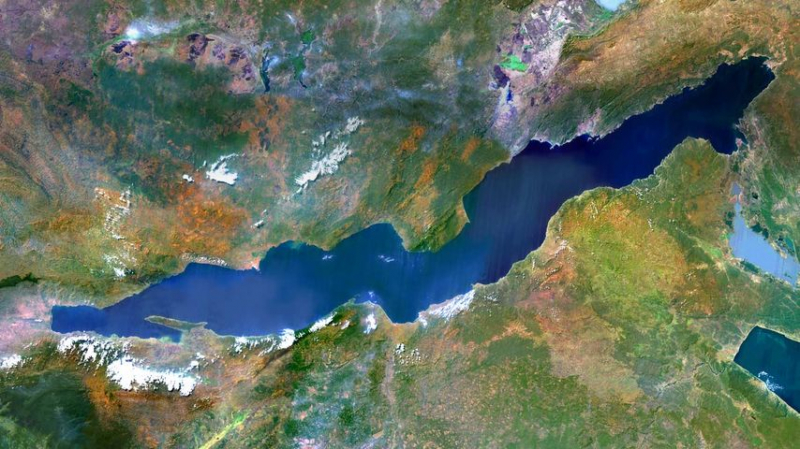
Lake Tanganyika

Top 4 in Top 5 Most Beautiful Lakes in Zambia
The English explorers Richard Burton and John Speke first introduced this immense inland sea to the rest of Europe in the middle of the nineteenth century. When they reached its shores in February 1858 after searching for it as the Nile's origin, they learned that the Ruzizi River in the north, which they believed to be the Nile, actually flowed into the lake rather than out of it. (The film "Mountains of the Moon" chronicles their extraordinary trek.)
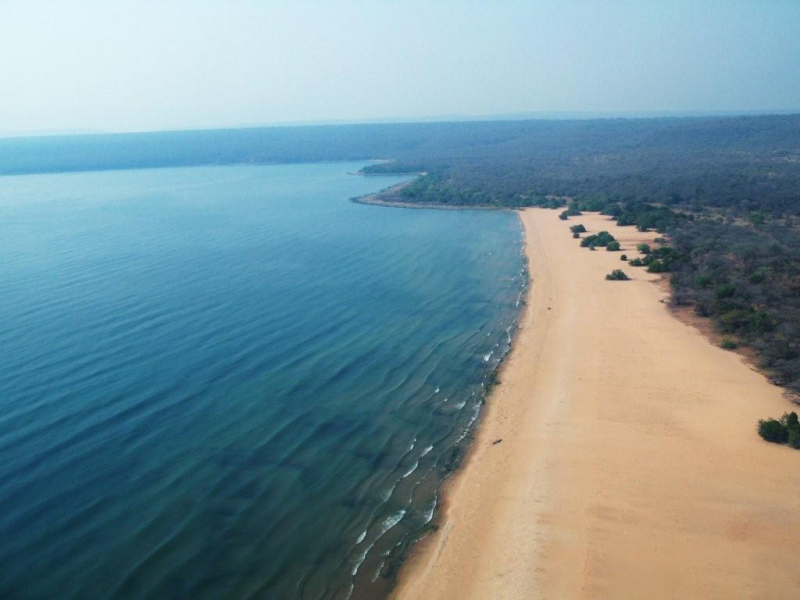
Tanganyika's waters border Tanzania, Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Zambia. It is the world's longest freshwater lake and the second deepest, behind Lake Baikal in Russia. The Great Rift Valley, which also formed the steep shoreline, is responsible for the tremendous depth. It has a depth of 1433 meters (4 700 feet), which is 642 meters below sea level. Although Zambia only claims 7% of its land area, it stretches 677 kilometers (420 miles) from north to south and is around fifty kilometers broad on average (31 miles). The pristine waters are home to over 350 different fish species and are widely known for aquarium fish exports and superb angling.
Lake Tanganyika is home to around 350 fish species, the majority of which are indigenous. Lake Tanganyika, like Lake Malawi, is exceedingly old, and the combination of its age and ecological isolation has resulted in the formation of distinct fish populations. Because new species are constantly discovered in these remarkable lakes, it is difficult to say which has the greatest diversity, but they do share the distinction of being the top two lakes in the world in terms of biodiversity, with Lake Tanganyika having the highest proportion of endemicity, concentrated primarily in the lake's Zambian waters.
To ensure that its biological richness is preserved, the Lake Tanganyika Biodiversity Project was established. The project's goal is to create a manageable and long-lasting system for protecting and preserving Lake Tanganyika's biodiversity.
Lake Tanganyika, considered one of the most biologically diverse environments on the planet, is also an evolutionary showcase due to its antiquity and stability. Tanganyika is home to 98% of the lake's cychlids (which account for two-thirds of the lake's fish). All seven crabs, five of the thirteen bivalve molluscs, more than half of the gastropod molluscs, and eleven of the thirty-three copepod crustaceans are also endemic.
The goliath tigerfish and Nile perch are among the fish that can be caught while sport fishing here. Except for the area around Mpulungu, most of the shoreline is inhabited by crocodiles, perhaps as a result of the noise made by people and motorboats. It is a true joy to swim in the lake (only in the Mpulungu area!). Warm, clean, salt-free water that occasionally shifts abruptly from smooth stillness to strong waves for excellent body surfing. The calm waters in the south are probably stirred up by storms from way up north.
Location: Within the Albertine Rift, the western branch of the East African Rift