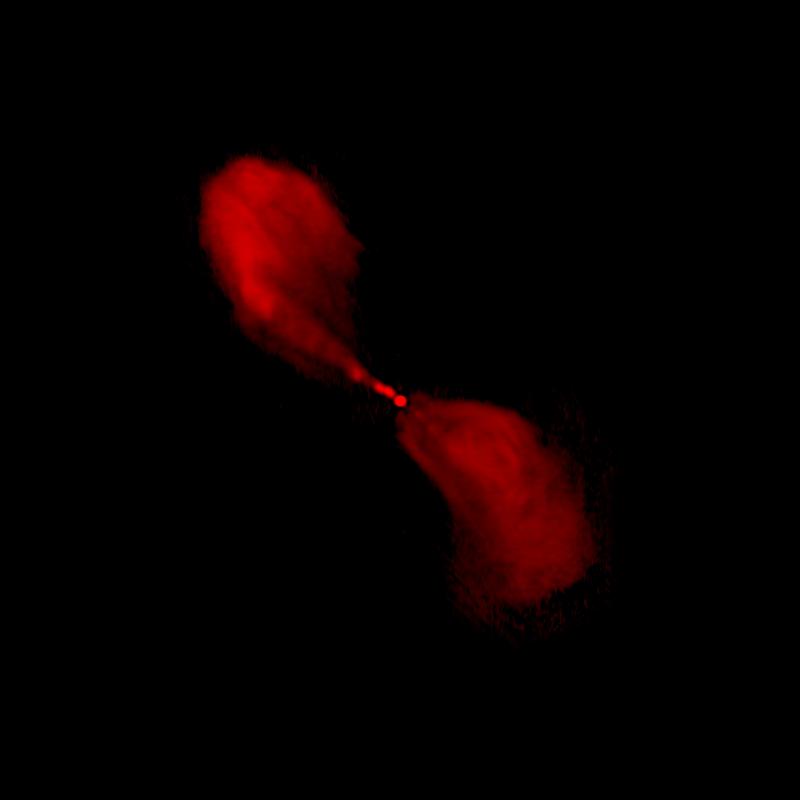
Centaurus A Radio Galaxy
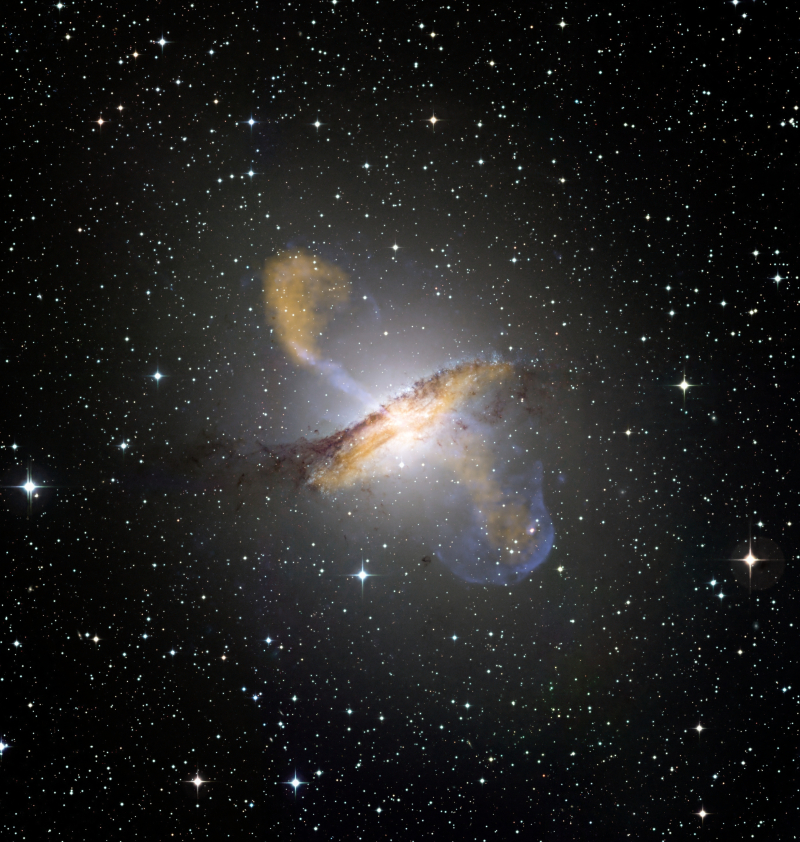
The Centaurus A Radio Galaxy is one of the most extensively researched objects in all astronomy, despite being the fifth-brightest galaxy visible from Earth's surface at night. This specific image, which displays the ferocious relativistic jets of the supermassive black hole in Centaurus A, is a composite of three independent photographs taken by three different detectors.
The light spectrum's many wavelengths are used by each device. The image's orange segments were obtained using the LABOCA on APEX instrument, its blue segments from x-ray data obtained using the Chandra X-ray Observatory, and its remaining components were obtained using the MPG/ESO telescope in La Silla, Chile.
A supermassive black hole in the galaxy's center, with a mass of 55 million solar masses, ejects a relativistic jet that causes emissions in the X-ray and radio spectrum. The inner components of the jet are thought to be flying at nearly half the speed of light, according to ten years' worth of radio measurements of it. As the jet collides with the surrounding gases and produces highly energy particles, X-rays are produced further away. Centaurus A has radio jets that are more than a million light-years long and X-ray jets that are thousands of light-years long.