Drawbacks
You are more likely to have the following side effects if you are between the ages of 18 and 60, do not take any other medications, or have any other medical conditions. This is the next thing to know about Azithromycin.
- Some of the more typical adverse effects include fatigue, headache, dyspepsia, flatulence, nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting.
- Liver damage and possible, possibly catastrophic, liver function effects. If any symptoms of liver dysfunction appear, the medication must be stopped.
- May alter how the heart beats, which could lead to the emergence of cardiac arrhythmias. People having a history of QT prolongation, those on other medications known to prolong the QT interval, those with low blood levels of potassium or magnesium, and those taking anti-arrhythmic medications such sotalol, amiodarone, and procainamide are at higher risk.
- Compared to amoxicillin, it has been linked to a two-fold increase in the rate of cardiovascular mortality in adults. This risk is not affected by pre-existing cardiovascular disease and was highest during the first five days of azithromycin dosage.
- Almost all antibacterial medications, including azithromycin, have the potential to cause severe diarrhea linked to Clostridium difficile.
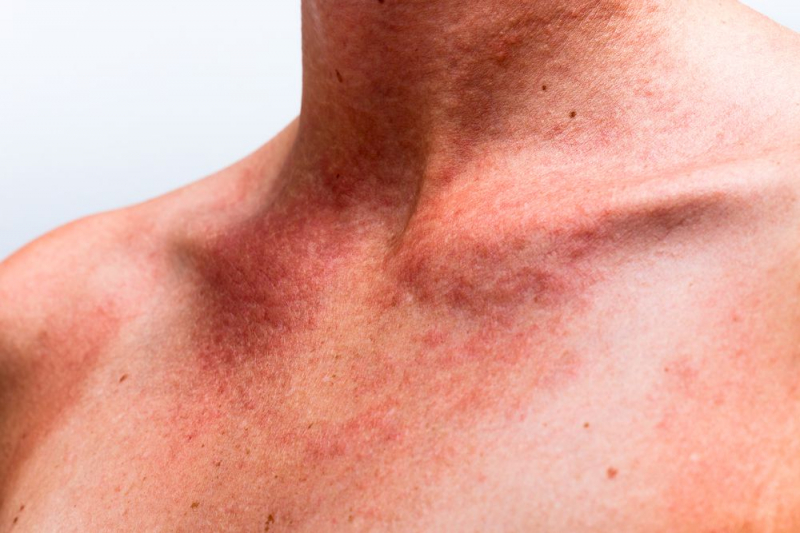
- May result in photosensitivity and serious skin responses (increased sensitivity to sunlight). If a rash appears, stop taking azithromycin and get medical help right once. has additionally been linked to life-threatening allergic responses.
- May have interactions with a number of other drugs, including warfarin and nelfinavir (see interactions below).
- In patients with renal disease, the dosage may need to be reduced, and patients with myasthenia gravis may not be a good candidate. Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis has been linked to use in newborns (IHPS). Treatment for gonorrhea or syphilis alone may not be successful.
- Has not been linked to a higher incidence of birth abnormalities when given to pregnant patients with bacterial infections. Prior to delivering a medication to pregnant women, weigh the risks and benefits. If it is decided to continue breastfeeding while taking azithromycin, the infant should be watched for diarrhea, vomiting, or a rash. Azithromycin has been found in human milk.