Top 8 Drugs that Changed the World
It’s easy to take a lot of today’s pharmaceutical offerings for granted. The medical field can move incredibly fast, but it wouldn't be able to move anywhere ... read more...if there weren't drugs that "changed the game" in the field. Here’s a look at some drugs that have changed the world, and forever altered the course of history and medicine.
-
The term "penicillin" refers to a class of -lactam antibiotics that were first derived from Penicillium molds, primarily P. chrysogenum and P. rubens. By employing deep tank fermentation and subsequent purification, P. chrysogenum produces the majority of penicillins that are used in medicine. Even though several natural penicillins have been found, only two pure compounds—Penicillin G (for intramuscular or intravenous usage) and Penicillin V—are currently used in clinical settings. Many bacterial illnesses brought on by staphylococci and streptococci were among the first conditions that penicillins were able to treat. Even though numerous bacteria have developed resistance as a result of repeated use, they are nevertheless often used today to treat various bacterial diseases.
Penicillin was first developed in 1928 by Scottish physician Alexander Fleming. But it wasn't until 1942 that it was actually used. The discovery of the first recognized antibiotic signaled a turning point in human history and paved the way for the treatment of many bacterial infections. The first human studies were conducted by Australian pathologist Howard Florey and his team after stabilizing penicillin. Penicillin was mass-produced with American funding, which changed the course of World War II, and thousands of military soldiers were treated with it. Penicillin is thought to have saved between 80 and 200 million lives, and without its discovery and use, 75% of today's population would not be alive today!
Discovered in: 1928Discovered by: Alexander Fleming
Usage: Treatment of infection
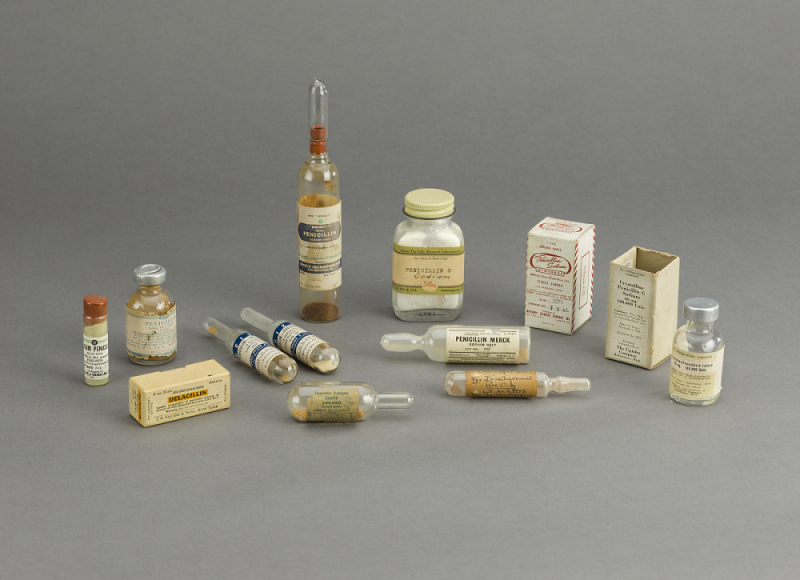
Photo: National Museum of American History Vieo: Pharmacology Animation -
Insulin is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the INS gene. It is thought to be the body's primary anabolic hormone. By encouraging the absorption of glucose from the blood into the liver, fat, and skeletal muscle cells, it controls the metabolism of carbs, lipids, and protein. High levels of insulin in the blood substantially impede the liver's ability to produce and secrete glucose. Low insulin levels in the blood have the opposite impact by encouraging extensive catabolism, especially of reserve body fat.
Insulin was discovered in 1921, and it immediately revolutionized and saved the lives of patients with diabetes. Prior to the disease's diagnosis, sufferers were made to eat on the verge of famine in order for their bodies to metabolize the carbohydrates they need. But the discovery that the hormone insulin would aid in turning sugar into energy provided a substitute. And in the end, it paved the way for alternative hormone replacement techniques. The number of people who have diabetes is rising worldwide. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as of 2012, in the US alone, there are 29 million people were diagnosed with this disease. therefore, insulin has been more important than ever. It is now on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, the most important medications needed in a basic health system.
Discovered in: 1921
Discovered by: Frederick BantingUsage: Treatment of diabetes
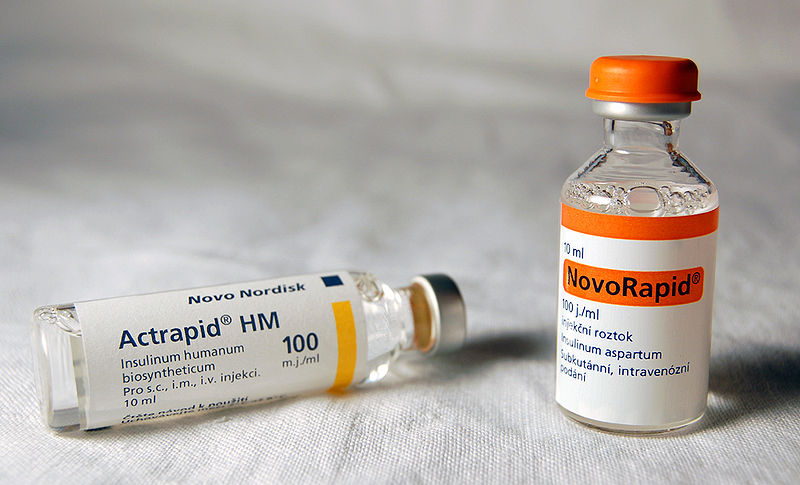
Photo: Wikipedia Video: Strong Medicine -
1981 saw the first reports of HIV infection in San Francisco and New York City; four years later, it was determined to be the primary cause of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). However, thanks to protease inhibitors, an antiretroviral medication class used to treat HIV by preventing the HIV virus from entering specific cells in the body and replicating itself, the outlook for HIV has significantly improved over time. These drugs aim to lower the viral load—the quantity of HIV present in the body—to undetectable levels. This helps treat symptoms and slows the spread of HIV.
Protease inhibitors were not the initial HIV medication, but when used with other AIDS medications, they allowed doctors to maintain HIV levels in their patients at such low levels that AIDS never formed in their bodies. Of the 26 drugs approved by the FDA for the treatment of HIV, 10 are protease inhibitors, including atazanavir (Reyataz), darunavir (Prezista), fosamprenavir (Lexiva), indinavir (Crixivan), lopinavir/ritonavir (Kaletra), nelfinavir (Viracept), ritonavir (Norvir), saquinavir (Invirase), tipranavir (Aptivus), atazanavir/cobicistat (Evotaz), darunavir/cobicistat (Prezcobix).
Discovered in: 1989 and 1994
Discovered by: Researchers working for the pharmaceutical companies of Hoffmann- La Roche Inc.
Usage: Help with the treatment of HIV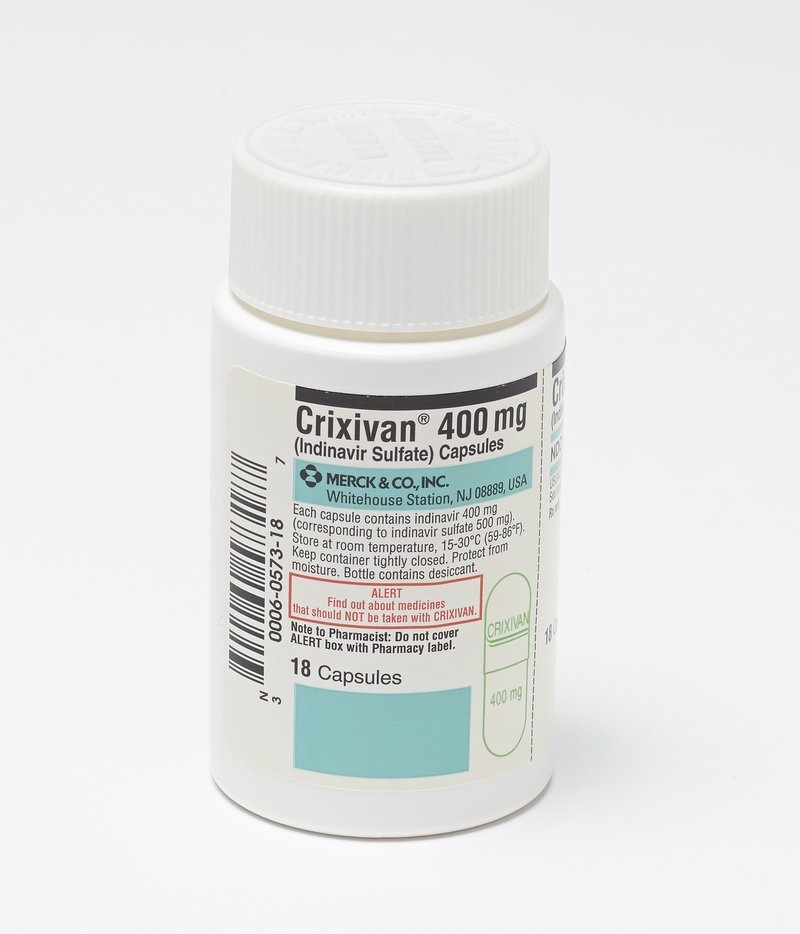
Crixivan HIV Protease Inhibitor - digital.sciencehistory.org Video: Mechanisms in Medicine -
The birth control pill is first developed in 1950 when Margaret Sanger, the founder of Planned Parenthood, approached Gregory Pincus about working on trustworthy, simple-to-use contraception. Pincus was employed by the Worcester Foundation for Experimental Biology, a private laboratory in Massachusetts. And it wasn’t until 1960 that the first birth control pill was approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
Birth control pills are a kind of medicine with hormones. If you take your medication on schedule every time, it is secure, inexpensive, and efficient. Beyond its obvious purpose, which is preventing pregnancy, the pill has lots of other health benefits including easing cramps and PMS symptoms, making your skin clearer, etc. The pill works by stopping sperm from joining an egg, therefore preventing the fertilization process so that no pregnancy can happen. The pill’s hormones also thicken the mucus on the cervix. This thicker cervical mucus blocks sperm so it can’t swim to an egg.
Currently, scientists are striving to develop a birth control pill that is effective on men. A drug that temporarily sterilizes men is reportedly closer than ever to being developed, according to researchers at the University of Minnesota College of Pharmacy, but there is no set deadline for FDA submission or for clinical trials.Discovered in: 1950
Discovered by: Gregory Goodwin Pincus, Carl Djerassi
Usage: Prevent unwanted pregnancy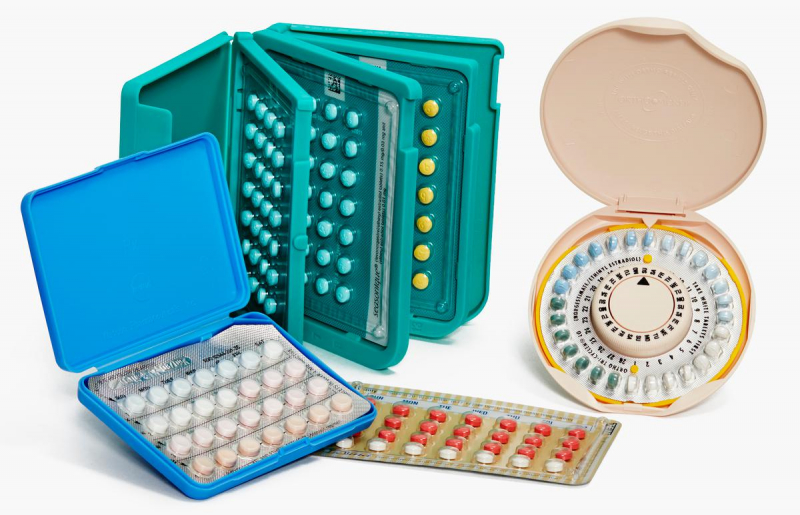
Different kinds of birth control pill - Planned Parenthood Video: Alila Medical Media -
Lipitor is a class of medication that has significantly decreased the incidence of heart disease. According to Pfizer, Lipitor showed an unexpectedly potent reduction in myocardial ischemia (a condition defined by the insufficient blood supply and oxygen to the heart) in patients with chronic stable angina (chest pain). So, how does Lipitor work? Lipitor functions by reducing the body's production of harmful cholesterol. The drug lessens and prevents the growth of existing fatty deposits in the arteries. Additionally, it reduces the risk that fatty deposits already present will fragment and form a blood clot (A heart attack or stroke can be brought on by a blood clot).
Developed in 1985 by Bruce Roth, Lipitor went on to become the best-selling drug of all time until this very day. The medication and other statins, however, may have certain undesirable side effects, such as the deterioration and discomfort of muscles. There are some positive Lipitor side effects, though. For instance, it may, in some circumstances, also stimulate your liver to produce more of the enzymes necessary for food and medicine digestion.Discovered in: 1985
Discovered by: Bruce Roth
Usage: Reduce heart disease
Photo: CBS News Video: Doctor O'Donovan -
Ritalin (also called methylphenidate) is a central nervous system stimulant that’s prescribed to people with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). This medication has been shown to be effective in reducing symptoms like impulsivity, hyperactivity, and difficulty concentrating. Ritalin affects behavior and problem-solving by elevating the concentration of neurotransmitters in the brain.
Many people take Ritalin and other ADHD drugs without a prescription even though they should only be used under a doctor's supervision to improve performance at work or school. As college students use it to concentrate before tests and eSports competitors use it as a performance-enhancing substance, it has been under the spotlight recently due to abuse concerns. The reason for that is that Ritalin is not supposed to be used as a brain-memory-enhancing drug. Ritalin might temporarily improve mental function, but it can negatively affect the brain's plasticity, making it difficult to plan ahead and reflect flexibility in behavior. Moreover, other side effects of Ritalin are Nervousness, Trouble sleeping, Loss of appetite, Weight loss, Dizziness, Nausea and/or vomiting, Headache, etc.
Discovered in: 1944
Discovered by: Leandro Panizzon
Usage: Treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
Photo: seasidepalmbeach.com Video: CNN -
Chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that involves the use of one or more anti-cancer medications (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a prescribed chemotherapy regimen. It is sometimes shortened as "chemo" and occasionally CTX or CTx. Chemotherapy may be administered with the intention of curing (which usually always requires drug combinations), extending life, or reducing symptoms (palliative chemotherapy). One of the main subspecialties of the medical field that is exclusively concerned with cancer medication is chemotherapy.
One of the earliest chemotherapy drugs to be used to treat cancer was mustard gas, which was first used as a weapon in World War I. Although it was shown to kill cancerous cells, it also severely injured healthy cells, providing little survival benefit. Methotrexate, which in 1956 treated a rare tumor known as choriocarcinoma, was the first medication to prove its effectiveness in treating cancer. Chemotherapy innovations and the development of several medicines with various modes of action over the ensuing decades of cancer research resulted in significant increases in patient survival and a decline in mortality rates nowadays. Today, 7 main types of chemotherapy are being used: Alkylating agents, Antimetabolites, Anti-tumor antibiotics, Topoisomerase inhibitors, Mitotic inhibitors, Plant alkaloids.
Discovered in: 1919
Discovered by: Eward Krumbhaar
Usage: Treat cancer
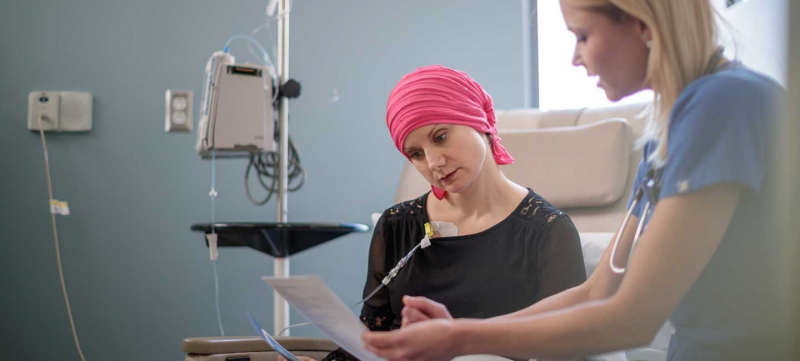
cancer patient being treated with Chemotherapy - Moffitt Cancer Center Video: UMC Health System -
Diazepam (first marketed as Valium) is a fast-acting, long-lasting benzodiazepine. Numerous problems, such as anxiety, seizures, alcohol withdrawal syndrome, muscle spasms, sleeplessness, and restless legs syndrome are frequently treated with it. Additionally, it could be administered during several medical operations to cause memory loss. It can be ingested orally, injected into the rectum, vein, or muscle, or sprayed into the nose. It can be detected in the body for up to 90 days. Depending on the route, you may begin to feel its effects anywhere from a minute to an hour after administration.
Before the invention of Diazepam, related drugs weren't sold as a "cure" for anxiety, but as a way to help people engage in psychotherapy, which was seen as the real solution. In 1959, Polish-American chemist Leo Sternbach and his research group chemically altered Librium to produce Diazepam - a cheaper, easily available drug, and made a huge impact. Diazepam created a culture of managing stress and anxiety with medication and paved the way for modern antidepressants. Therefore, it is now on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.
Discovered in: 1959
Discovered by: Leo Sternbach
Usage: Treat anxiety
Photo: Verywell Mind Video: Dr Matt & Dr Mike




























