Top 5 Interesting Facts about Anders Celsius
Anders Celsius was a Swedish astronomer, physicist, and mathematician who lived from November 27, 1701 to April 25, 1744. From 1730 to 1744, he was an ... read more...astronomy professor at Uppsala University, but he traveled from 1732 to 1735, visiting major observatories in Germany, Italy, and France. In 1741, he established the Uppsala Astronomical Observatory, and in 1742, he developed the Centigrade temperature scale, which was ultimately renamed Celsius in his honor. Here are the 5 interesting facts about Anders Celsius you should know.
-
One of the most interesting facts about Anders Celsius you should know is that he was born into an educated family. Anders Celsius was born on November 27, 1701, in Uppsala, Sweden. His ancestors came from the town of Ovanker in the province of Hälsingland. Doma, also known as Höjen or Högen (locally as Högen 2), was their family estate. Celsius is a Latinized version of the estate's name (Latin celsus "mound").
Celsius selected a career in science as the son of an astronomy professor, the nephew of botanist Olof Celsius, and the grandson of mathematician Magnus Celsius and astronomer Anders Spole. Anders Celsius was a gifted mathematician from a young age. Anders Celsius studied at Uppsala University, where his father was a professor, and became a professor of astronomy there in 1730.
Olof Celsius was a Swedish philologist, botanist, and clergyman. He was a professor at Sweden's Uppsala University. Celsius was a mentor of the botanist and scientist Carl Linnaeus. In 1745-47, Celsius wrote Hierobotanicon, his most famous work on biblical flora. Magnus Celsius (16 January 1621 - 5 May 1679) was a Swedish astronomer and mathematician who deciphered the staveless runes. Olof Celsius, Nils Celsius, and Johan Celsius were his children.

Olof Celsius -en.wikipedia.org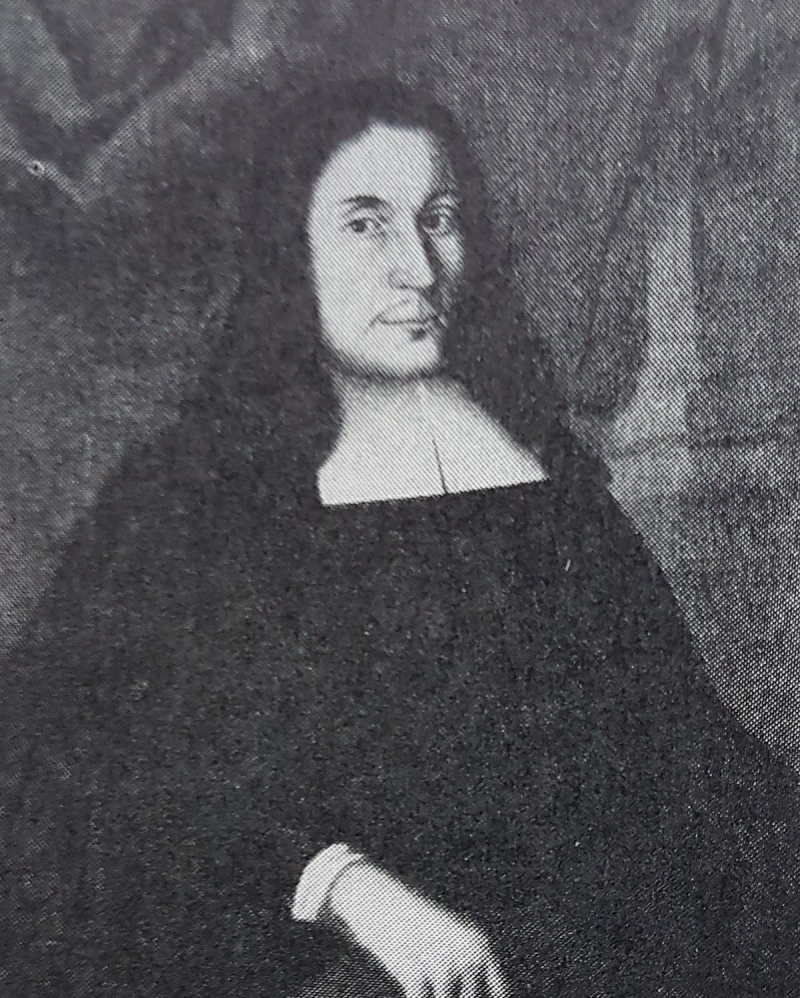 
Magnus Celsius -en.wikipedia.org -
It is a fact that he traveled to Germany, Italy, and France to visit major observatories from 1732 to 1735. Celsius traveled extensively in the early 1730s, visiting most of the main European observatories in Germany, Italy, and France. He proposed measuring an arc of the meridian in Lapland in Paris. In 1736, he took part in an expedition planned by the French Academy of Sciences to measure a degree of latitude, directed by the French mathematician Pierre Louis Maupertuis (1698-1759). The French Academy of Sciences (French: Académie des sciences) is a learned institution formed in 1666 at the proposal of Jean-Baptiste Colbert by Louis XIV to support and defend the spirit of French scientific study. It was one of the first Academies of Sciences and was at the forefront of scientific discoveries in Europe in the 17th and 18th centuries. Pierre Louis Moreau de Maupertuis was a mathematician, philosopher, and writer from France. On the invitation of Frederick the Great, he became Director of the Académie des Sciences and the first President of the Prussian Academy of Science.
The trip's goal was to measure the length of a degree along a meridian near the pole and compare the results to a previous voyage to Peru, which is now in Ecuador near the equator. The missions supported Isaac Newton's theory that the earth's shape is an ellipse flattened toward the poles.

The French Academy of Sciences -en.wikipedia.org 
Pierre Louis Maupertuis -commons.wikimedia.org -
One of the most interesting facts about Anders Celsius you should know is that Celsius founded the Uppsala Astronomical Observatory. He published De observationibus pro figura telluris determinanda (Observations on Determining the Shape of the Earth) in 1738. Celsius's participation in the Lapland trip earned him high regard from the Swedish government and his peers, and he was instrumental in raising interest from the Swedish authorities in giving the funds needed to build a new modern observatory in Uppsala. Celsius was granted his request, and the Uppsala Astronomical Observatory was established in 1741. The observatory was outfitted with instruments purchased during his long journey overseas, which included the most advanced instrumental technology of the period.
The Uppsala Astronomical Observatory (UAO, Astronomiska observatoriet I Uppsala) is Sweden's first and oldest astronomical observatory. It was formed in 1741, however, there has been a professorial chair of astronomy at the University of Uppsala since 1593, and the university archives contain astronomy lecture notes dating back to the 1480s. Anders Celsius conducted his studies there in the 18th century, and the first proper observatory was established in 1741. Celsius persuaded the university consistory to purchase a big stone mansion of medieval antiquity in central Uppsala, where he built an observatory on the roof. Celsius used the residence for both professional and personal living quarters. This observatory was used until 1853, when the new observatory, now known as the "old observatory", was completed.
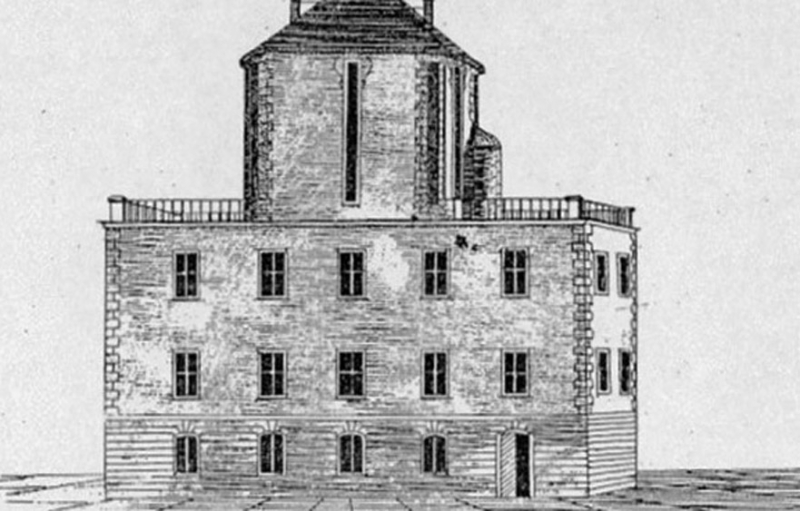
The Uppsala Astronomical Observatory -memolands.com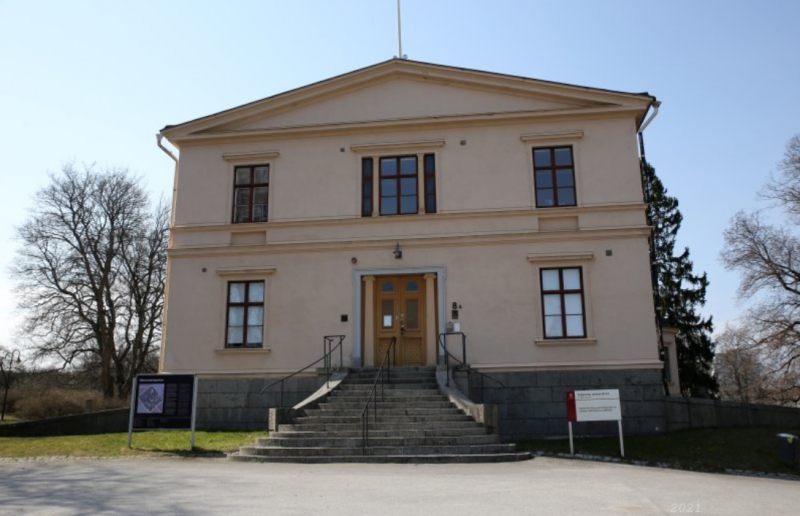 
astrofriend.eu -
It is a fact that Anders Celsius devised a temperature scale in 1742. The degree Celsius is a temperature unit on the Celsius scale, which was formerly known as the centigrade scale. The degree Celsius (symbol: °C) can refer to a specific temperature on the Celsius scale or a unit used to represent the difference or range between two temperatures. It is named after Anders Celsius, who invented a temperature scale identical to this one in 1742. The measure was previously known as centigrade, from the Latin centum, which means 100, and gradus, which means steps, until being renamed to honor Anders Celsius in 1948.
Anders Celsius devised a temperature scale in 1742 that was the inverse of the scale currently known as "Celsius": 0 indicated the boiling point of water, while 100 represented the freezing point of water. He described his tests showing that the melting point of ice is basically unaffected by pressure in his work Observations of two persistent degrees on a thermometer. He also determined the boiling point of water as a function of air pressure with amazing accuracy. In a report to the Royal Organisation of Sciences in Uppsala, Sweden's oldest scientific society, founded in 1710, he introduced the Celsius temperature system in 1742. His thermometer was set to zero for the boiling temperature of the water and one hundred for the freezing point. He advocated calibrating the zero point of his temperature scale, which is the boiling point, at the mean barometric pressure at mean sea level. This is referred to as one standard atmosphere. After Celsius's death, the scale was reversed by Carl Linnaeus in 1745 to facilitate more practical measurement.
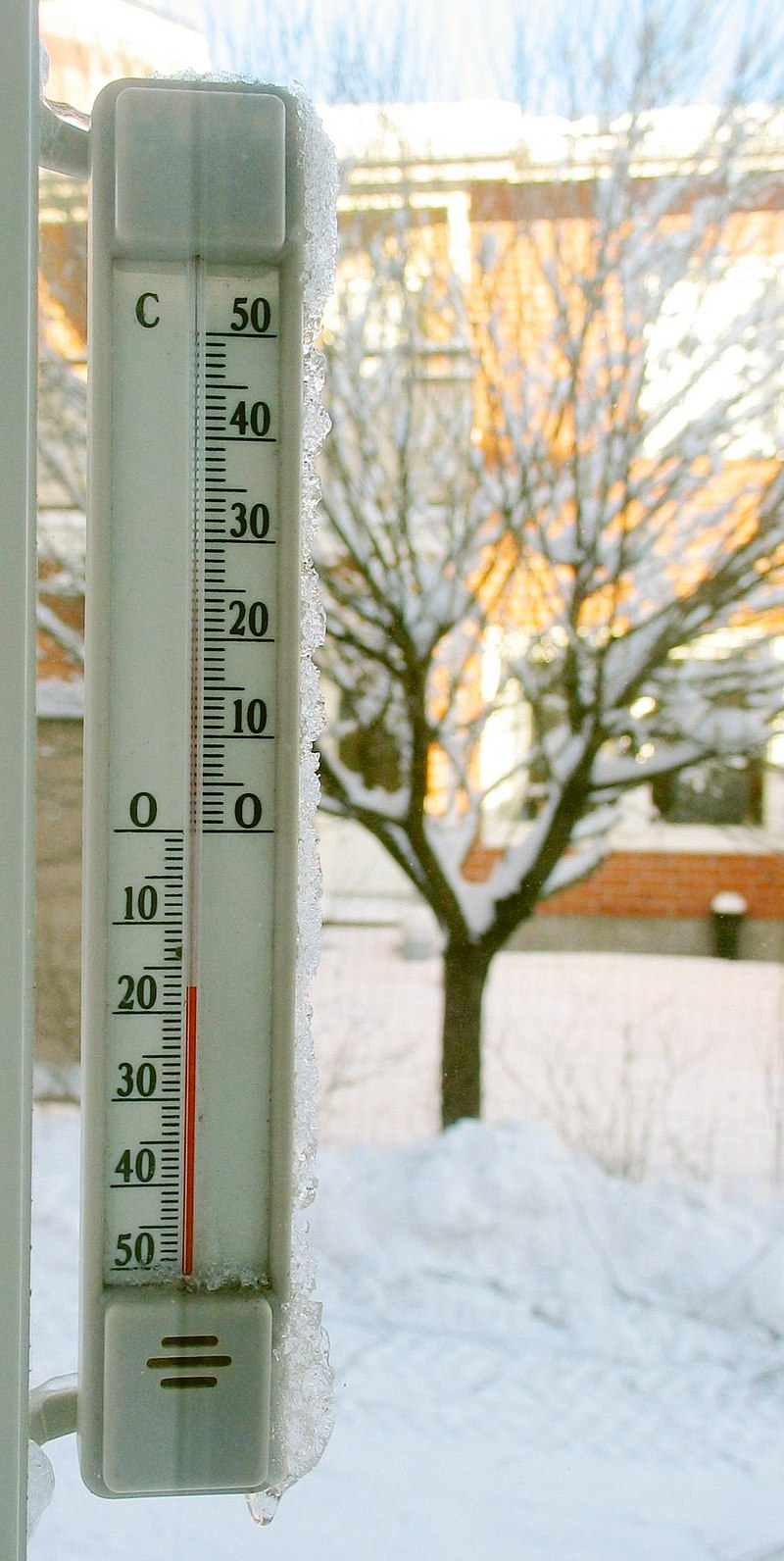

The degree Celsius -vi.wikipedia.org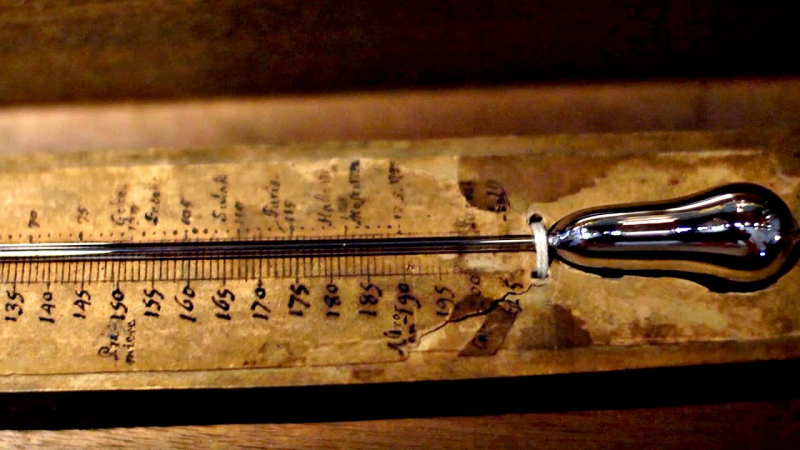 
Anders Celsius's thermometer -youtube.com -
One of the most interesting facts about Anders Celsius you should know is that he was passionate about the aurora borealis. Celsius published the Nova Methodus distantiam solis a terra determinandi in 1730 (New Method for Determining the Distance from the Earth to the Sun). His research also included the investigation of auroral phenomena, which he carried out with the assistance of his assistant, Olof Petrus. Olof Petrus was an astronomer from Sweden. Following his studies in the Netherlands, he was appointed lecturer at the University of Uppsala in 1732 to replace the vacancy left by Anders Celsius, who was then on his grand tour of European observatories. He researched the aurora phenomena and other astronomical matters with Celsius beginning in 1737.
An aurora, often known as the polar lights, is a natural light display in the sky that is most commonly seen in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). It exhibits dynamic patterns of bright lights that appear as curtains, rays, spirals, or dynamic flickers that cover the entire sky. Celsius was the first to propose a link between the aurora borealis and variations in the Earth's magnetic field. He studied the variations of a compass needle and discovered that larger deflections were associated with the more auroral activity. In 1733, he published a collection of 316 observations of the aurora borealis recorded by himself and others between 1716 and 1732 in Nuremberg.
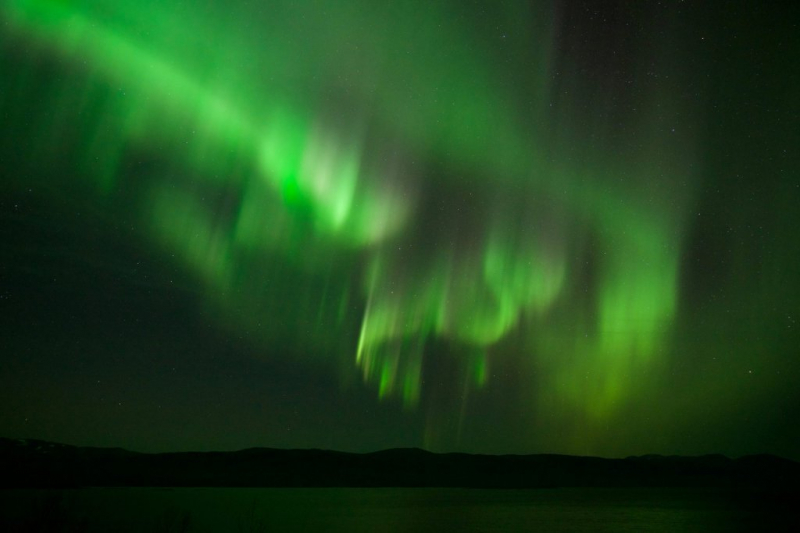

Auroral phenomena -irf.se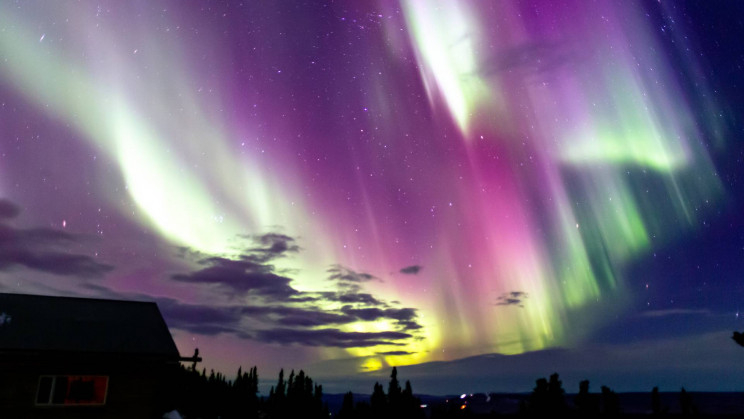 
Auroral phenomena -interestingengineering.com


























