Top 9 Questions About Skin Answered
Beauty and skincare are inextricably linked. Taking care of your skin is essential since it serves as the greatest barrier against all types of illness. To ... read more...keep this barrier robust, you must take care of your skin on a daily basis. Paying attention to how your skin looks and feels, as well as maintaining a consistent skincare routine, may help keep it healthy. Healthy skin not only protects you from illness, but it also leaves you feeling invigorated and healthy. Here are some frequently requested skin-care questions.
-
You've undoubtedly observed your fingers pruning if you've ever had a lengthy bath or spent time in a pool. The tips of your fingers, and sometimes the entire finger, acquire wrinkles and creases similar to those on a prune. Pruning is normally innocuous and disappears on its own. However, prolonged trimming or pruning that does not occur as a result of water might be a sign of an underlying medical problem.
Pruning was formerly thought to be caused by your fingers soaking water, according to the medical establishment. Pruny fingers are now understood to be caused by blood vessels that constrict underneath the skin's surface. The condition is linked to nervous system function. Water can have this impact, but there are other factors to consider. For example, the pruning might be caused by fluid or nerve injury, both of which can indicate an underlying medical problem.
This occurs because the top layer of skin on fingers and toes (called the stratum corneum) is more porous than the layers of skin underneath, making it better at absorbing water. However, instead of expanding, our fingers and toes shrivel due to the way the layers of skin are connected: the top, swelling layer of skin is attached underneath to tissue that does not swell, thus the skin bends to fit the greater surface area. As a result, your fingertips have the appearance of prunes. Alternatively, raisins. The water from your skin evaporates into the air as you dry, and your skin rapidly returns to normal.

memd.me https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wERUAyX5boo -
Your skin is an extremely complicated organ, which is understandable given that it is the biggest in your body! Humans must maintain a specific amount of internal body temperature in order to be happy and healthy; on average, this is roughly 37°C. Your skin is made up of three layers: the epidermis, the dermis, and the hypodermis. When you get too hot, the first thing your body does is enlarge the blood capillaries in your dermis, enabling more blood to flow near the skin's surface. This generates heat by a mechanism called as radiation, which is similar to the heater in your bedroom rather than a nuclear power plant.
The human body cools itself via sweating through its three million sweat glands. Skin nerves alert the brain that your body is becoming heated, and the brain instructs the sweat glands to work hard. Each gland functions as a little pump, drawing water from adjacent capillaries and delivering it to the skin to chill it down. Sweat glands are like wells that tap into a vast ocean since up to 60% of the body is water. Sweat glands are classified into two types: eccrine glands and apocrine glands. The eccrine glands are especially built for cooling the body; during extreme activity or exercise, they may pump up to 2 quarts (1.9 liters) of water each hour.

istockphoto 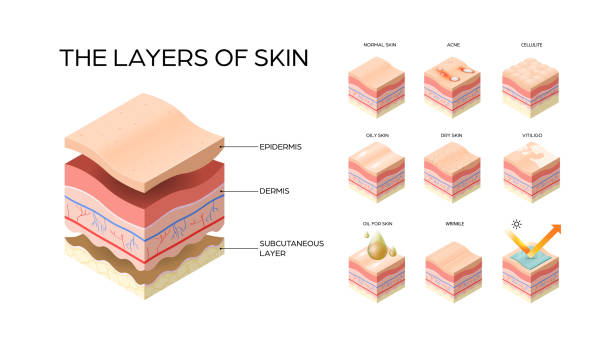
istockphoto -
Melanin is classified into two types: pheomelanin and eumelanin. In general, the more eumelanin there is in your skin, the darker it will be. People with higher levels of pheomelanin have lighter skin with freckles. The kind of pigment in your skin, like other features, is governed by DNA. Each of these genes works together to produce the end outcome - your skin color.
Melanin is produced by melanocytes, which are unique cells. These cells are present in your skin's epidermis. People can develop distinct skin colors in three ways. One approach is that the less melanin, the lighter the skin. Another method is for people to have fewer melanocytes. The third method is a little more involved and has to do with the type of pigment produced. Melanin may be divided into two categories. Pheomelanin is red or yellow pigmentation, whereas eumelanin is brown or black pigmentation.
Melanin is classified into two types: phaeomelanin (red to yellow) and eumelanin (green to yellow) (dark brown to black). Four to six genes determine both the quantity and the kind. A individual inherits one copy of each of those genes from his father and one copy from his mother. Each gene has numerous coding sequences, resulting in a wide range of skin hues. Sunlight also has an effect on skin tone.

istockphoto 
istockphoto -
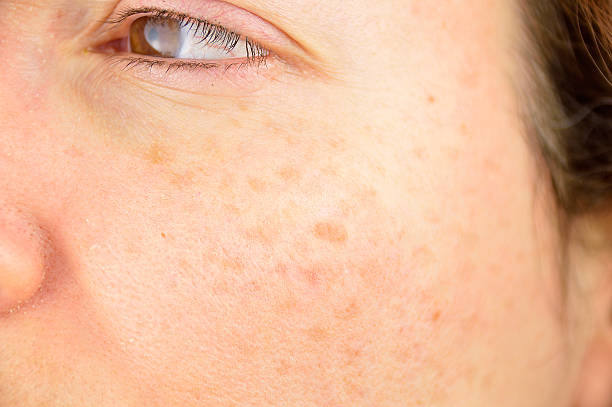
Freckles are concentrated specks of the pigment protein melanin. Melanin is produced when ultraviolet light (UV) strikes the skin. UV rays are harmful, and melanin protects the skin by darkening it—imagine your skin putting on a pair of sunglasses. Melanin is generated by melanocytes, a kind of cell. Melanocytes are equally distributed in certain persons, and sun exposure results in a smooth wash of melanin, popularly known as a tan. In others, melanocytes congregate, and the light forms bizarre melanin constellations, a.k.a. freckles.
Melanin is produced by melanocytes, which are unique cells. These cells are present in your skin's epidermis. People can develop distinct skin colors in three ways. One approach is that the less melanin, the lighter the skin. Another method is for people to have fewer melanocytes. The third method is a little more involved and has to do with the type of pigment produced. Melanin may be divided into two categories. Pheomelanin is red or yellow pigmentation, whereas eumelanin is brown or black pigmentation.
Scientists uncovered another gene responsible for freckles in Chinese cultures around a decade ago. Other genes may also be involved—scientists have yet to discover all of the genetic reasons of freckles, which appear in a wide range of ethnic groups. Freckles are always a family business, regardless of the specific genetic mechanism: Freckles are passed down across families, as are their positions on the body. While some pigmented skin conditions can induce freckling, freckles on their own are not a reason for worry (unlike moles, which are elevated lumps on the skin, freckles are flat). However, if you have freckles, use lots of sunscreen since the places where the freckles aren't will be more vulnerable to sunburn.
istockphoto 
istockphoto -
If the itch between your toes is strong enough, you may be more concerned with relieving it than with determining what's causing it. However, in order to properly control the itch between your toes, you must first analyze the most likely source. Tinea pedis is the scientific word for what most people call athlete's foot. It is a contagious fungal illness that causes red, cracked skin between your toes and on your foot soles. It can also cause a lot of itching and burning between your toes. If the fungal infection spreads, so will the stinging and burning.
Itchy toes can often be treated at home without any issues. Other instances, though, you may require the advice of your doctor. This is because the appropriate treatment will be determined by the underlying reason of the itch. Certain infections may necessitate the use of a prescription drug. However, you may not always be certain of the source of your itch. Some circumstances will occasionally resemble one other. For example, eczema on your foot may look to be athlete's foot, but you wouldn't treat both ailments the same way. Eczema will not react to antifungal cream, and an eczema therapy may not be effective in treating athlete's foot. However, if you know what’s causing your itch, you may be able to treat it at home.

istockphoto 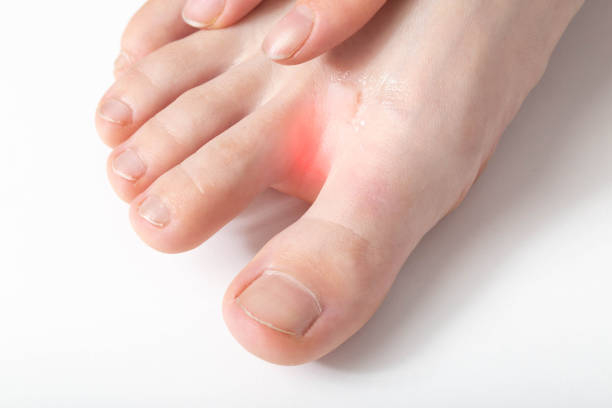
istockphoto -
Your belly button serves as a reminder of the location where the umbilical cord once joined you to your mother. When you are born, the umbilical chord is severed, leaving a little remnant known as the umbilical stump. This stump comes off one to two weeks after delivery, leaving only your belly button. As a result, your belly button looks like a scar. It all depends on how your skin heals and whether it's an innie or an outie.
The appearance of your belly button is primarily due to chance. It has nothing to do with the size or weight of your stomach. Overweight people might have relatively small belly buttons, whereas underweight people can have bigger belly buttons. Obese people, on the other hand, are more likely to have a funnel-shaped belly button, which may seem as a deep belly button like an open mouth.
Another interesting fact: some people do not have belly buttons. This is generally due to a problem affecting the umbilical cord during birth. Bladder exstrophy, gastroschisis, omphalocele, and cloacal exstrophy are a few examples. The intestines in most of these diseases develop or extend beyond the abdominal wall, preventing the umbilical cord from falling off and causing the usual scarring that results in a belly button.

istockphoto 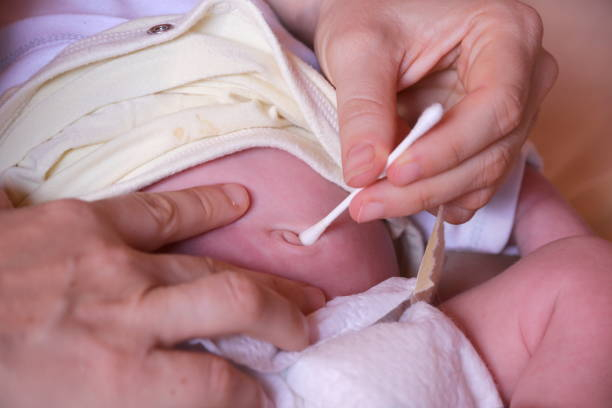
istockphoto -
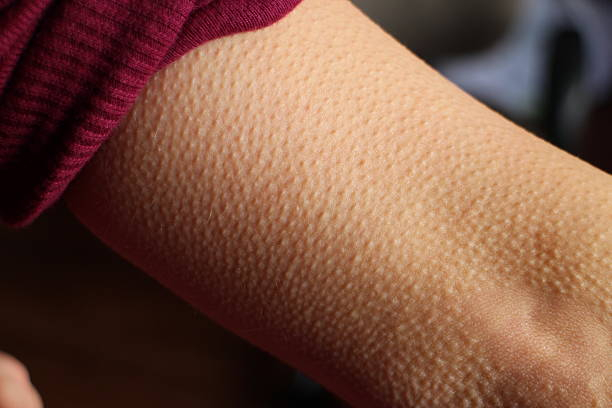
Goosebumps form when the arrector pili muscles contract, drawing the hairs erect. On parts of the body with little or no hair, or with just light hair, a person may detect only the erect hair follicle and not the hair itself. Erect hair follicles seem bloated and larger than normal. This allows them to keep their hair upright and generates goosebumps. A variety of unique causes can cause goosebumps. When it is chilly, many individuals have goosebumps. They may also appear when someone imagines himself to be chilly, as as when watching a frigid scene in a movie. Some people feel goosebumps when they have chills, which they connect with a fever or illness.
Certain emotionally intense events induce the body to produce hormones that create goosebumps. Certain medications might also induce goosebumps. A 2016 research, for example, discovered two sisters who reported goosebumps after taking the medicine milnacipran hydrochloride. Taking medicines that induce activity comparable to those in the body that generate goosebumps may also cause the phenomena. Scientists generally believe that goosebumps are involuntary in normal situations. This is due to the smooth nature of the arrector pili muscles, which create goosebumps. Unlike skeletal muscles, which people may actively utilize to move their legs and flex their limbs, smooth muscles are often uncontrollable.
Goosebumps are not a medical condition. They do not require therapy, and no treatment can entirely eliminate goosebumps. Keratosis pilaris symptoms can be managed with the correct therapy. Some such solutions include:
- regularly moisturizing the skin with a thick moisturizing cream
- using chemical exfoliators, such as lactic acid or salicylic acid, to remove dead skin
- trying laser treatment, if other strategies do not work

istockphoto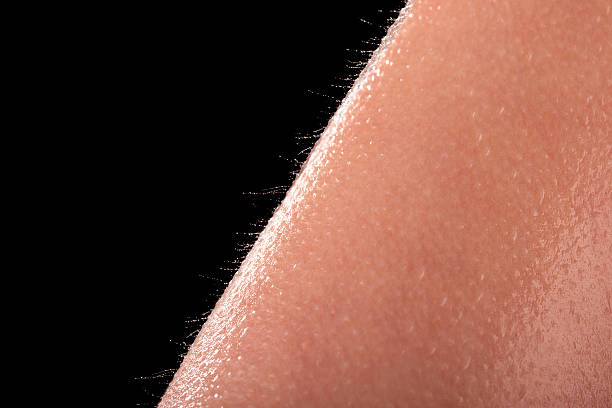 
istockphoto -
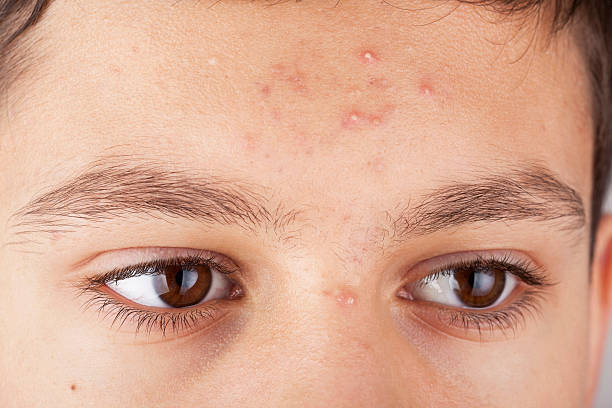
Forehead acne frequently appears as solid red pimples called papules. You may also see lumps with an accumulation of pus on top. These are known as pustules. Acne should be treated appropriately no matter where it appears. To assist the pimples heal faster, you can take over-the-counter (OTC) or prescription medication. To avoid scarring, avoid picking at your acne.
The etiology of acne is the same regardless of where it appears on your face. Sebum is an oil that generally lubricates and protects your skin. Sebum is created by sebaceous glands, which are microscopic oil glands. Oil enters your skin's surface via microscopic openings known as pores. Sometimes debris, excess oil, and dead skin cells obstruct pores. Bacteria develop on the interior, causing large lumps. Pimples are those bumps. Many people get acne throughout adolescence. A spike in hormone levels causes an increase in oil production, which causes pimples. One of the most typical sites for these early breakouts is the forehead. Acne on your forehead might also be caused by your hair.
If you don't wash your hair frequently enough or have oily hair, the oil can accumulate on your forehead and block pores. Irritation from clothes or cosmetics chemicals can also trigger forehead acne, especially if you have sensitive skin. You may get a breakout after using a new cosmetics brand or wearing a hat or headband that irritates your skin.
istockphoto 
istockphoto -
People's bodies change in various ways as they age, affecting how their cells and organ systems work. These changes happen gradually, evolve over time, and are unique to each man and woman. We all lose height as we age, and by the age of 80, our height may have dropped by two inches (five centimeters). Modifications in posture, vertebral development, and joint changes all contribute to our loss of height. Hair follicles generate less melanin, the pigment that gives hair its color, as we age. Hair lightens, grays, and finally whitens. The nails also alter with age, becoming slower to grow, dull and brittle, and yellowed and opaque.
The outer skin layer (epidermis) thins with age, and the number of pigment-containing cells (called melanocytes) diminishes, while the size of the remaining melanocytes increases. As a result, aging skin appears thinner, paler, and more transparent. Changes in connective tissue weaken the strength and suppleness of the skin, resulting in wrinkled, leathery skin.

istockphoto 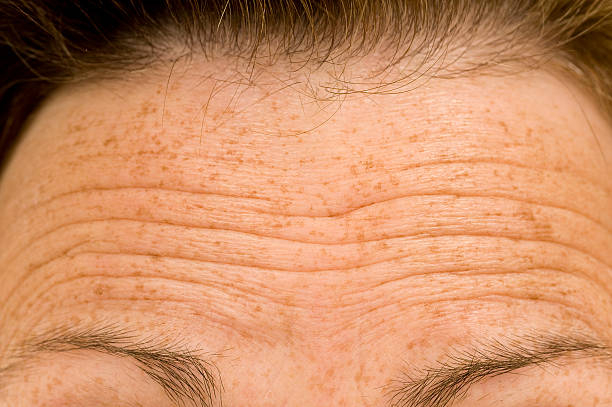
istockphoto