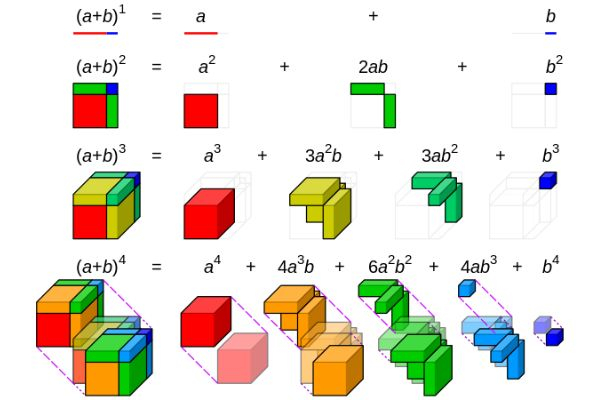
The Binomial Theorem 1665
The generalized binomial theorem, which is true for any rational exponent and one of the major accomplishments of Isaac Newton, was discovered in 1665 and is attributed to Isaac Newton. It is still widely applied in mathematics. Other than the binomial theorem, Newton made significant contributions to the study of power series and theory of inequalities. He also discovered Newton's identities, which have applications in a variety of mathematical fields, such as Galois theory, invariant theory, group theory, and combinatorics. He also developed Newton's method, which can be used to quickly find the reciprocal of a number and solve transcendental equations.
The technique was employed by Newton himself to identify the regions beneath curves. He saw several patterns that emerged concerning curves in the integer binomial sequence, extended them to rationals, and eventually discovered the generalized binomial sequence and the generalized binomial theorem.
Today, we apply Newton's approach to determine a function's minimum or maximum. The generic equation (A + B)n can be used to expand a binomial, and the binomial theorem offers a straightforward way for figuring out the coefficients of each term. This Isaac Newton theorem has been widely applied in the fields of statistics and probability.