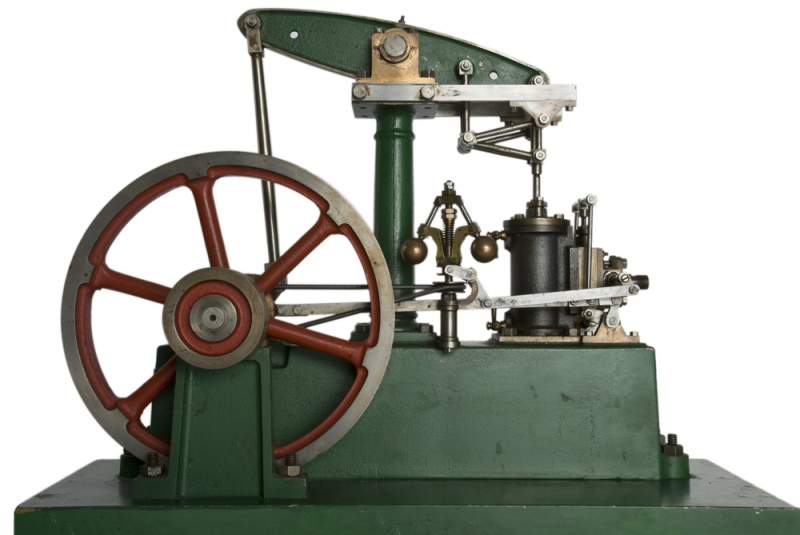
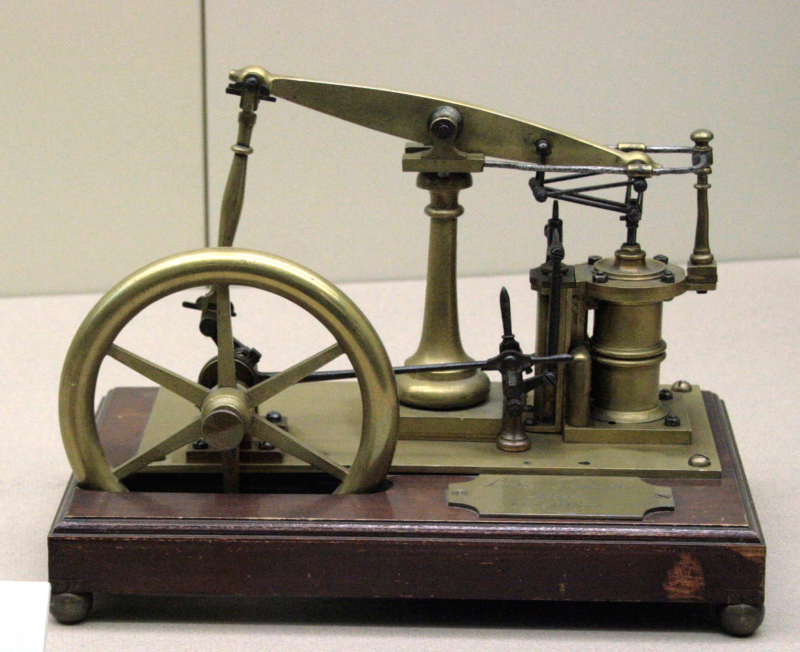
A steam engine
A steam engine is one of the major causes of the Industrial Revolution. A steam engine is a type of heat engine that uses steam as its working fluid to produce mechanical work. The force produced by steam pressure is used by the steam engine to propel a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be converted into a rotating force for work by using a connecting rod and crank. The word "steam engine" normally refers only to the reciprocating engines described above, not to the steam turbine. Steam engines are external combustion engines that separate the working fluid from the combustion products. The Rankine cycle is the optimum thermodynamic cycle utilized to examine this process. In general, the phrase steam engine can apply to either whole steam plants (including boilers and other components), such as railway steam locomotives and portable engines, or to the piston or turbine machinery alone, as in the beam engine and stationary steam engine.
Although steam-powered devices were known as early as the aeolipile in the first century AD, with a few other usages documented in the 16th century, Jerónimo de Ayanz y Beaumont patented the first steam-powered water pump for emptying mines in 1606. Thomas Savery is credited with developing the first commercially available steam-powered device, a steam pump that employed steam pressure to operate directly on the water. Thomas Newcomen invented the first commercially viable engine capable of transmitting continuous power to the machine in 1712. In 1764, James Watt made a major innovation by diverting spent steam to a separate vessel for condensation, significantly increasing the amount of work produced per unit of fuel consumed. Stationary steam engines powered the enterprises of the Industrial Revolution by the nineteenth century.
It resulted in the transformation of not only work but also of the entire society for whom that work was done. While a variety of other inventions and devices contributed significantly to the march toward industrialization, it was the steam engine, above all, that established the place and importance of the machine in the modern world and enabled the construction of large factories, which were among the most significant undertakings of industrial civilization.