Top 10 Coolest Things Human Found in Space Using Telescopes
Our knowledge of the universe has substantially increased since the 1920s. The famous Hubble Space Telescope was named after Edwin Hubble, whose views of the ... read more...Andromeda galaxy helped dispel the myth that our galaxy was the only galaxy in the cosmos. We now have a brand-new era of astronomy to look forward to with the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope and its final cosmic docking location in Earth's L2 Lagrange point. Once the telescope's instruments are fully operational, it will be able to look back in time to the first luminous glows that emerged after the Big Bang. However, this does not imply that observatories like the Hubble Space Telescope will cease to exist, as the telescope is still in use 32 years after its launch for ground-breaking scientific research. Today, let's take a look at the ten most gorgeous photos ever captured in the history of humankind.
-
Naturally, the first photograph of a black hole would never be absent from a list of the best astronomy pictures ever shot (or, in this case, produced). Supermassive black hole M87, also known as Messier 87, is located in the heart of a supergiant elliptical galaxy. The galaxy offers a singular view of a relativistic jet emerging from one end of the galaxy and is located within the Virgo constellation.
When we watch the relativistic jet from Earth, it appears to be traveling at a speed of 4–6 times the speed of light because of how quickly it is travelling. The Event Horizon Telescope, a global collaboration of several radio observatories, captured the first photograph of the black hole in 2019. In essence, the EHT has connected 9 observatories to create an interferometer the size of the Earth.
The EHT team has been investigating M87 in even more detail since that initial image from 2019. Another photograph of the supermassive black hole was just made public last year, demonstrating how the star monster's magnetic field disturbs the accretion disk material. Since then, the EHT team has declared that Sagittarius-A, the supermassive black hole that resides at the Milky Way's center but has never been directly imaged, will be the focus of its network of observatories.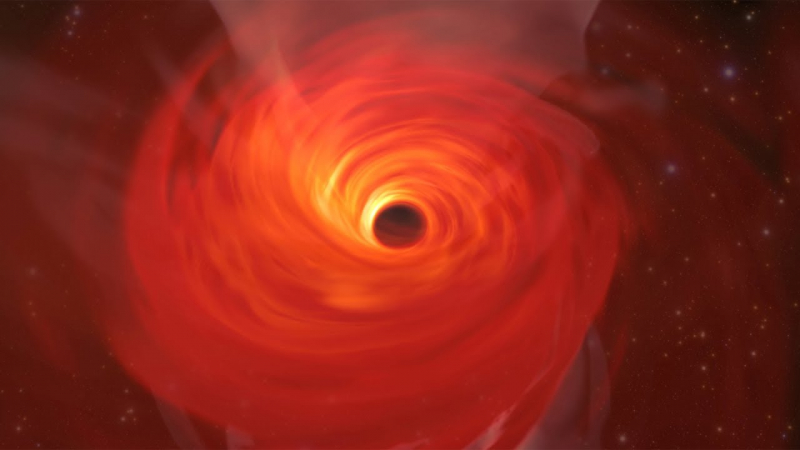
https://www.google.com/ 
https://www.google.com/ -
The Ring Nebula, which is located 2,000 light-years from Earth, provides a glimpse of the ominous destiny that our solar will eventually face after billions of years. When stars like our own pass away, they don't erupt violently like supernovae. Simply said, they aren't big enough for it. They gradually shed their outer layers instead, eventually spreading out like the Ring Nebula. They also leave a white dwarf, which is a piece of the star's core, behind.
This stunning photograph, taken by Hubble in 1998, contains each of these characteristics. A careful examination of the planetary nebula has recently revealed that the blue regions, which are made up of helium, hydrogen, and oxygen, are actually shaped more like a football that is intersecting with the red colored donut-shaped nitrogen and sulfur gasses.
Initially, it was believed that the Ring Nebula was shaped exactly as we see it. If we looked at the nebula from a different angle, it may appear more like a football had been spiked straight through the reddish gasses.

https://www.google.com/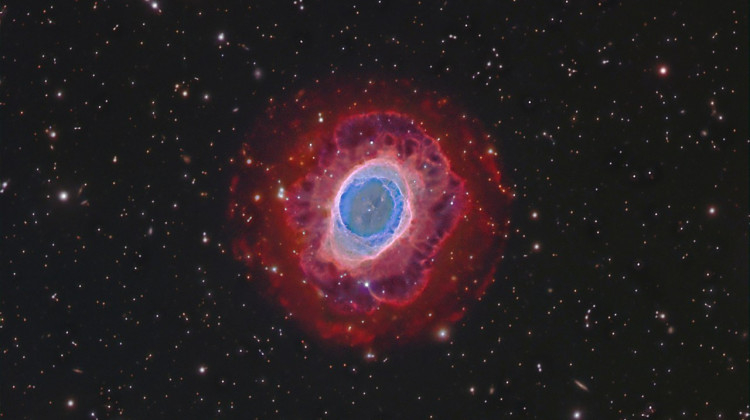 
https://www.google.com/ -
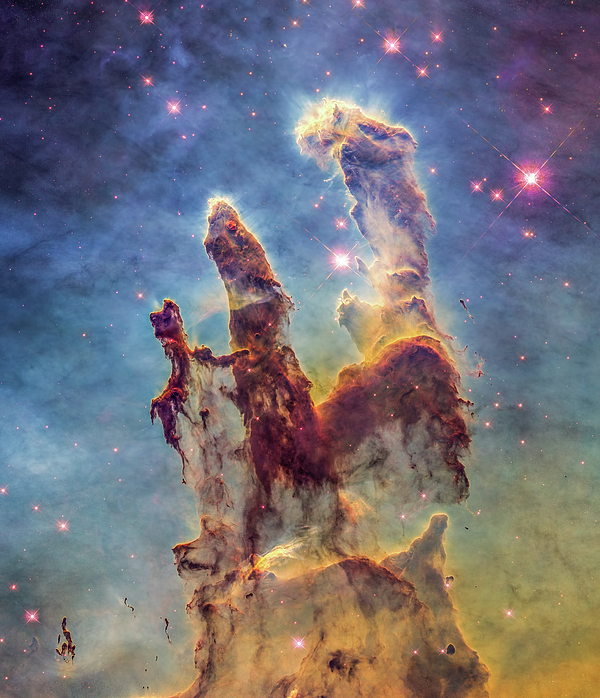
The Eagle Nebula, around 7,000 light-years from Earth, is also the location of one of Hubble's most well-known photographs, the Pillars of Creation. The Pillars of Creation consist of three trails of gorgeous multicolored dust and gas that span four to five light-years, resembling the twisted and writhing hand of a dead god.
Although the elements that make up the Pillars are nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, and sulfur, what is most amazing about this formation is that it is home to a number of recently born stars. Unfortunately, the structure is also deteriorating due to the light from those brand-new stars.
Hubble first captured the formation in 1995, and it has subsequently been seen two more times. Herschel Space Observatory of the ESA snapped a picture of the building in 2011, and Hubble then tried again to commemorate the observatory's 25th birthday.

https://www.google.com/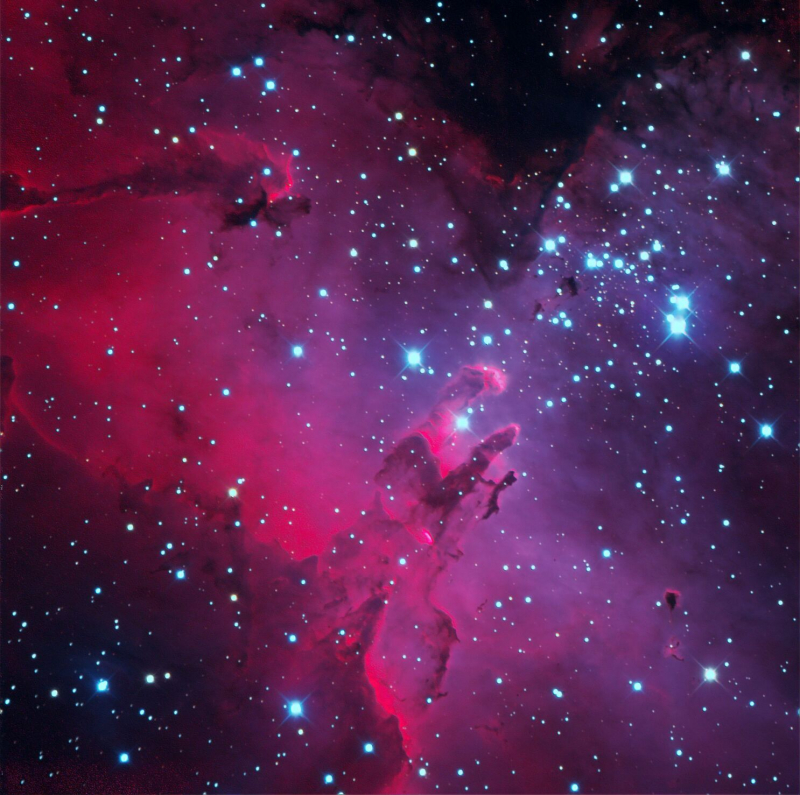 
https://www.google.com/ -
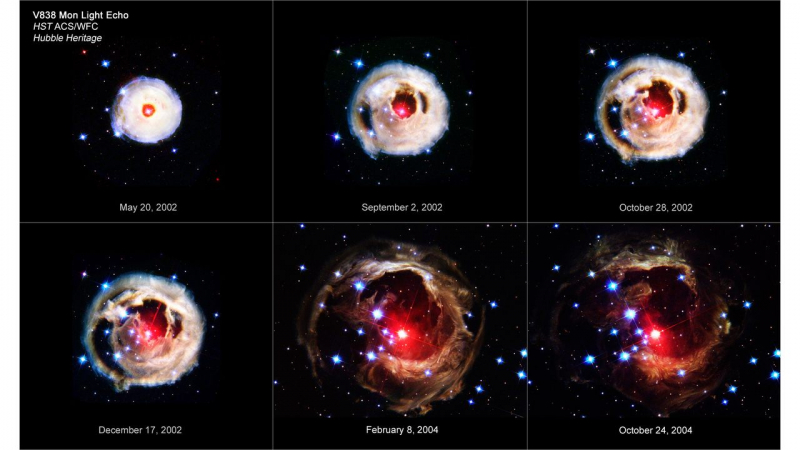
Variable star V838 Monocerotis has an interstellar dust structure encircling it. After the start of 2002, when V838 Monocerotis brightened dramatically, Hubble was able to take this amazing picture. The variable star was 600,000 times brighter than the sun for a brief period of time (cosmologically speaking, of course). This star brightened from January to April of 2002, and the reason behind the flare is yet unknown. But as a result of the star's brightness, we got this incredible image of a "light echo."
NASA claims that V838 Mon's light "propagates outward. Every new light echo observation produces a distinctive "thin-section" through the surrounding interstellar dust. In other words, even after the star has quieted down, we may still see the star's light as it travels to us reflected on the interstellar gas that surrounds the star. V838 Monocerotis is still one among the Milky Way's brightest stars, though.

https://www.google.com/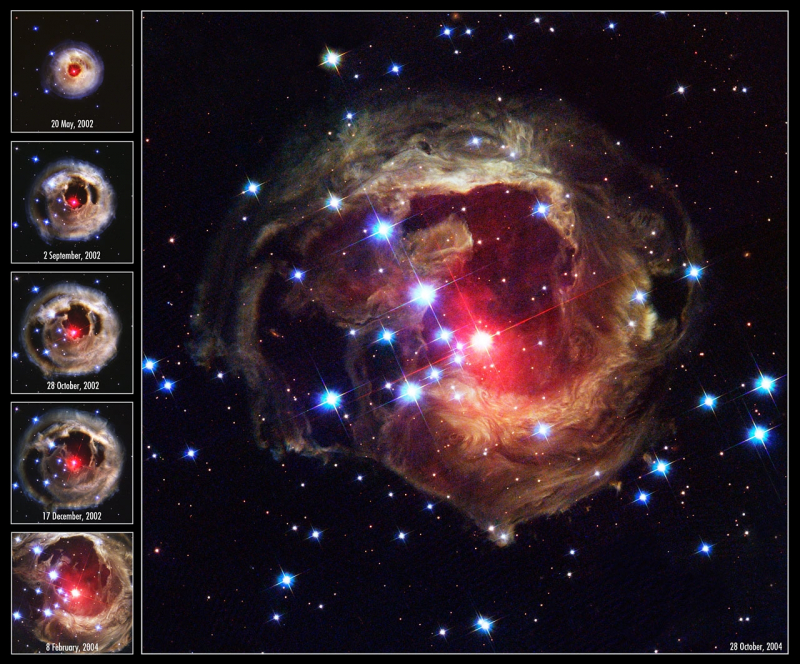 
https://www.google.com/ -
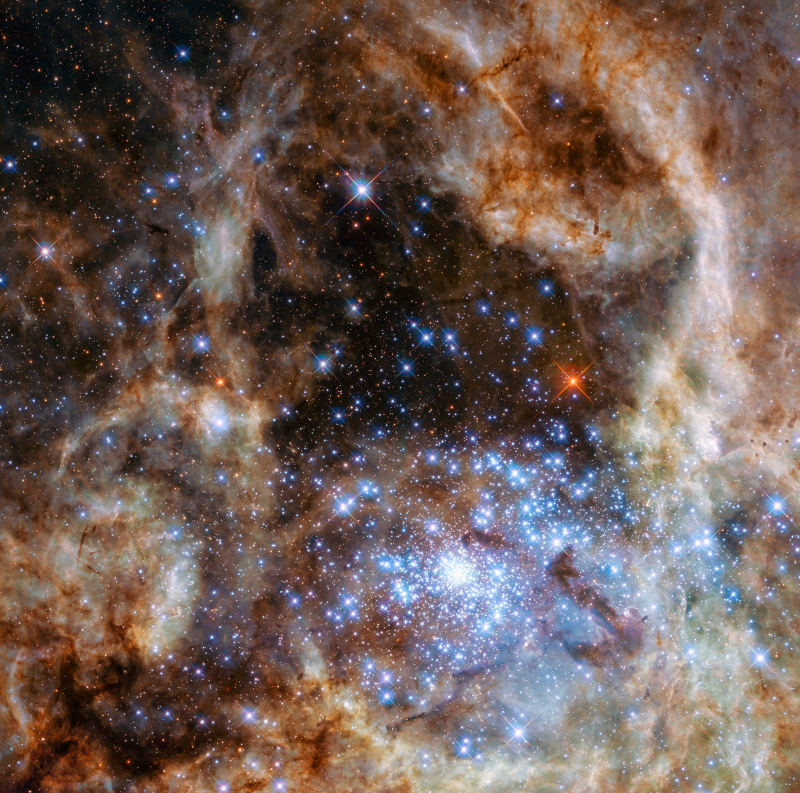
Star cluster R136 is a beautiful object that can be found within the Tarantula Nebula, which is situated within the Large Magellanic Cloud. In this area of the nebula, there are hundreds of brand-new blue stars. Some of the largest stars in the universe can be found here. In order to study the Tarantula Nebula using Hubble's spectrograph instrument, astronomers from NASA and the European Space Agency collaborated to use the Hubble Space Telescope. Nine heavyweight stars with masses 100 times that of our sun, Sol, are among these bright blue stars, which are 170,000 light-years away from us.
The NGC 2070 star cluster, which is located in the center of the Tarantula Nebula in the Large Magellanic Cloud, contains a concentration of stars known as R136 (formerly known as RMC 136 from the Radcliffe Observatory Magellanic Clouds catalogue). 72 class O and Wolf-Rayet stars are known to be present within 5 parsecs (20 arc seconds) of the cluster's center, while when it was first designated it was an unresolved stellar object (catalogued as HD 38268 and Wolf-Rayet star Brey 82). This region of the LMC is a starburst region due to the extreme quantity and concentration of young massive stars there.

https://www.google.com/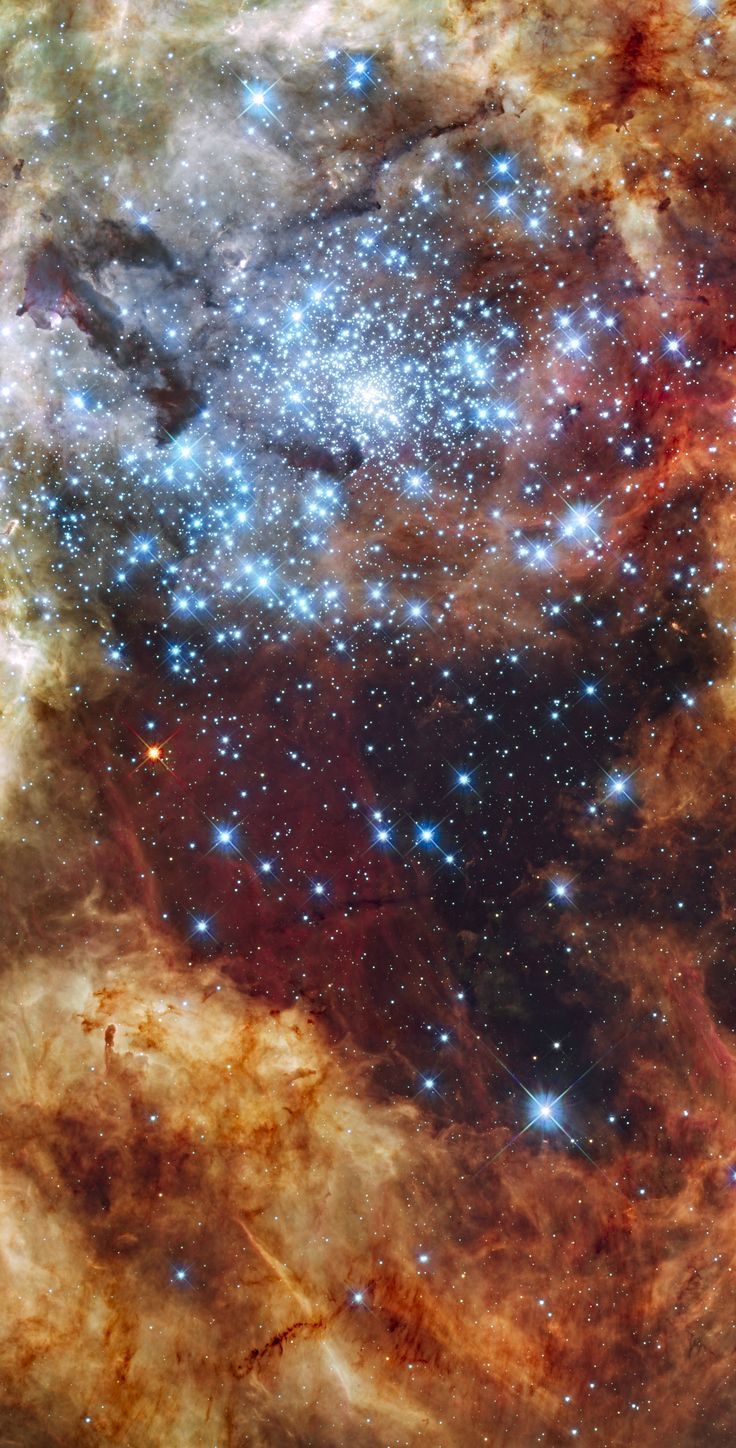 
https://www.google.com/ -
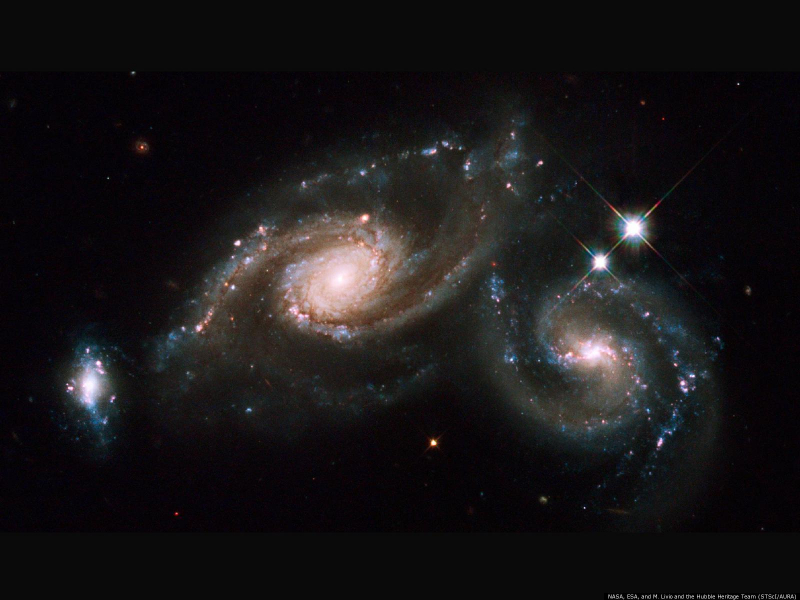
Since its launch in 1990, Hubble has had a remarkable career. The Milky Way and Andromeda Galaxies are predicted to collide and merge at some point in the future (although some data indicates that the process may have already begun). Andromeda, the constellation, not the galaxy, comes to mind. This picture shows ARP 273, a collision between two galaxies 300 million light-years away from our tiny, meager solar system.
While some sources claim that this interaction resulted in the formation of what appears to be a lovely rose or flower, other sources describe the galaxy that makes up the "stem" of the flower as performing a terrifying kamikaze dive into the other spiral galaxy. The active distortion of both galaxies into their present shapes by gravitational forces gives us a glimpse of what might occur once the Milky Way and Andromeda Galaxy are farther along in their merger.

https://www.google.com/ 
https://www.google.com/ -
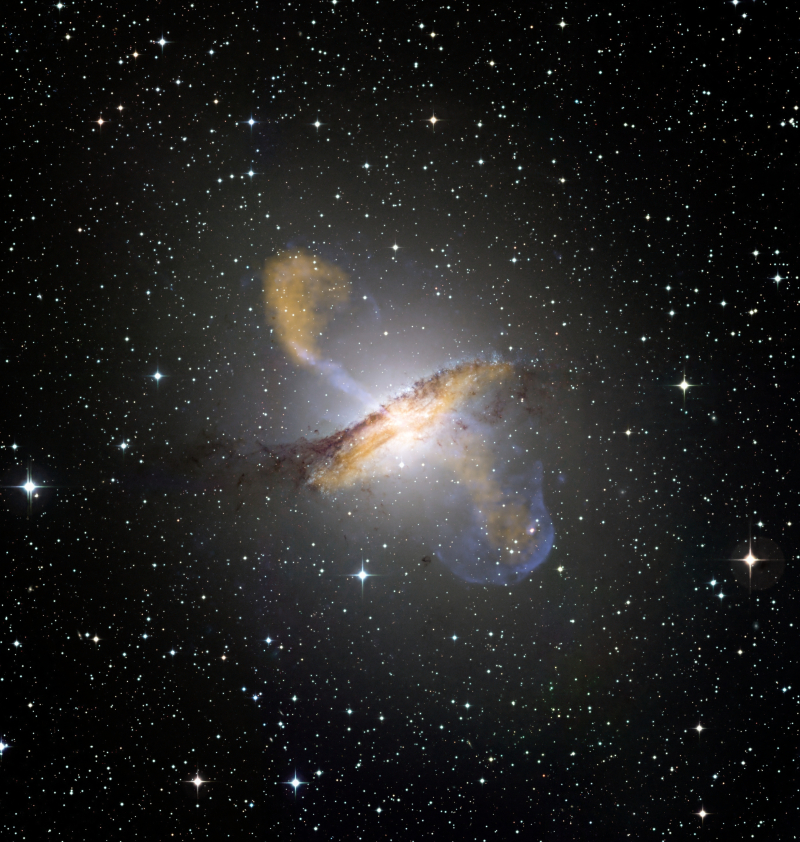
The Centaurus A Radio Galaxy is one of the most extensively researched objects in all astronomy, despite being the fifth-brightest galaxy visible from Earth's surface at night. This specific image, which displays the ferocious relativistic jets of the supermassive black hole in Centaurus A, is a composite of three independent photographs taken by three different detectors.
The light spectrum's many wavelengths are used by each device. The image's orange segments were obtained using the LABOCA on APEX instrument, its blue segments from x-ray data obtained using the Chandra X-ray Observatory, and its remaining components were obtained using the MPG/ESO telescope in La Silla, Chile.
A supermassive black hole in the galaxy's center, with a mass of 55 million solar masses, ejects a relativistic jet that causes emissions in the X-ray and radio spectrum. The inner components of the jet are thought to be flying at nearly half the speed of light, according to ten years' worth of radio measurements of it. As the jet collides with the surrounding gases and produces highly energy particles, X-rays are produced further away. Centaurus A has radio jets that are more than a million light-years long and X-ray jets that are thousands of light-years long.

https://www.google.com/ 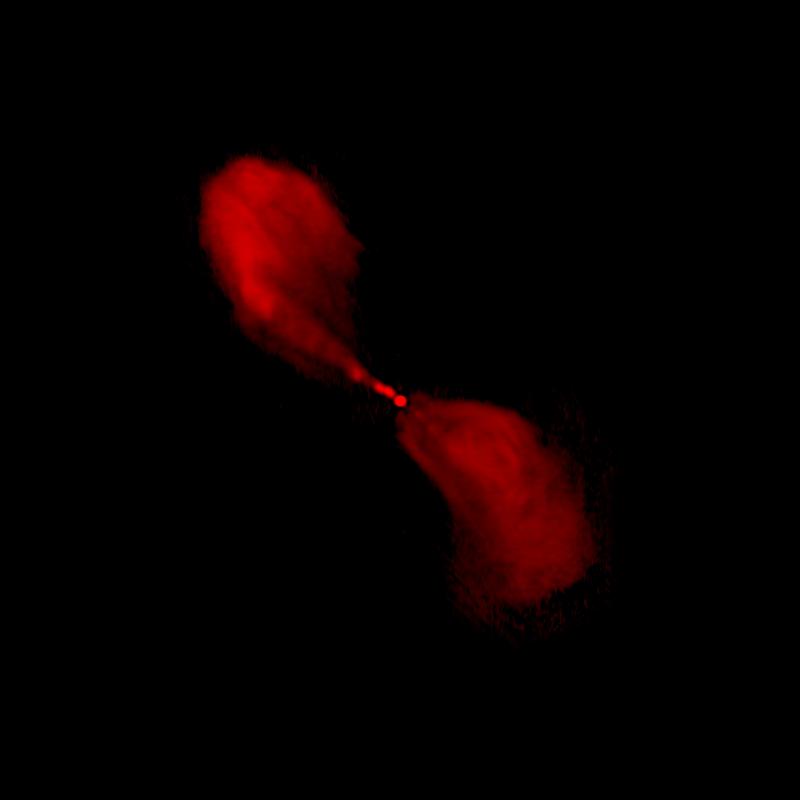
https://www.google.com/ -
The Hubble Space Telescope's image of the N44 nebula, which is part of the Large Magellanic Cloud, is extremely lovely to look at, but what's more significant are the cosmic phenomena that help to create its breathtaking beauty. There is currently no single explanation for why N44 has a large hole in it, however stellar winds from big stars and a supernova remnant have both been proposed as possibilities. The titular super bubble spans over 250 light-years.
Many of the stars that have sculpted N44 and contributed to its fluctuating density may someday explode as supernovae. This variable density is most likely the result of earlier supernovae in the area. The fact that N44 emits x-rays adds more evidence to the consequences of supernovae in the past.
Because of the huge areas of ionized hydrogen it contains, N44 is categorized as an emission nebula. The nebula's three strongest emission lines, however, are produced by neutral hydrogen atoms, which emit the hydrogen-alpha line at a red wavelength of 656.2 nm, doubly-ionized oxygen atoms, which emit at a blue-green wavelength of 500.7 nm, and singly ionized oxygen atoms, which emit at an ultraviolet wavelength of 372.7 nm.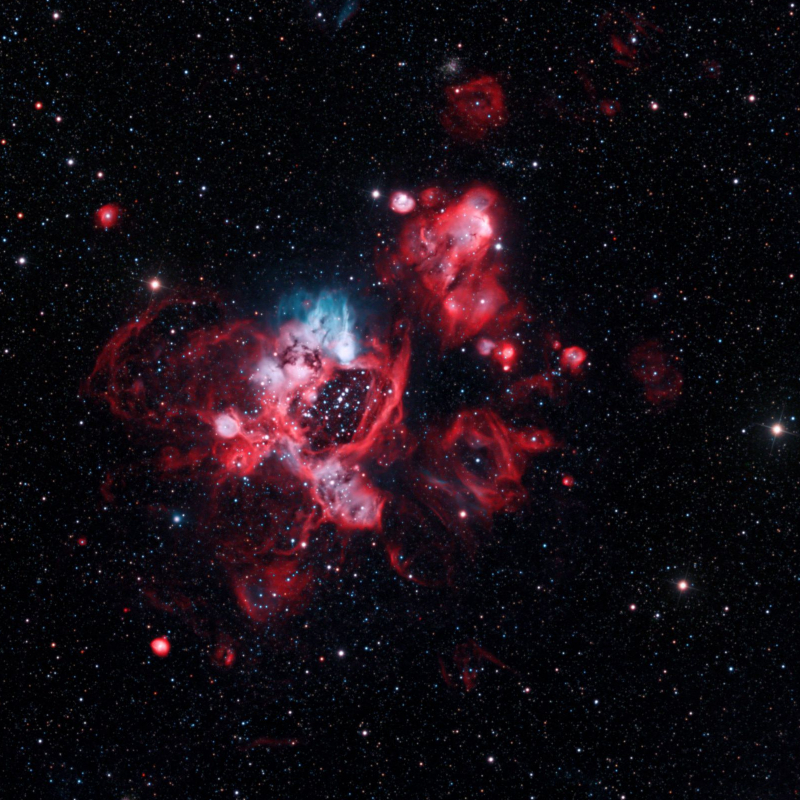
https://www.google.com/ 
https://www.google.com/ -
Typically, black holes are portrayed as silent, ominous monsters who wait in the shadows of space to devour innocent planets and stars. Yet, we probably wouldn't be here if it weren't for them. One is that our galaxy is bound together by the supermassive black hole in the center of the Milky Way, which enables our own existence.
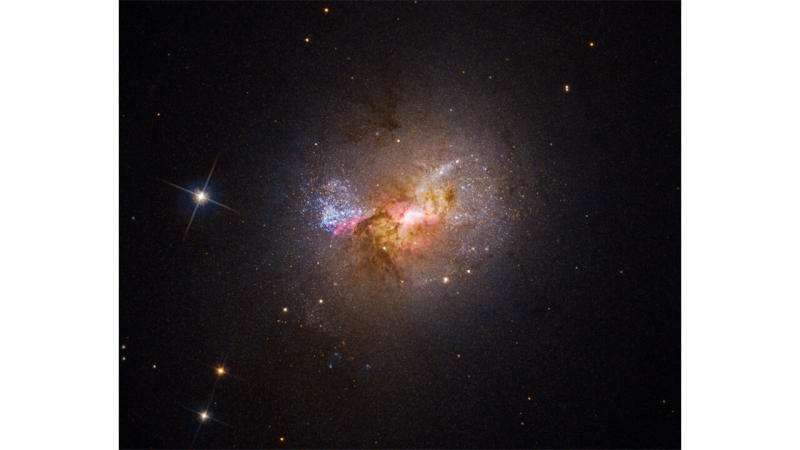
However, evidence that black holes aid in the creation of new stars may have been found by the Hubble Telescope in a dwarf starburst galaxy 34 million light-years from Earth.
Since the finding of what looks to be a giant black hole at the galaxy's center, Henize 2-10 has been the subject of great dispute.
However, studies suggest that the object at the galaxy's center may also be a supernova remnant. But in these breathtaking new Hubble photos, we can detect a gas outflow from the object that travels straight to a star nursery. If this object is a black hole, it will demonstrate the crucial role black holes play in the creation of new stars.

https://www.google.com/ 
https://www.google.com/ -
A cosmic cow is what? No, at least not yet, we haven't sent a helpless cow into orbit; instead, the name refers to a particularly luminous subtype of supernovae. Astronomers using two distinct telescopes, the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array and the Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory, worked together to find the first of these cow-like flashes of light in 2018. The recently found celestial explosion was given the name AT2018cow, which simply sort of stuck and has since come to refer to any supernovae that fit its particular description.
Cow-like supernovae are very short-lived, and AT2018cow was 100 times more luminous than a typical supernova, emitted brilliant ultraviolet and blue light, and was 100 times more luminous than a supernova. Additionally, these recently found explosions account for only 0.1 percent of all cosmic explosions that have been seen in the night sky.
And in the beginning of this year, data from the Spektrum-Roetgen-Gamma (SRG) satellite telescope revealed another cow-like event. As opposed to the original cosmic bovine, this one is 200 times brighter. Yuhan Yao, an astronomer at Caltech, believes that these occurrences are very certainly the result of a collapsing star producing a black hole or neutron star with a strong magnetic field.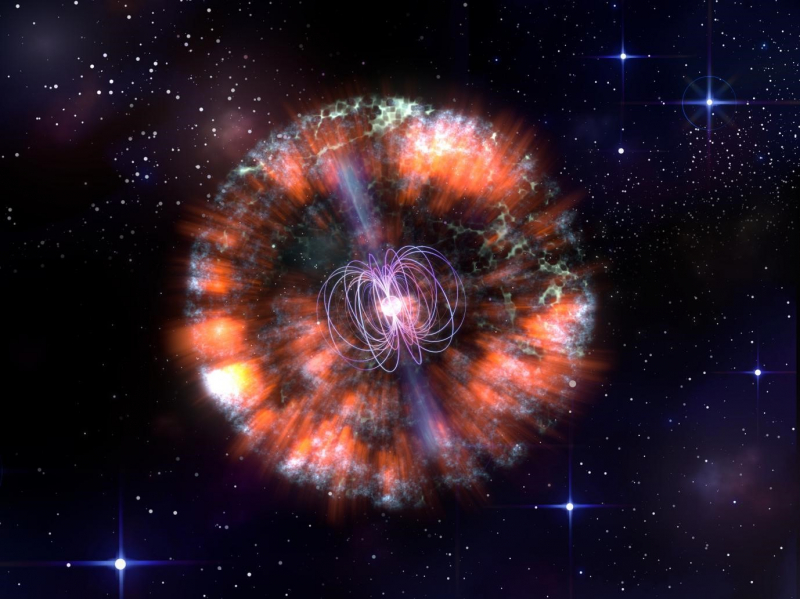
https://www.google.com/ 
https://www.google.com/































