Hunger Crisis

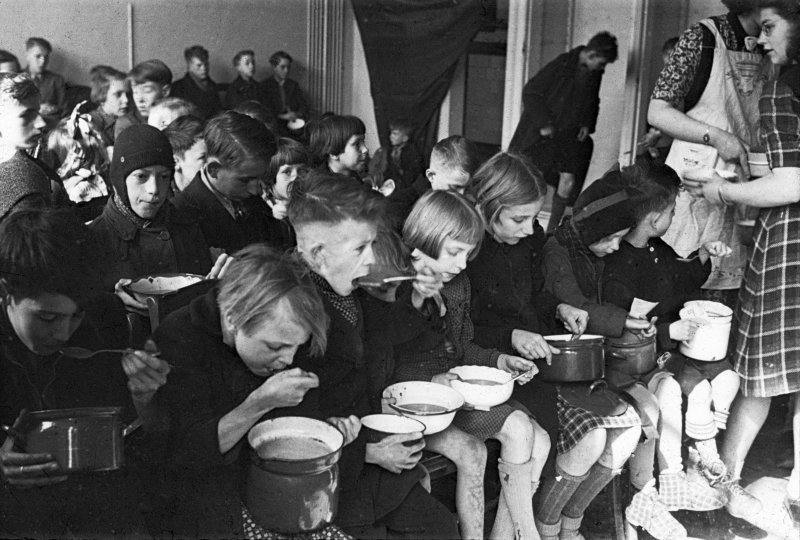
World War II led to lots of serious hunger crises, which caused a large number of casualties. It could potentially have long-term effects on adult health and socioeconomic status.
For instance, since the beginning of the German invasion, the nutritional condition of the non-German people in Poland has been terrible. The average consumption of the Polish people in 1941 was roughly 930 calories. The Warsaw Ghettos, on the other hand, were among the worst conditions, with average food rations of only 186 calories each day in 1941. In Greece, a catastrophic famine killed 100,000 to 200,000 inhabitants.
From 1944 to 1945, the Netherlands experienced a terrible hunger crisis as a result of food restrictions and severe winters. Furthermore, the battle cut off the food supply from occupied nations. In 1945, the Office of Military Government for Germany established a target of 1550 calories each day in the US occupation zone, which was regularly not achieved. In some locations, the average daily calorie consumption was about 700. During this time, adult mortality rates grew by four, while infant death rates rose by ten.