Top 10 Major Accomplishments of Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan, an American politician who lived from 1911 to 2004, was the 40th President of the United States and the 33rd Governor of California. ... read more...Reagan's biggest foreign policy accomplishment was ending the Cold War peacefully with the help of Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev. The major accomplishments of Ronald Reagan, one of the most significant presidents in American history, are listed here.
-
Jimmy Carter, the incumbent Democratic president, was Ronald Reagan's Democratic opponent in the 1980 presidential election. Reagan became the 40th President of the United States after winning the most electoral votes of any non-incumbent presidential candidate. Reagan was a successful presidential candidate in 49 of the 50 states in 1984. His victory that year was the highest electoral college victory ever thanks to his 525 electoral votes, 59 percent of the popular vote, and other factors.
Ronald Reagan ran for president of the United States in 1980 against Democratic incumbent Jimmy Carter after the Republicans were unable to secure the Republican ticket in the presidential elections of 1976. Reagan easily prevailed in the election. He carried 44 states and received 489 electoral votes. Carter, in contrast, only received 49 electoral votes, which came from six states and Washington, D.C. On January 20, 1981, Reagan took the oath of office as the country's 40th president.
He was sworn in as president at age 69, making him the oldest person to do so at the time. Donald Trump beat Ronald Reagan's record in 2016 by winning the presidency at the age of 70. Reagan was re-elected in the US presidential elections of 1984. He won a record 525 electoral votes, 49 out of 50 states, and 59 percent of the popular vote. The biggest electoral college victory in American history was won by Reagan in a landslide in 1984.
Photo: tuoitre.vn 
Photo: hstoday.us -
The Soviet Union's influence was growing at the start of Ronald Reagan's presidency, and he devised a fairly contentious strategy for dealing with it and the Cold War in general. The Reagan Doctrine, which he devised, saw the United States support the anti-communist elements in communist regimes that were backed by the Soviet Union. The power of the Soviet Union declined in a few areas as a result, which helped to bring an end to the Cold War. This is one of the major accomplishments of Ronald Reagan.
The Soviet Union was becoming more powerful and had just invaded Afghanistan when Ronald Reagan took president. Administrators believed the Cold War would last for the foreseeable future since US policy toward the USSR during the preceding 10 years had been one of Détente ("relaxation of tension"). Reagan, on the other hand, thought that because of the Soviet Union's fragile economy, more pressure would cause it to collapse. He took a more assertive stance and overturned the Détente strategy by directing a significant increase in US military might.
In order to encourage anti-communist forces in communist countries supported by the Soviet Union in Africa, Asia, and Latin America, Reagan established a strategy known as the Reagan Doctrine. The contentious program did lessen Soviet influence in some areas, though. For instance, the Reagan administration supported the Afghan guerrillas in Afghanistan, which ultimately resulted in the end of the Soviet occupation of that country. The Reagan Doctrine's proponents view it as a crucial factor in the Cold War's eventual termination.
Photo: thoughtco.com Video: The Daily Wire -
Between 1985 and 1988, Ronald Reagan and Soviet Premier Mikhail Gorbachev participated in four summit meetings. The Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty (INF Treaty), which they both signed in 1987, removed nuclear and conventional missiles; more than 2,000 warheads were destroyed as a result. This agreement lowered tensions between the USA and the Soviet Union and helped put an end to the Cold War which is the major accomplishments of Ronald Reagan.
When Mikhail Gorbachev assumed leadership in the USSR, Ronald Reagan changed his approach to the Soviets from one of "peace through strength" to one that combined firmness and certainty. Between 1985 and 1988, the two presidents participated in four summit meetings. Reagan and Gorbachev signed the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty (INF Treaty) during the third summit in December 1987. All short- and intermediate-range nuclear and conventional missiles were rendered obsolete by the INF Treaty. It led to the destruction of 2,692 such weapons.
Reagan's stern but fair approach to dealing with the Soviet Union was crucial in bringing about the peaceful end of the Cold War. Mikhail Gorbachev's rise to power and Eastern Europeans' rejection of communist governments are two more significant causes. It should be highlighted that Reagan would not have been able to bring an end to the Cold War without these crucial elements. The Berlin Wall was opened in November 1989, ten months after Reagan left office. At the Malta Summit on December 3, 1989, the Cold War was unofficially declared to be finished, and on December 26, 1991, the Soviet Union fell.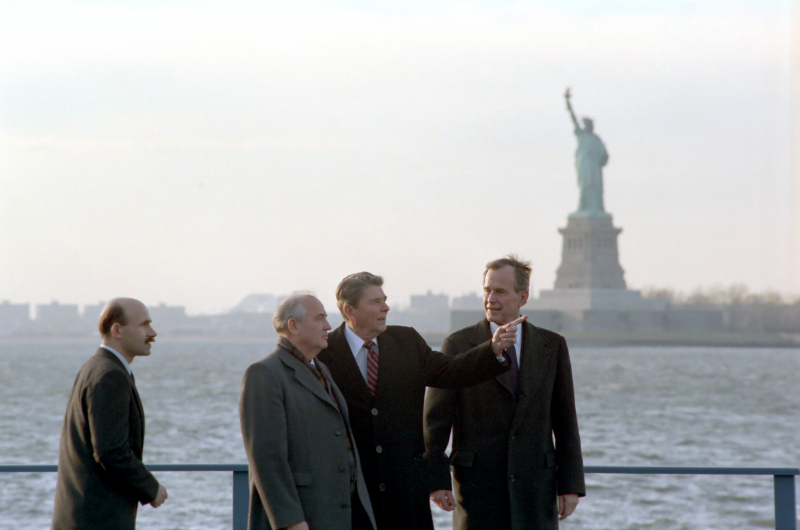
Photo: commons.wikimedia.org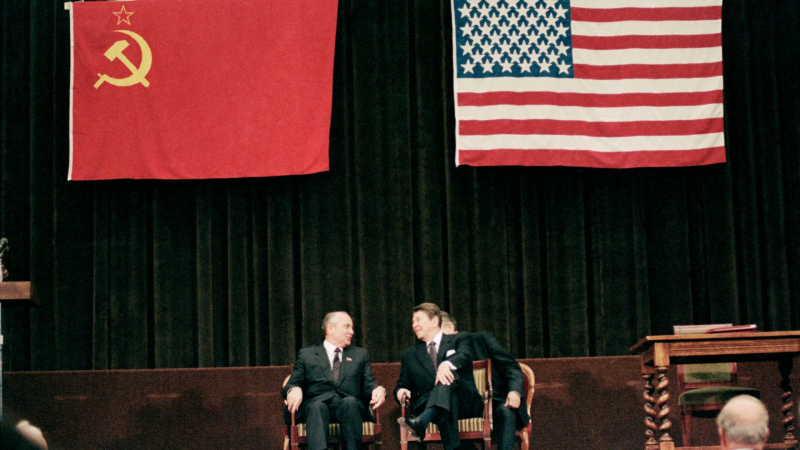 
Photo: www.livescience.com -
Between 1967 and 1975, Ronald Reagan held two terms as governor of California. Reagan approved tax increases during his first term in order to balance the budget and froze government hiring. As a result of his changes, California's budget went from being in deficit to being in surplus during his second term, when he concentrated more on the welfare system.
Ronald Reagan visited Hollywood in 1937. He appeared in more than 50 films during the course of his more than 25-year acting career. Being a union leader was connected to his earliest political actions. From 1947 to 1952 and again from 1958 to 1959, Reagan presided over the Screen Actors Guild, the actors' union. Following his well-known "A Time for Choosing" speech in support of Republican nominee Barry Goldwater during the 1964 US presidential election campaign, Reagan's national political career took off.
In the 1966 California governor's race, Republican Ronald Reagan outpolled incumbent Democrat Edmund G. Brown by nearly a million votes. He was re-elected in 1970, and from 1967 to 1975, he presided as governor of California. He did not run for a third term in office. Reagan implemented significant reforms to the welfare system during his second term as governor after first freezing government hiring and approving tax increases to balance the budget. During his tenure as governor, Reagan turned California's budget deficit into a surplus.
Photo: www.politico.com Video: C-SPAN -
Reaganomics is a set of policies that Ronald Reagan came up with to help the state's economy, which had weak economic growth and a high unemployment rate. He ordered limited government expenditure, lower tax rates, lessening of government regulation, and tightening of the money supply as his four main measures. His Reaganomics were quite effective, as evidenced by the fact that the unemployment rate decreased from 7.1% to 5.5 percent.
Among other things, Ronald Reagan's administration saw the top marginal tax rate on individual income drop from 70% to 28%, the corporation income tax rate drop from 48 to 34%, and the majority of the poor were exempted from individual income tax. At an annual rate of 1.8 percent, real GDP per working-age adult increased. This rate was merely 0.8 percent annually during the Carter administration.
A record number of 18.7 million new employment were produced between November 1982, when Reagan's economic initiatives started to take hold, and November 1989, just before he left office. Moreover half of these positions had yearly salaries of over $20,000. A record-breaking $30 trillion worth of products and services were generated throughout this seven-year span, setting yet another milestone. One of the biggest economic booms in American history occurred during peacetime as a result of Ronald Reagan's economic initiatives. Reagan also cut the number of tax benefits and reduced the number of tax brackets to four, simplifying the tax law.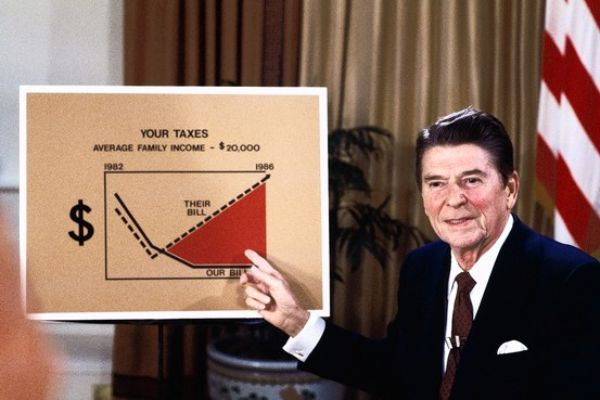
Photo: www.wsj.com 
Photo: www.wbur.org -
Reagan achieved the best improvement record since President Harry Truman and it is one of the major accomplishments of Ronald Reagan because to Reaganomics, which strengthened the economy as a whole. During his presidency, the GDP growth increased from -0.3 to 4.1 percent, but it wasn't all Reagan accomplished. He set two records: the first is that more than 18 million jobs were created between 1980 and his departure, and the second is that an estimated $30 trillion in wealth was generated during this time.
Prior to the Reagan era, the US economy went through a decade of stagflation, which is characterized by high inflation, sluggish economic development, and persistently high unemployment. Ronald Reagan's economic strategy, or "Reaganomics," was founded on four key tenets: limited government expenditure, lower tax rates, lessening of the role of the government in society, and tightening the money supply to fight inflation.
The unemployment rate fell by 1.6 percent under the Reagan administration, from 7.1 percent in 1980 to 5.5 percent in 1988, and the inflation rate decreased from 13.5 percent in 1980 to 4.1 percent in 1988. Reagan's administration saw the most improvement since Harry S. Truman, with the misery index - the product of inflation and unemployment - falling from 19.99 to 9.72.
Photo: Twitter Video: American Experience | PBS -
The Professional Air Traffic Controllers Organization (PATCO) went on strike on August 3, 1981, calling for 32-hour workweeks, increased compensation, and improved working conditions. A federal provision that forbids government unions from striking was broken by the strike. As air traffic carried aircraft for airborne early warning and control, the strike also had an impact on national security (AWACS). Ronald Reagan warned that the air traffic controllers would be fired if they didn't go to work within 48 hours after the PATCO strike was labeled a "peril to national safety." Of the almost 13,000 controllers, just about 1,300 went back to work. Reagan dismissed the 11,345 striking air traffic controllers who disobeyed the order on August 5 and permanently barred them from federal employment.
One of the most significant moments in US labor history of the 20th century was the PATCO strike's failure. Reagan's move, albeit debatable given its wide-ranging effects, resulted in a sharp decline in illegal work stoppages against the federal government. Prior to 1981, there were over 300 major work stoppages annually on average; by the 2000s, that number had dropped to under 30.

Photo: Youtube Video: Reagan Foundation -
The First Lady Nancy Reagan conducted an anti-drug campaign when her husband, Ronald Reagan, served as President. They created the "Just Say No" campaign because they thought that drugs posed a threat to society, particularly among kids and teenagers. Reagan signed the Anti-Drug Abuse Act in 1986, allocating $1.7 billion for the War on Drugs. Along with mandated minimum sentences, he also introduced greater law enforcement.
Reagan believed that drugs posed a serious threat to American society. He campaigned on a platform of expanded drug treatment, drug-free workplaces, and tougher law enforcement. He enhanced drug enforcement during his first five years in office by establishing mandatory minimum sentences and the seizure of money and property for drug offenses.
Reagan signed the Anti-Drug Abuse Act of 1986 into law on October 27, 1986, allocating $1.7 billion to finance the War on Drugs. The Act provided funding for AIDS research, drug counseling, and international collaboration to reduce drug manufacture, among other things. Through her "Just Say No" campaign to raise drug awareness among children and teenagers, Nancy Reagan, Ronald's wife, played a significant role in his War on Drugs. She visited 65 places across 33 states to spread the word about the risks associated with drug use.
Photo: www.dailysignal.com 
Photo: www.bustle.com -
The Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), started by Ronald Reagan, was viewed as controversial by many. Reagan's policy was to defend the United States against nuclear weapons by intercepting and destroying incoming missiles because he believed that it was preferable "to save lives than to avenge them." Some thought that this was a pretext for beginning an economic conflict with the Soviet Union. The United States undoubtedly gained a competitive edge in the area of missile defense, though.
Mutually assured destruction (MAD) is a military tactic and national security policy that states that if one side is attacked with nuclear weapons, the other side will respond with full force, potentially escalating the conflict and annihilating both sides. Both sides employed MAD to prevent direct conflict during the Cold War. Reagan was an outspoken opponent of MAD. He unveiled the Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI) in 1983, which sought to defend the US from nuclear ballistic missile attacks by intercepting and destroying the assailants' missiles.
Because it threatened the "assured annihilation" necessary for MAD, it was viewed as risky. Some believe that Reagan's SDI initiative was an attempt to instigate an economic conflict by escalating a defensive arms race against the already fragile Soviet economy. The Soviet Union was under pressure from SDI to develop its own anti-ballistic missile system. Despite the fact that SDI was never completely completed, the research and technology it produced helped shape some of the anti-ballistic missile systems in use today and offered the US a competitive edge in the missile defense market.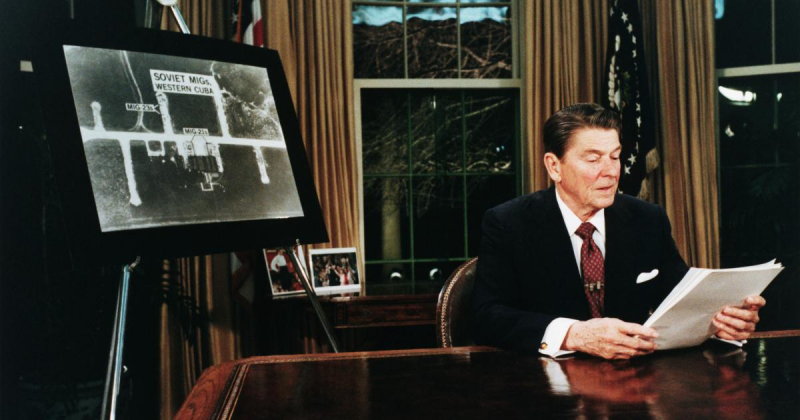
Photo: www.heritage.org Video: Reagan Library -
One of the highest British organizations, the Order of the Bath, elevated Reagan to the honorary rank of Knight Grand Cross in 1989. He and George H. W. Bush are the only two US presidents to have won the distinction. He received Japan's highest honor, the Supreme Order of the Chrysanthemum, in the same year.
Ronald Reagan was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom, the nation's highest civilian honor, on January 18, 1993. He was listed among the top 100 figures in the 20th century by TIME magazine in 1999. Reagan was chosen as The Greatest American in 2005 by millions of Discovery Channel viewers. One of the most significant American presidents is regarded as being Ronald Reagan. He still has a legendary status among the Republican Party. The conservative "Reagan Revolution" he led had a lasting influence on US foreign and domestic policy, and the years of his presidency are referred to as the Reagan Era.

Photo: www.usnews.com 
Photo: www.history.com