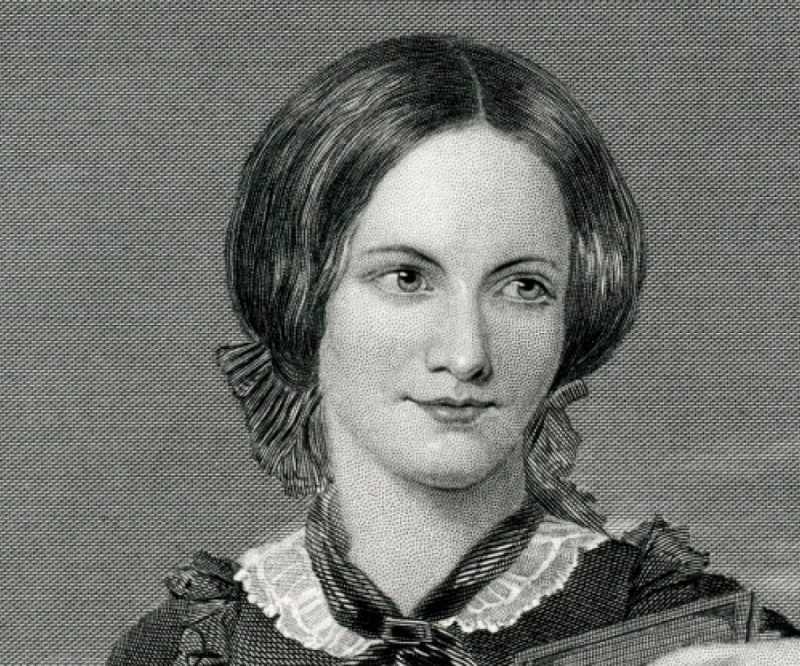
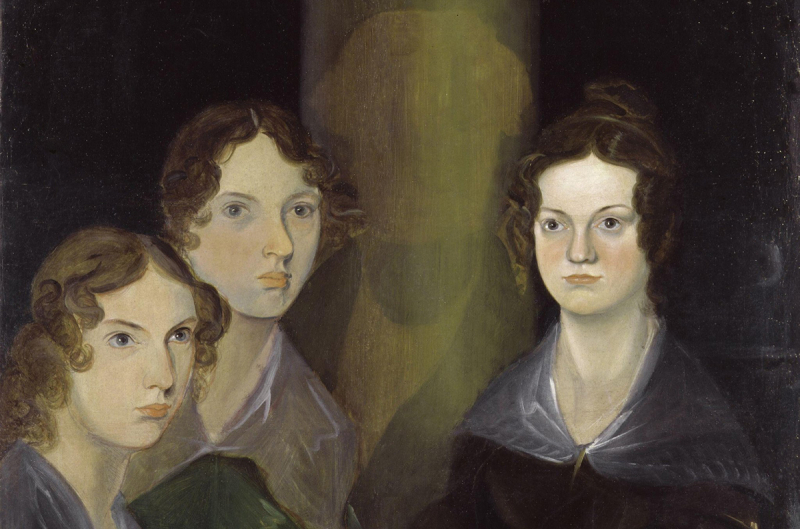Charlotte Brontë

Charlotte Brontë (April 21, 1816 – March 31, 1855) was an English novelist and poet. She was the eldest of the three Brontë sisters who lived to adulthood and whose works became English literary classics.
Charlotte Brontë left a vast legacy of written work, including classic works such as "Jane Eyre," "Shirley," and "Villette." She was the eldest of the three Bronte sisters—Charlotte, Emily, and Anne—all of whom were accomplished authors and poets. She was a strong and ambitious lady from an early age, refusing to follow the social conventions that were imposed on women at the time. She was a fiercely independent woman who presented a new kind of heroine to the literary world, one who resisted societal expectations to emerge as a brave and ethical individual in her own right.
Charlotte Brontë read Romantic authors including Sir Walter Scott, William Wordsworth, and Lord Byron as a child. The three Bronte sisters encouraged and supported one another in their undertakings, and they offered a constructive critique of one another's work. Charlotte, as the eldest of her surviving siblings, was responsible for caring for them financially, and she did so by working as a teacher and subsequently as a governess. Later, the sisters partnered and worked together to make money from their writings. The remarkable sisters' writing careers were cut short, however, by illnesses that claimed all three of them far too soon. With the treasure of works she left behind, she is always mentioned when it comes to the best female novelists ever.
Nationality: U.K