Medicines
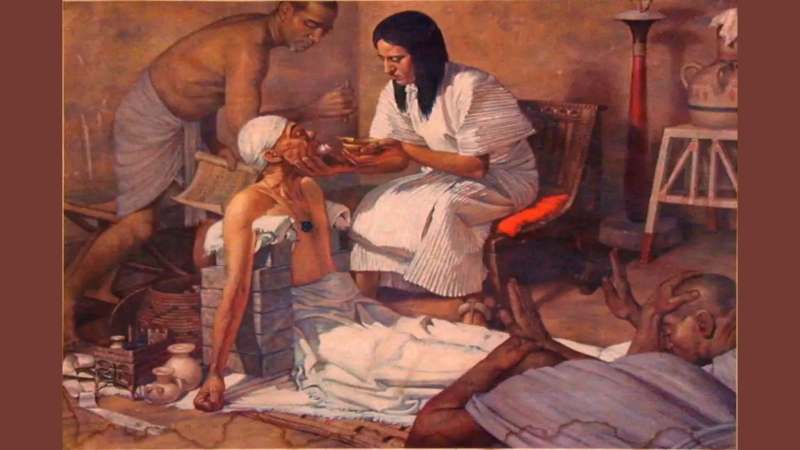
Earlier civilizations, such as those that evolved in Mesopotamia, viewed physical and mental disorders as the work of the gods and attempted to treat them with religious and magical medicines administered by priests or even exorcists. Medicine, as we know it today, originated in ancient Egypt. Although the supernatural continued to play a significant role in their understanding of health, the Egyptians took a considerably more scientific approach to cure illness, developing medications from natural resources such as minerals, plants, and animal products, and performing early types of surgery. As early as 2200 BC, there were organizations known as Houses of Life where doctors and priests practiced medicine. These facilities, which are committed to enhancing and safeguarding human life, might even be viewed as a precursor to hospitals.
They spent a lot of time learning about the art of human anatomy, which dates back to 3000 B.C.E. Egyptian physicians were well-known for their ability to amputate limbs, mend shattered bones, and patch up wounds in the ancient world. Opium was utilized as a painkiller, and they regularly ate foods like onions and garlic for their health benefits. Due to their intense concern for maintaining good dental hygiene, they were the first to develop and utilize a toothbrush and toothpaste. They employed numerous herbs to cure wounds and performed quite intricate surgeries using several bronze surgical tools since the word surgery was first mentioned in ancient papyrus about 2700 B.C.E. For all of these reasons, Egyptian doctors were well-known throughout the Mediterranean.
Not only did the Egyptians pioneer a plethora of innovative medical concepts, but they also established the world's first public health system. Around 1500 BC, the settlement of Deir el-Medina was founded for the craftsmen and laborers working on the nearby Valley of the Kings' royal tombs. These workers received a shared doctor to take care of their medical issues and aid in the healing of any complaints in addition to their monthly income, food supply, and servants. The laborers may have continued to collect their meals even when they were ill: this is the earliest known instance of sick pay! As good-natured as this may sound, it is crucial to keep in mind that the pharaohs only instituted this system in order to guarantee a steady supply of laborers to build their spectacular tombs.
Nevertheless, the advancements gained in sanitation, diagnosis, and treatments demonstrate how much contemporary medicine owes to the discoveries and knowledge acquired by the ancient Egyptians.