Top 8 Interesting Facts About Jacob Grimm
Jacob Grimm is one of the Grimm brothers who are famous for the collection Grimm’s Fairy Tales. In fact, Jacob and his brother Wilhelm did not create these ... read more...fairy tales, but collected them and researched them as folklore and traditional stories. There are some interesting facts about Jacob Grimm that may surprise you a lot.
-
One of the interesting facts about Jacob Grimm is that he was not always dependent on his brother and he did more than only collect fairy tales. Grimm worked extensively with historical literature, including tales passed down through the generations, old civilization's laws, and evolving human ideas.
Additionally, he had a keen interest in German philology, which is the study of language structure and how it developed. Jacob Grimm's influence in that field led to the naming of a linguistics statute in his honor. In the book Grimm's Geschichte der deutschen Sprache (History of the German Language), he studied history hidden in the words of the German language. In terms of German grammar, Grimm's famous Deutsche Grammatik (German Grammar) was the result of Jacob Grimm's purely philological work. He drew on the work of earlier generations, starting with the humanists, and consulted a vast library of generally unreliable and uncritical text editions, dictionaries, and grammar.
Über den altdeutschen Meistergesang (1811), which is of a purely literary character, was the first work of Jacob Grimm published. Grimm's contributions as a jurist helped shape the history of law, particularly in Northern Europe. His 1816 essay Poetry in Law (Von der Poesie im Recht) presented a comprehensive Romantic philosophy of law.

Photo: IMDb 
Photo: Quizz Club -
Grimm's family had five brothers and one sister, with Jacob and Wilhelm being the oldest. Their father, Philipp Wilhelm was a lawyer and also a town clerk in Hanau and later justiciary in Steinau. This is a small Hessian town where his father and grandfather had served as Calvinistic Reformed Church ministers. The brothers enjoyed playing in the wide-open fields that surrounded their home when the family relocated to the countryside in the town of Steinau in 1791. They were provided with a strict Lutheran education at home and they later attended neighborhood schools.
After his father died of pneumonia in 1796, the family experienced lots of financial troubles. Their mother had to rely on her father and sister for financial support, and they had to give up their servants and spacious home. Jacob and Wilhelm left their home in 1798 to enroll in Kassel's Friedrichsgymnasium, a school that prioritized music and foreign languages. During this time, the two brothers developed a close relationship.
And then the mother passed away in 1808 leaving Jacob, who was 23, in charge of four brothers and one sister. Wilhelm was taller, had a softer face, and was social and appreciative of all the arts, whereas Jacob, a scholarly type, was short and slim with precisely cut features.
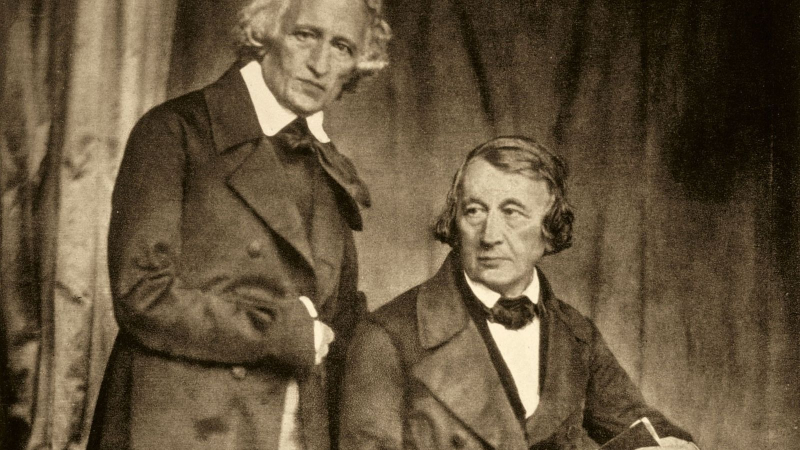
Photo: Wordpress Source: Top Bear -
Another interesting fact about Jacob Grimm was that before collecting and studying fairy tales, Jacob Grimm was going down a different path in life. Prior to discovering his love for linguistics, Grimm intended to become a lawyer. He enrolled at the University of Marburg in 1802, where he pursued his father's original career path of studying law. After recovering from a serious illness, his brother joined him in Marburg a year later and started studying law as well. Up to this time, Jacob Grimm had only been driven by a general need for knowledge, and his energies had been directed purely toward the practical goal of securing his place in life.
They were influenced by Friedrich Karl von Savigny, a co-founder of the historical school of jurisprudence, and Clemens Brentano at Marburg. Friedrich Karl von Savigny taught them a method of antiquarian study that served as the true foundation for all of their later work.
Jacob, however, came to realize that he greatly liked being a linguist through a variety of influences, and by 1816, the brothers were cooperating in the Elector's Library in Kassel, Germany. Jacob had given up his legal career to pursue literary analysis. He did not want to follow his father's way.

Photo: In your pocket Source: DW News -
Jacob Grimm and his brother strongly disobeyed the norms of the period. Romanticism, which involved romanticizing objects and engaging in great fantasy, was fashionable during their lifetimes. For a period, Jacob Grimm and his brother shared a home. They were both steady workers who led modest lives without making large amounts of money. They might be better categorized as Realists. Their time's social and political upheavals, as well as the challenges they brought, had a big impact on them. The Grimm brothers developed a passion for researching the past to understand why things were the way they were by reading works from many different nations.
In addition to their teaching and academic study, Jacob Grimm and his brothers were dedicated to building German national identity and supporting liberal democratic reforms in government. They were expelled from the University of Gottingen in 1837 for joining a select group of academics known as the "Gottingen Seven" who opposed King Ernest Augustus's political agenda.
The Grimms had to leave the city and returned to Kassel. The brothers were appointed by Friedrich Wilhelm IV, the king of Prussia, to the Academy of Sciences at the University of Berlin in 1841. There, they gave lectures and published works on lexicography, linguistics, philology, translation, literature, jurisprudence, and other topics.
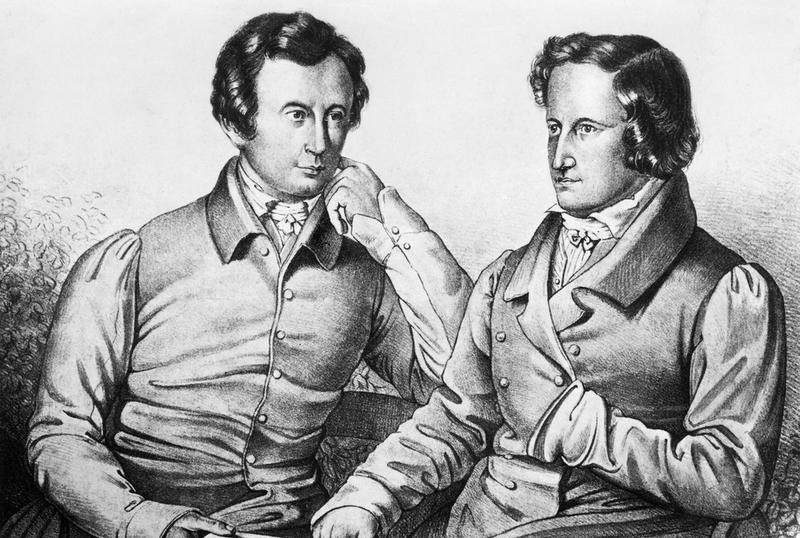

Photo: History Daily Source: DW News -
One of the most important and interesting facts about Jacob Grimm is that he helped build the foundation for the “Science” of folklore. It simply means that Grimm contributed to the development of a standardized method for studying and gathering folklore. However, he didn't come up with this on his own. Grimm was introduced to folk poetry by a man named Clemens Brentano. And Friedrich Karl von Savigny gave him the fundamental strategy he employed while studying by teaching him how to investigate ancient artifacts.
Later, he truly concentrated on studying folklore, poetry, and music. He produced writings on the value of folk literature and how it differs from all other forms of writing. Folk poetry, in his opinion, is the only form of poetry that truly captures the universal emotions of people.
He and his brother amassed folktales for their renowned Grimm's Fairy Tales compilation. That collection included more than 200 tales, such as Snow White, Little Red Riding Hood, and Sleeping Beauty. Many of the tales were gathered from oral tradition, which means they had previously only been spoken orally and not in writing. German folklore was collected by Jacob Grimm in 1816, although it wasn't quite as well-known.

Photo: National Geographic Source: Mythology Unleashed -
The formation and organization of language also attracted Jacob Grimm's interest. Grimm began translating and publishing many ancient writings, including ancient legal doctrines and beliefs in Germany, after releasing the collections of folklore. He also translated an Irish folklore work from the language into German. These initiatives served as an inspiration for several other nations, who followed his lead. Soon after, he released his own work on Germanic grammar, which covered the family of languages that included both German and English as well as German grammar. Grimm was the first to chart the evolution of the German language.
Another fascinating fact about Jacob Grimm is that he had a law named after him, Grimm’s law, which demonstrates that specific letters in old languages consistently evolve into other letters in the new language. In his Deutsche Grammatik (1819–37; "Germanic Grammar"), Jacob Grimm described the regular correspondences in Indo-European languages. It highlighted notable similarities between the Germanic and other Indo-European languages of Europe and western Asia. It is crucial for historical linguistics it indicates that sound change is a regular phenomenon rather than a random process affecting only some words, as had previously been studied before.

Photo: DW Source: Xidnaf -
The Deutsches Wörterbuch, a massive dictionary of the German language by Grimm, was first published in 1854 after beginning in 1838. Jacob Grimm and his brother expected it to span six to seven volumes over a period of ten years. They couldn't finish it since it was started on a scale that was too great for them to handle. As far as Grimm himself was involved, the dictionary has been described as a high-quality compilation of disjointed antique writings.
The dictionary wasn't finished until more than 100 years after Grimm's death, carried on by generations of successors. Jacob Grimm only lived to see the letter F completed. Later researchers finally completed it in 1961 and added to it in 1971. With 33 volumes and about 330,000 headwords, it is still a widely used work of reference today.
Many Germanists carried on the enormous dictionary effort after the death of the two brothers. But it wouldn't be finished for another 107 years after the first volumes were released. The Prussian Academy of Sciences oversaw the creation of the dictionary at the beginning of the 19th century, and renowned members like the physicist Max Planck pushed for its completion. Both East and West Germany carried on with business during the Cold War. On January 4, 1961, the 32nd and last volume were released. Zyypressenzweig was the final submission for Z. (cypress branch).

Photo: Pinterest 
Photo: Wikipedia Commons -
Prior to delving into linguistics, Jacob Grimm held a variety of government roles. Jacob traveled to Paris with Savigny in 1805 to conduct research on legal writings from the Middle Ages; the following year, he was appointed secretary to the Kassel war office. Wilhelm's health prevented him from working regularly until 1814. Following the French invasion in 1806, Jacob was appointed private librarian to King Jérôme of Westphalia in 1808 and then auditor of the Conseil d'État the following year. After Napoleon's defeat, however, he returned to Hessian service in 1813.
Jacob Grimm twice traveled to Paris (1814–1815) while serving as the legation's secretary to retrieve priceless literature and artwork that the French had plundered from Hesse and Prussia. He participated in the Vienna Congress from September 1814 to June 1815. Jacob joined Wilhelm there in 1816 after Wilhelm had already taken on the position of secretary at the Elector's library in Kassel (1814).
By that time, the brothers had definitely given up pursuing a legal profession in favor of solely literary studies. They built the foundations for their lifelong interests in the years they lived frugally and worked steadily.
Photo: Pinterest 
Photo: Global Times





























