Top 12 Interesting Facts about Rabbits
Rabbits are significantly more complex creatures than the cartoonish, carrot-eating stereotype would have you believe. They can build complex tunnels, get as ... read more...big as 20 pounds, and even consume their own excrement. Here are some more interesting facts about rabbits.
-
A rabbit in the wild is not likely to be by alone. Traveling in couples and large groups, rabbits defend one another from predators. Rabbits loathe being alone, despite the fact that they occasionally require some alone time. Due to this, bunnies are frequently sold and kept as bonded couples.
As gregarious creatures, one of the interesting facts about rabbits is they are likely to experience loneliness and depression if they live alone. Reason would suggest that the survival instinct is partly to blame. Wild rabbits are aware that safety comes in numbers. The possibility of spotting predators increases with the number of rabbits living together.
It's always a good idea to keep rabbits in pairs if you want to keep one. It would be ideal if you could locate a pair of bunnies that had already formed a bond. They should not be separated since they will stay together. Without another rabbit to keep him company, your rabbit will probably start to feel lonely. The social nature of rabbits is hard-wired. Wild rabbits naturally seek out other individuals because they live in vast colonies.
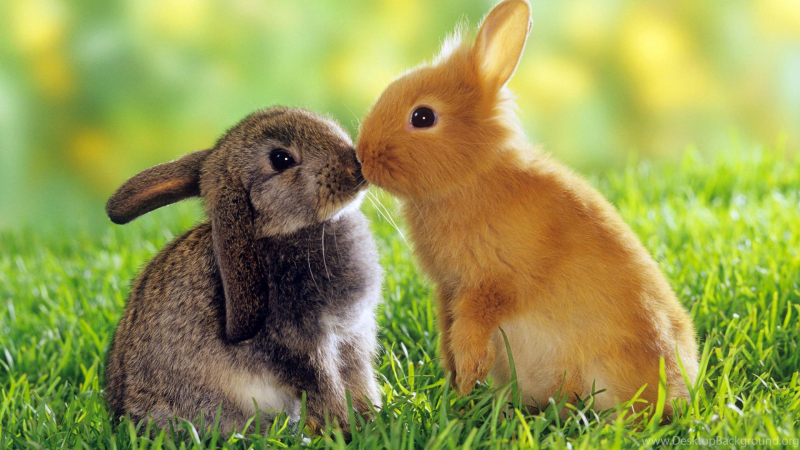

Photo: wallpaperdig 
Photo: wallpaperflare -
Just like any other species, a rabbit has distinct nutritional needs, and we are aware that what we feed our pet bunnies directly impacts how long they live. A rabbit's entire health and nutrition are intertwined, and if it isn't getting the right amounts of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and other nutrients in its diet, it won't be healthy and won't live as long.
According to Fetch by WebMD, the majority of domestic rabbits can live for eight years or even up to 12 years. Domestic rabbits have secure hiding places and a steady supply of food, in contrast to wild rabbits who must contend with risk factors like stress and predators in the wild.
Like dogs, different kinds of rabbits have variable life spans, claims Fetch by WebMD. In general, purebred rabbits live shorter lives than rabbits of mixed breeds, while larger rabbit breeds live shorter lives than dwarf types. But there are exceptions, and every rabbit is unique. More so than genetics, how well you care for your rabbit will determine how long it lives.

Photo: humanesociety 
Photo: hickoryridgehollands -
Similar to rodents, rabbits are known for having a fast rate of reproduction; many females have many litters annually. Given that the gestation period is just around one month, it is usual for the ordinary female rabbit to have several litters. Each of these litters may contain three or four infants or as many as seven, eight, nine, or even more. In addition, a few days after giving birth, the mother is physically capable of getting pregnant again.
Rabbits frequently create subterranean burrows and live in social groups. A warren is a network of rabbit burrows. A buck is the name for a male rabbit, and a doe is the name for a female. A kitten or kit is the name for a young rabbit.
The sum of the numbers quickly begins to grow. A well-built burrow and a plenty of food will promote prolonged survival and resources for the young, which will result in faster breeding. The rate of breeding will slow down if the rabbits are experiencing trouble finding food.Young rabbits can become sexually mature at around six months of age, therefore the breeding pair could have several litters during the same year, some of which might also become sexually mature and produce their own litters. Once more, the population keeps on increasing!
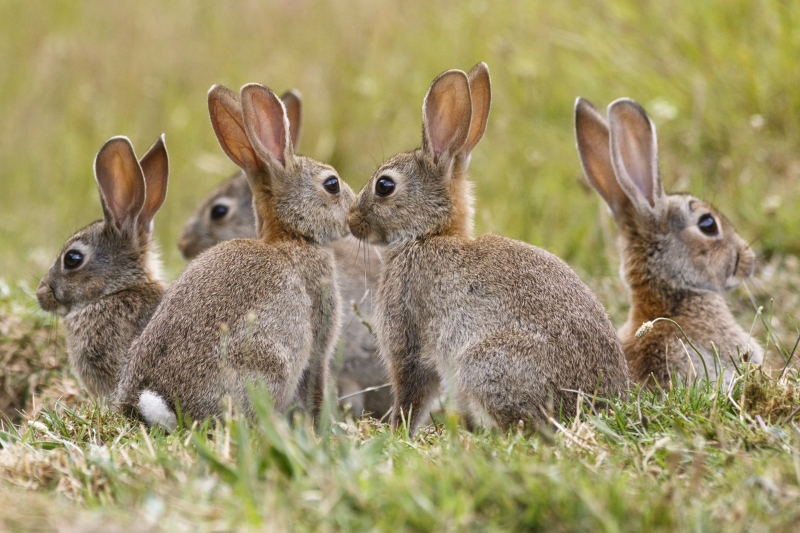

Photo: phys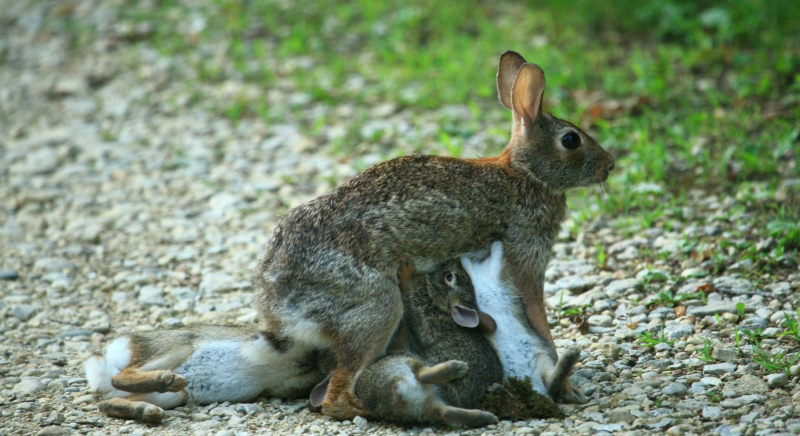 
Photo: reconnectwithnature -
The large front teeth of the rabbit are known as incisors. Although they receive all the attention, an adult rabbit has a complete set of 28 teeth. Two on top, two on bottom, and two "peg teeth" make up the total of six incisors. These little teeth are situated just behind the upper incisors. Along the sides of their jaws, rabbits also have "cheek teeth" that are 12 on top and 10 on the bottom. Rabbits cut through the hard, fibrous plants they eat with the help of their incisors, which have sharp edges. Their cheek teeth assist them in breaking down their food into smaller, simpler-to-swallow chunks.
In the wild, this set of teeth is beneficial. Because they are herbivores and eat thorny plants, rabbits are the reason for this. Without a doubt, rabbits would enjoy munching on carrots all day long like Bugs Bunny. However, the majority of them must eat other foods to thrive. They consume weeds, hay, fibrous grasses, leaves, twigs, and even small pieces of tree bark. These foods wear down their teeth as they are consumed. Thankfully, rabbit teeth have another distinctive characteristic.
The exposed roots in a rabbit's teeth allow them to develop continuously. In actuality, they grow three to five inches longer every year. Because rabbits eat such hard stuff, one of the interesting facts about rabbits is their teeth are never stop growing.
While beneficial for wild rabbits, pet rabbits raised in captivity may experience dental issues as a result of their continual tooth growth. Pellets, which are fed to most pet rabbits, do not wear down the teeth as quickly as real grass does. Owners of rabbits must therefore combine fresh Timothy hay and wooden chew toys with pellets. This aids the constant tooth-grinding of their dogs.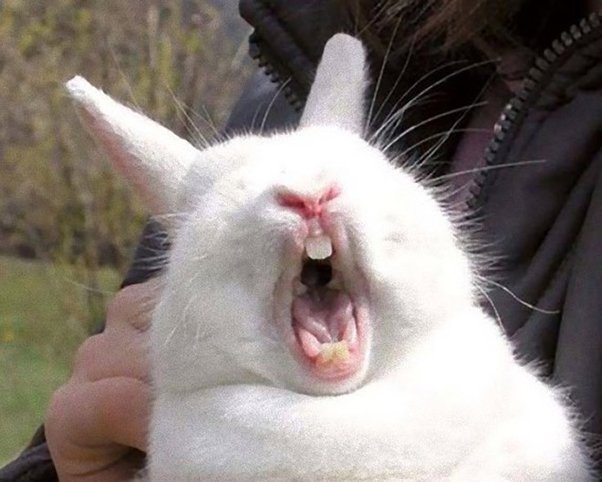
Photo: quora 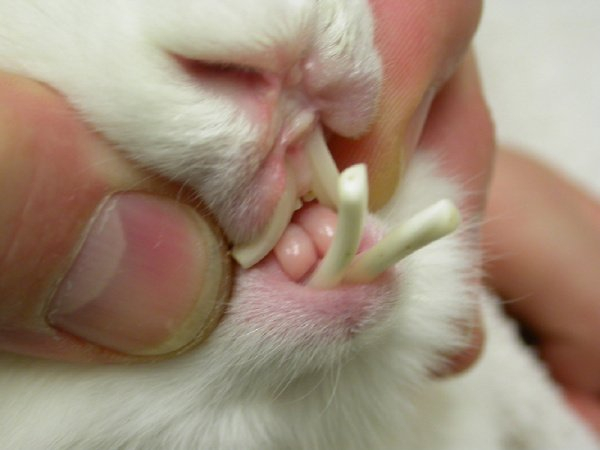
Photo: vcahospitals -
Perhaps you've noticed that rabbits have enormous eyes. But unlike most creatures we're accustomed to seeing, rabbits have a considerably higher proportion of their eyeballs on the sides of their heads than they have on the front. When these two characteristics are combined, rabbits have a very wide field of vision.
Rabbits are able to see everything around them without even turning their heads. This entails being able to spot any predators that may be approaching from behind. In reality, a rabbit's field of vision spans nearly 360 degrees, including the space above it. There is just one blind spot for them, and it is right in front of their nose. Fortunately, a rabbit's keen nose and whiskers enable them to discern what is in front of them.
If you own a lop rabbit, you might be curious as to whether they can see behind things. Do their ears not obstruct the view? The rabbit cannot see behind them because of the way their lop ears hang down the sides of their heads. This is a major factor in the rarity of lop rabbits in the wild. They are less adept at seeing predators lurking in the shadows. Primarily due to domestic breeding, lop rabbits have long, floppy ears today.
Photo: pinterest 
Photo: istock -
Rabbits can, and often do, sleep with their eyes open. Rabbits are able to and frequently do so when they are sleeping. Although they have the ability to do so, rabbits often only close their eyes when they are sleeping if they feel quite secure. Because they never close their eyes, your rabbit may give the impression that they never sleep, but in fact, they are taking a nap right in front of you.
You can tell when your rabbit is sleeping because of certain cues in their behavior. Your rabbit is likely resting if its nose fully stops moving. Additionally, they frequently move their jaws slightly or twitch when they sleep and dream. Besides, instead of being erect or attentive, their ears will be relaxedly positioned down their back.
There are three positions in which rabbits will sleep. They'll curl up into a soft ball and most likely be wide awake while dozing off. The rabbit may even spread out or flop down on its side if it feels extremely secure and at ease. The rabbit may decide to sleep with its eyes closed in various positions.Rabbits sleep with their eyes open, but why? The main focus is on surviving. Because their light receptors will continue to function, rabbits in the wild keep their eyes open. The signals from the approaching predator will still reach the rabbit's brain, allowing them to react to danger far faster than if they had closed their eyes.

Photo: squeaksandnibbles 
Photo: petkeen -
The fact that rabbits only blink once every five minutes is one of the interesting things about rabbits. Humans blink 10–20 times each minute in comparison. That is fifty times as often as a rabbit blinks.
Because their third eyelid, a flimsy membrane that covers the eye, is so thin, rabbits can get away with rarely blinking. You cannot see anything of this membrane because it is entirely translucent. A rabbit's eye is protected from dust and debris and kept moist by its third eyelid. Because the membrane of the third eyelid does the majority of the job, your rabbit doesn't need to blink very frequently.
Rabbits who blink less frequently are better able to maintain their alertness. A rabbit can survey the surroundings for danger without having to often avert their eyes by blinking. Additionally, it is because of this membrane that rabbits can easily sleep with their eyes open.

Photo: pinterest 
Photo: sym.edu.vn -
Rabbits only have photoreceptors for seeing blue and green light, yet they are not entirely color-blind. Red, green, and blue are the three categories of color receptors that humans have in their eyes, but since rabbits lack red light receptors, these wavelengths are likely to appear to the rabbit as grayscale or as different shades of green and blue.
Rods and cones are used by the retinas of animal eyes to detect color and light. Animals' ability to discern fine details and various color wavelengths means that their world is not entirely black and white. Rabbits lack the category of cones that can detect red wavelengths of light, and have significantly fewer cones than humans.
It is thought that humans developed strong color perception because it enables us to distinguish between the hues of various fruits and berries while foraging. Although rabbits can eat berries, historically they have mostly consumed grasses, leaves, and roots. Red vision wouldn't have had much of an impact on their survival, even though color vision on the green and blue spectrums had some advantages.

Photo: vetcarepethospital 
Photo: petmd -
Since rabbits are not nocturnal, they lack the unique feature of the eye that reflects light and enables animals to see in complete darkness (called the tapetum lucidum). When there is total darkness, a rabbit must rely on their other senses to find their way.
However, the vision of a rabbit is still much superior to that of a human. Rod cells, which are useful in dim light, make up a substantially higher fraction of the retina in rabbit eyes. Therefore, rabbits will have a less precise, grainy night vision as long as there is some moonlight. Similar to when you attempt to take a photo in the dark and it produces a highly blurry image. The image is not nice, but you can tell what's in it.
Instead, rabbit eyes were designed to perform well in dimly lit environments. The times around dawn and dusk, when it's not completely dark but also not too bright, are typically when rabbits are the most active. At this time of day, rabbits have the upper hand over nocturnal predators, who see best in the dark, and nocturnal predators, who see best in bright light.
Photo: flickr 
Photo: istock -
One of the interesting facts about rabbits is a rabbit's eyesight is somewhat hazy up close because, like farsighted humans, their eyes are designed to focus more on distant objects. Naturally, when objects are far away, rabbits will perceive them more clearly.
This implies that when predators and threats are further away, a rabbit will be more likely to notice them. A rabbit has a better chance of surviving if it has more time to recognize danger and flee. It's just one more way in which rabbit eyes are made to last.
In close proximity, rabbits can locate food and small objects that might be in the way by using their keen sense of smell and their whiskers. Therefore, having good close vision is not as important. Rabbits can also see close-up things, albeit they will appear a little hazy.
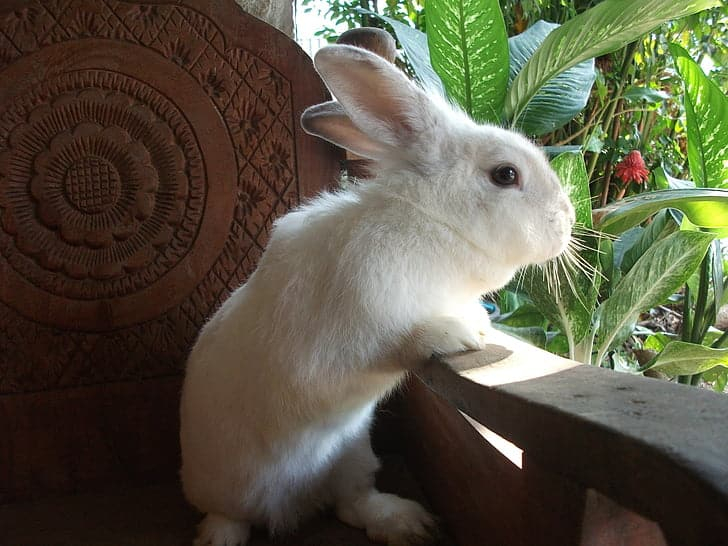

Photo: petcosset 
Photo: thehealthypetclub -
A rabbit should not be kept in a cage or hutch for any more reason than a dog or cat should not be kept inside of a cage. Because they are curious creatures, rabbits require a lot of enrichment to exhibit their natural behaviors and keep their minds active. In order to run, investigate, explore, and dig, they require a lot of space (in a safe and secure yard), as well as toys to play with and gnaw on.
Despite their reputation for being quiet, bunnies are constantly expressing themselves. Unfortunately, a lot of individuals are simply not very good at "reading" body language. A "binky" is a rabbit's springing into the air and flicking out its back legs as a sign of joy. To alert their loved ones to danger or to convey their wrath, they may thud their feet. Additionally, they have a variety of vocalizations, albeit they tend to communicate more frequently through body language.
For instance, if you're particularly fortunate, a rabbit may run about you while emitting a low humming noise as a sign of their liking. They may grunt at you to tell you to leave, and males may 'honk', especially if they haven't been neutered. A piercing cry indicates intense pain or suffering.
Photo: natgeokids 
Photo: bunnyparents -
Although carrots were formerly a favorite of rabbits, they shouldn't make up a significant portion of your rabbit's diet today. Herbivores include rabbits. Their natural diet contains a lot of fibrous plant matter, which maintains the health of their digestive tract.
Carrots include some healthy elements, but they also have a lot of sugar. Although bunnies adore them, they work best as treats. The delicate balance of the intestinal flora in your rabbit's stomach might be altered by eating too much sugar and starch, which will interfere with his sensitive digestion.
Most bunnies over three months old won't be harmed by a small amount of carrot given every other day, but you need to watch that they are also getting other, less appetizing foods that their bodies require. Grass or hay should make up the majority of a pet bunny's diet, with rabbit pellets and occasional treats filling in the gaps.
It's okay for your rabbit to chew on a carrot every day if he doesn't have any medical conditions. but only in little doses. Bunnies should only occasionally eat these sugary goodies.
Photo: squeaksandnibbles 
Photo: petkeen

































