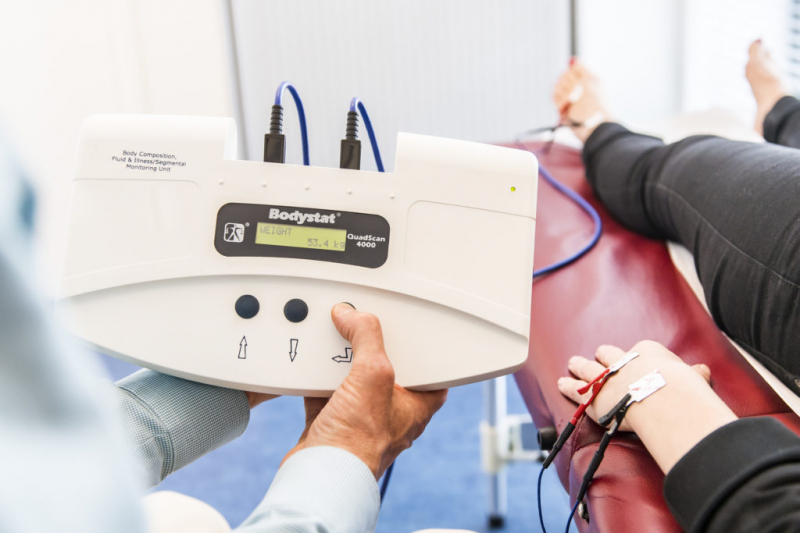
Bioimpedance Spectroscopy (BIS)
The accurate measure of a patient's total body water, extracellular, and intracellular fluid volumes in a clinical context is bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS). Healthcare professionals may use this detailed data to help in the early detection, assessment, and treatment of chronic conditions.
Because both BIS and BIA measure how the body reacts to small electrical currents, they are comparable. Devices for BIS and BIA appear similar but use different technology. In addition to high and low frequencies, BIS uses a significantly greater number of electrical currents than BIA to mathematically predict your body fluid content. BIS also analyzes the information differently, some experts think that BIS is more accurate than BIA. In fact, BIS is more accurate than consumer-grade BIA devices but has a similar error rate to more advanced BIA models (3–5% fat).