the process of repairing muscle cells after exercise-induced damage.
According to some experts, consuming roughly 1.1 ounces (30 grams) of protein after exercise helps muscle recovery. For instance, 1 ounce (29 grams) of cooked salmon contains 4 ounces (113 grams). Omega-3 fats found in fatty fish may help reduce DOMS, fight inflammation, and promote muscular building. To maintain optimal muscle recovery, experts recommend consuming 0.06–0.11 ounces (1.8–3 grams) of omega-3 fatty acids after exercise. This may be easily acquired by eating fatty fish like salmon or taking an omega-3 supplement after working out.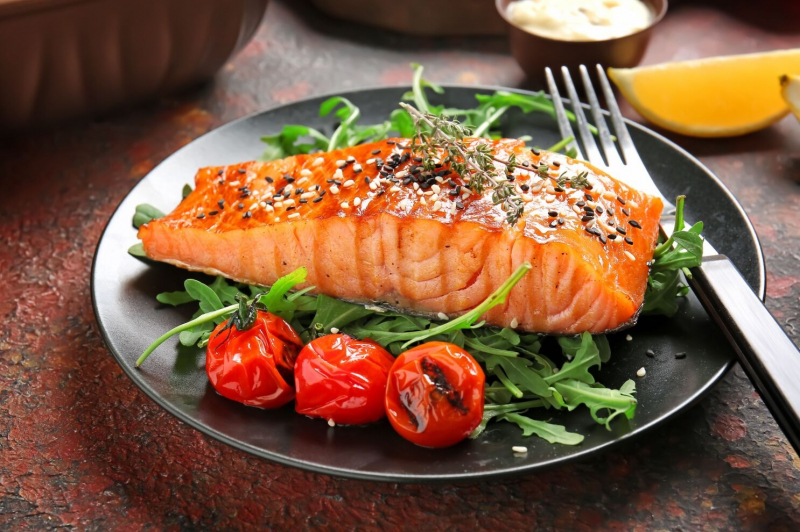
Fatty fish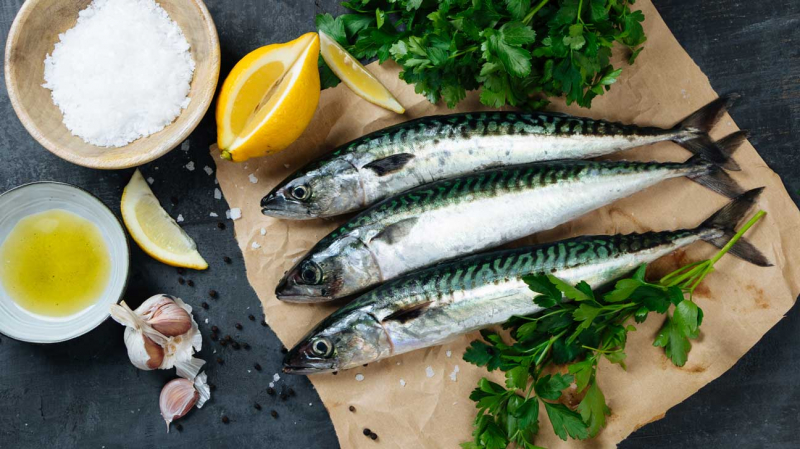 
Fatty fish -
Polyphenols, which are plant compounds with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, are abundant in pomegranate juice. Pomegranate juice, as a result, may aid muscle recovery.
9 elite weightlifters drank 8.5 ounces (250 mL) of pomegranate juice or a placebo three times a day for three days before Olympic Weightlifting training sessions in a small 2017 research. 1 hour before training sessions, they were given an additional 16.9 ounces (500 mL) of juice or a placebo. Pomegranate juice decreased the release of malondialdehyde (MDA), an oxidative stress marker, and boosted antioxidant defenses when compared to placebo treatment. This shows that the drink may help with muscle recovery. Pomegranate juice and supplements have also been demonstrated to reduce DOMS, lower inflammatory markers, and speed up muscle recovery in other studies.
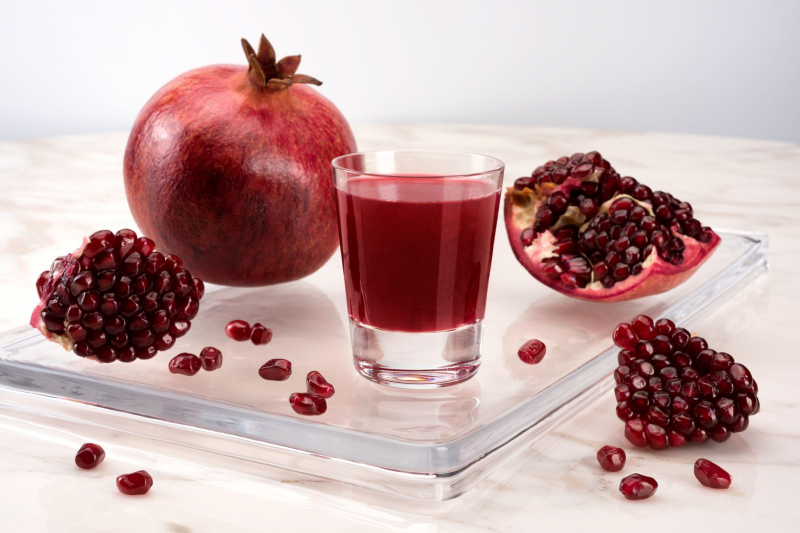

Pomegranate juice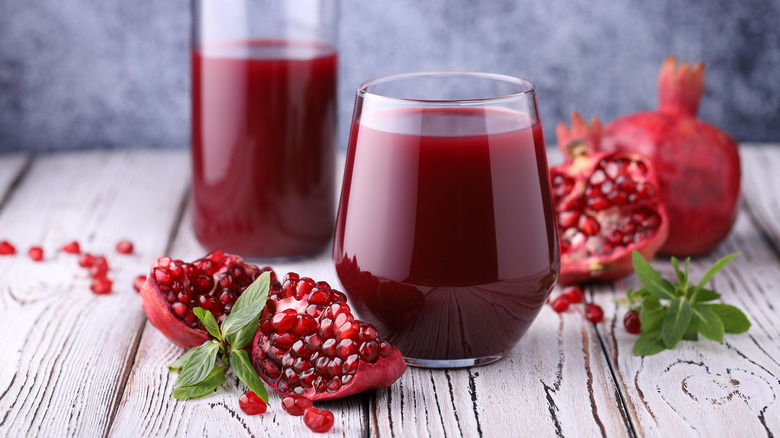 
Pomegranate juice -
Beet juice is high in dietary nitrates and pigments called betalains. Dietary nitrates may increase the efficiency of mitochondria, which are organelles or parts of cells that provide the energy that fuels your cells. Meanwhile, betalains may help to minimize oxidative stress and inflammation.
A 2016 research of 30 active men found that drinking beetroot juice immediately after heavy activity, 24 hours later, and 48 hours later decreased muscular pain and sped muscle recovery more than a placebo. Furthermore, a 2021 research of 13 soccer players found that consuming beet juice for 3–7 days before, on the day of, and 3 days after exercise decreased DOMS. During the recovery period, it also increased workout performance.
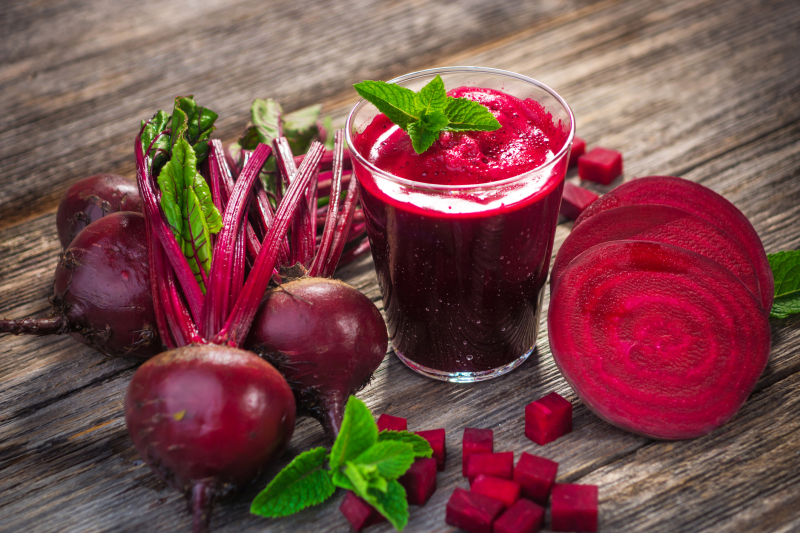

Beet juice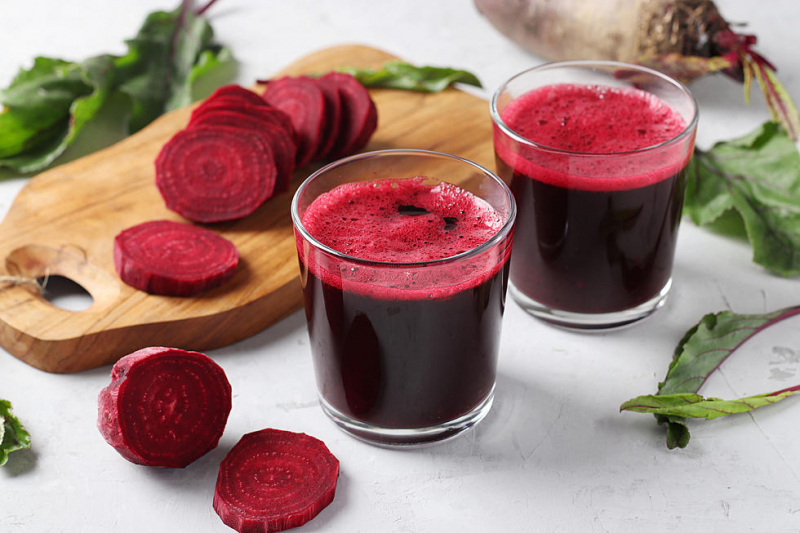 
Beet juice -
Whey protein is used by athletes and gymgoers for many reasons. Some people aim to develop muscle growth and strength. Others want to shed weight and improve their workout results. This supplement can help even those who do not exercise. Whey protein boosts resistance, lowers blood pressure, and increases sensitivity to insulin. It may reduce your risk of diabetes when taken as part of a well-balanced diet.
Whey protein may help muscle recovery after exercise in both athletes and nonathletes, according to some studies. Before physical fitness tests, 92 men with obesity were given 0.4 milligrams per pound (0.9 grams per kg) of whey protein divided into three doses per day. Whey protein significantly decreased muscle damage markers when compared to a control group, however, it did not improve DOMS. After resistance exercise, whey protein may help to enhance muscle function. In several studies, whey protein had little effect on muscle repair after exercise. As a result, additional study is needed to see whether taking whey protein after exercise will help with muscle recovery.
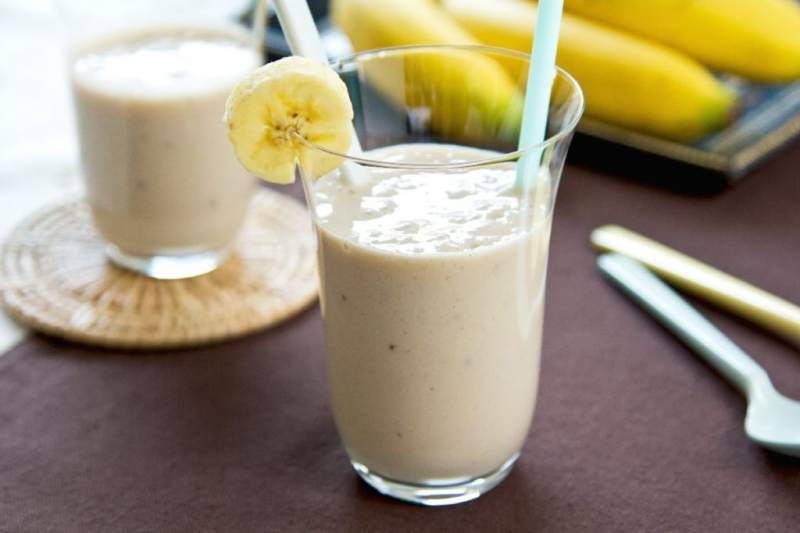

Whey protein shakes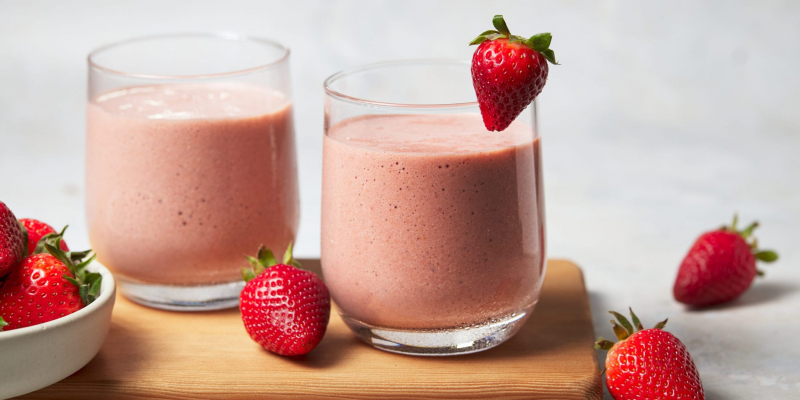 
Whey protein shakes -
Eggs are a nutrient-dense food that athletes choose because of their high bioavailable protein content. After an exercise, consuming them helps muscle recovery. Although many people prefer to eat only egg whites after a workout, research suggests that whole eggs may be a superior choice.
Participants in a short 2017 research of 10 males ate a meal with either whole eggs or egg whites right after weight exercise. Even though all of the meals included the same amount of protein, the whole-egg meals resulted in more muscle growth. This might be because the nutrient-dense yolk contains vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids including vitamin A, selenium, zinc, and the fatty acid palmitate, all of which may help muscle protein synthesis speed up.
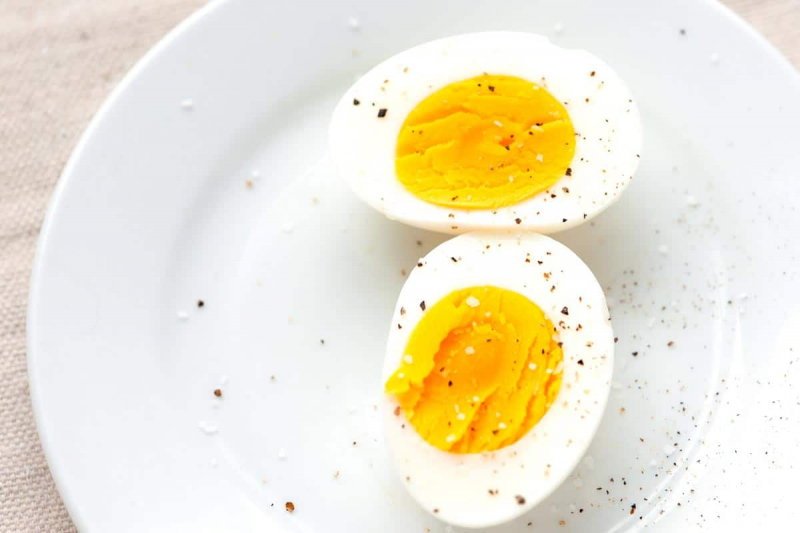

Eggs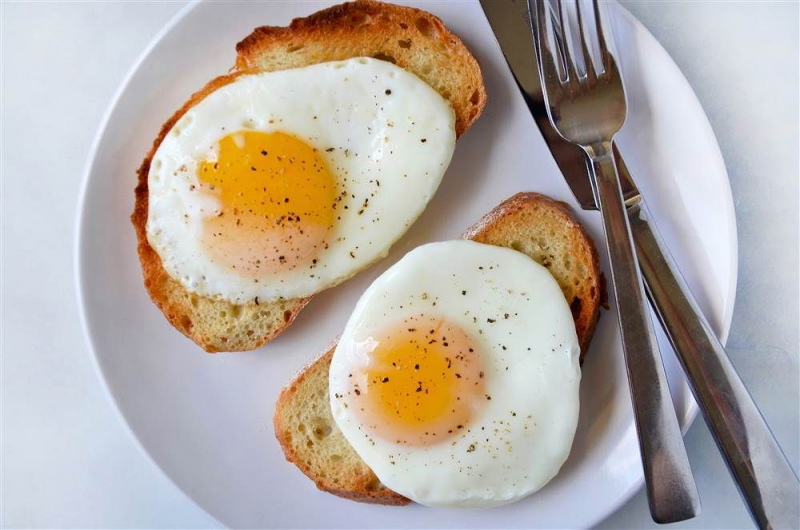 
Eggs -
Milk and milk products such as yogurt and cottage cheese are popular post-workout fuels. Milk is isotonic (osmolality of 280-290 mosmol/kg), and its combination of high-quality protein, carbohydrate, water, and micronutrients (especially sodium) makes it uniquely ideal as a post-exercise recovery drink in many workout scenarios.
Milk is abundant in protein, which gives your body the nutrients it needs to rebuild muscles. As a result, EIMD may be reduced. Carbs can also be found in milk and dairy products. Combining carbohydrates and protein in your diet promotes muscle growth and helps your muscles restore glycogen stores, which are the stored form of glucose, or sugar. Cow's milk has been shown in certain tests to considerably improve workout performance and muscle recovery. Chocolate milk may boost exercise performance and recovery, according to a study of 12 research published in 2019.

Dairy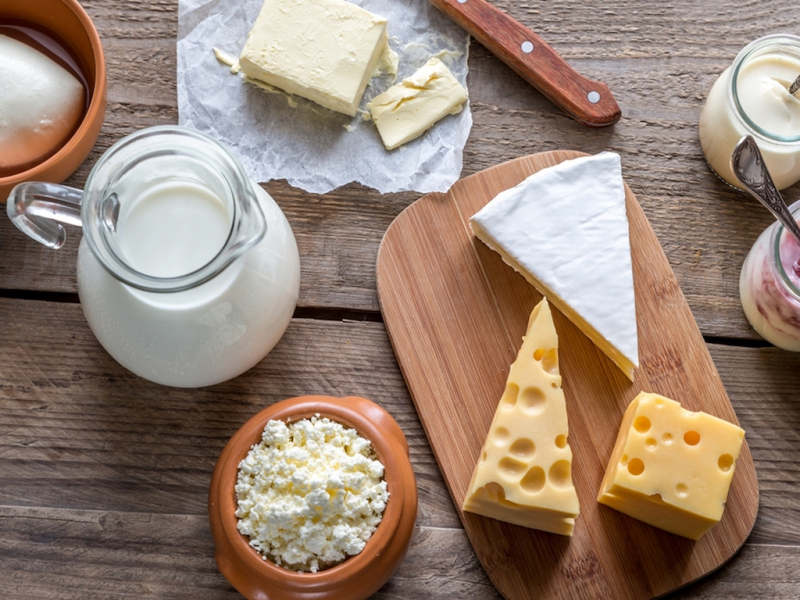 
Dairy -
Plant-based diets emphasize whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruits, which are unprocessed and unrefined. Many of these foods are high in minerals, which are important for muscle repair, and many plant-based meals are also high in protein, which helps to build and maintain muscle.
When you exercise hard, your muscle stores of glycogen, the stored form of glucose, are exhausted. It's critical to have enough available glycogen in your muscles for maximum athletic performance, thus it's critical to replenish these stores after exercises. This is especially true for athletes who engage in strenuous activity. Muscle glycogen is replenished when carbohydrates are consumed. Post-workout, starchy veggies like sweet potato, butternut squash, and potatoes are a good source of carbohydrates. Combining starchy veggies with a protein source like eggs or chicken is a delicious and effective way to replenish glycogen stores while also supplying the protein your body requires for muscular repair.

Starchy vegetables 
Starchy vegetables -
Coffee may help minimize DOMS when consumed before or after exercise. This is because the caffeine in coffee blocks adenosine receptors. Adenosine is a chemical produced in response to injury, it stimulates your body's pain receptors.
When compared to a placebo, consuming coffee 1 hour before an intense upper-body workout dramatically reduced muscular pain on days 2 and 3 after exercise, according to a 2013 research of 9 males who typically consume low doses of caffeine. In addition, compared to a placebo, caffeine consumption 24 and 48 hours after intensive exercise increased muscular power recovery and decreased DOMS in both men and women, according to a 2019 research. Men, rather than women, experienced greater reductions in DOMS after consuming coffee. Caffeine doses of 2.3–2.7 mg per pound (5–6 mg per kg) have been demonstrated to be effective in reducing DOMS. The caffeine content in an 8-ounce (237-mL) cup of coffee is roughly 95 mg. For a 150-pound (68-kg) person, this corresponds to around 345 mg of caffeine.

Coffee 
Coffee