Top 9 Interesting Facts about Earth
Only one astronomical object, Earth, which is third from the Sun, is known to support life. Although the Solar System contains enormous amounts of water, only ... read more...Earth is home to liquid surface water. The oceans cover around 71% of Earth's surface, dwarfing its lakes, rivers, and polar ice. Although this is planet that we live, but there are existing some interesting facts about Earth that certainly we don't know. Let's follow Toplist in this article to know more about Earth.
-
The "Blue Marble," as astronauts have dubbed Earth, is round, as several images from space can confirm. However, appearances can be deceptive. In actuality, Earth is not exactly round.
The globe rotates about its axis, which causes an additional 0.3 percent bulge near the equator. The diameter of the Earth is 12,714 kilometers (7,900 miles) from the North to the South Pole and 12,756 kilometers (12,756 miles) through the equator (7,926 miles). The distance between the two points, 42.78 kilometers (26.58 miles), is roughly 1/300th of the diameter of the Earth. The planet appears spherical to the human eye because this variation is too small to be visible in images of Earth taken from space.
Various dynamic causes the formation of the Earth to vary over time. Those gravitational anomalies are changed by the planet's internal mass movement. Plate tectonics causes valleys and mountains to appear and vanish. The surface is occasionally cratered by meteors. Earth tides are also produced by the moon and sun's gravitational pull in addition to ocean and atmospheric tides.
Additionally, according to geophysicist Richard Gross of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, the shifting weight of the oceans and atmosphere can result in deformations of the crust "on the order of a centimeter or so." Another phenomenon is a postglacial rebound, in which the crust and mantle that were lowered by the enormous ice sheets that covered the earth during the last ice age are now rising at a rate of about a centimeter each year.

Photo; livescience Source:National Geographic youtube chanel -
One of the interesting facts about Earth is only the planet Earth has plate tectonics in the Solar System. In essence, the Earth's crust is divided into sections called tectonic plates. These can interact with one another and are perched on top of the Earth's magma core. One plate will subduct (move underneath another) when two plates contact, and where they rip apart, another crust will form.
There are several reasons why this process is crucial. It is essential to the carbon cycle and causes tectonic resurfacing as well as geological activity (such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, mountain-building, and the creation of oceanic trenches). The ocean's small plants sink to the bottom as they die.
The carbon-rich remains of this life are recycled over a very long time period inside the Earth's interior. This removes carbon from the atmosphere, preventing us from experiencing a runaway greenhouse effect like Venus did. Without plate tectonics, the Earth would become hot and hellish, since there would be no way to recycle this carbon.
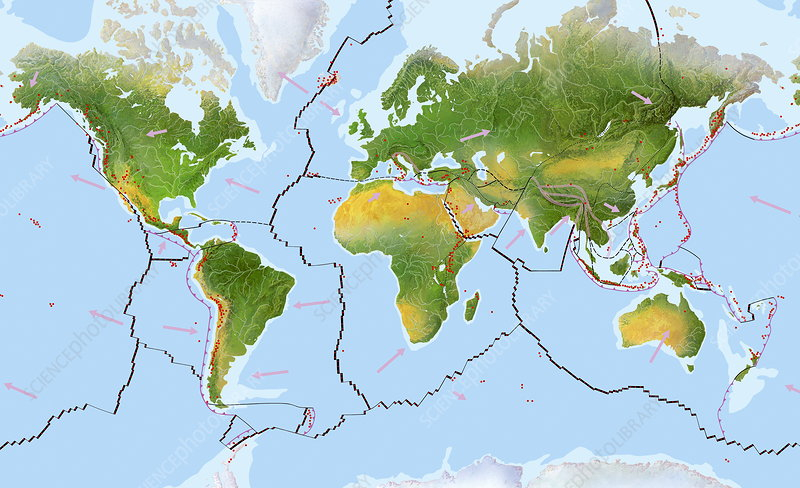
Photo: sciencephoto 
Photo: education.nationalgeographic -
The Earth's atmosphere is thickest during the first 50 km or so from the surface, although it extends out into space for around 10,000 km. The troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere are its five principal layers. As one ascends higher into the sky and moves away from the surface, air pressure and density often drop.
Near the surface of the Earth, the majority of the atmosphere is located. In actuality, the first 11 km above the planet's surface contain 75% of the atmosphere. The greatest layer is the exosphere, which starts at the base of the top of the thermosphere at an altitude of roughly 700 km above sea level and extends to a distance of about 10,000 km (6,200 mi). Exosphere and empty space in outer space, where there is no atmosphere, converge.
The exosphere is primarily made up of heavier molecules including nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide as well as hydrogen and helium, both of which have extremely low densities. The exosphere no longer functions like gas because the atoms and molecules are so wide apart, and particles are continually escaping into space. These free-moving particles travel in and out of the magnetosphere on ballistic trajectories, and may also move with the solar wind.
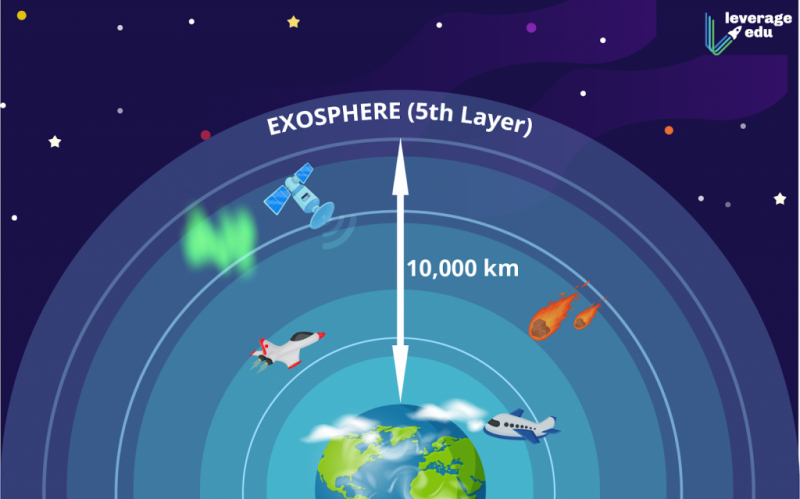
Photo: nigeriaschoolnews Source: Pooja Luthra youtube chanel -
The Earth experienced numerous severe climatic upheavals known as ice ages between 600 and 800 million years ago. The "snowball Earth" idea proposes that Earth nearly or totally froze multiple times as a result of the extreme cold. Earth would have been blanketed in glacial ice from pole to pole during four such times of alternate freezing and thawing that may have been caused by decreases in greenhouse gases like methane and carbon dioxide. The planet would have had an average temperature of roughly -50 degrees Celsius (-74 degrees Fahrenheit), with the equator similar to Antarctica today, because the majority of the sun's energy would have been deflected into space by ice.
The most recent ice age trend started around 40 million-year-old and got worse around 3 million-year-old during the Pleistocene. Since then, glacial and thawing cycles have occurred repeatedly in high- and middle-latitude regions, roughly every 21,000, 41,000, and 100,000 years. The Last Glacial Period, sometimes known as the "last ice age," lasted for around 11,700 years and left significant areas of the continents buried in ice up to the middle latitudes.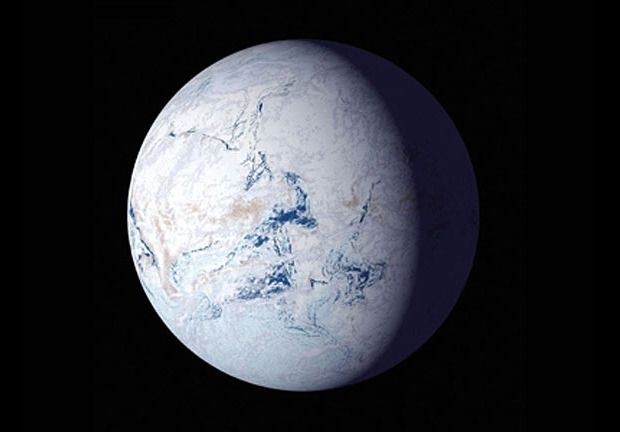
Photo: livescience 
Photo: news.cnrs.fr -
Astronomers refer to this period of time as a Sidereal Day because it takes the Earth 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds to circle once entirely around its axis. What does that mean exactly? Doesn't it imply that a day is 4 minutes shorter than we believe it to be? You could assume that as time passes, day by day, the night will eventually become day, and vice versa.
However, keep in mind that the Earth revolves around the Sun. The Sun travels by around 1° per day, or about the size of the Moon in the sky, in relation to the background stars. Due to the Earth's orbit around the Sun, we can observe a small amount of motion from it. If you add this to the Earth's rotation on its axis, you get a total of 24 hours.
Contrary to a Sidereal Day, the length of time it takes the Sun to return to the same location in the sky is what is known as a Solar Day. Knowing the difference between the two entails understanding how long it takes for the sun to rise and set once, as well as how long it takes for the stars to appear at the same location in the sky.
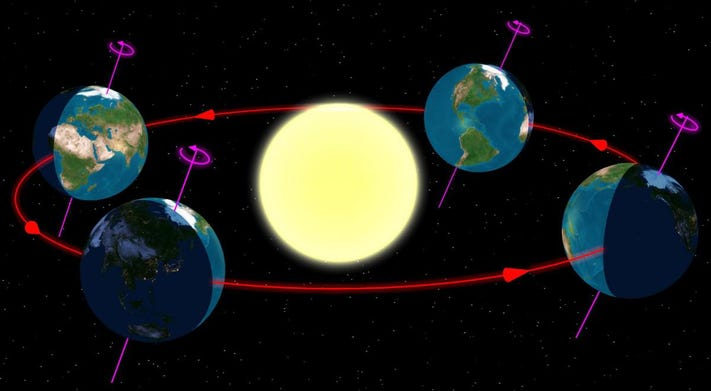
Photo: forbes 
Photo: meteorologiaenred -
You probably already know that Earth has one moon (aka. The Moon). There is a lot that is known about this object, but did you know that there are also two other asteroids in co-orbital with the Earth? These two asteroids, named as 3753 Cruithne and 2002 AA29, are a member of a larger group of asteroids known as Near-Earth Objects (NEOs).
One of the interesting facts about Earth, Asteroid 3753 Cruithne, which is also known as "Earth's second moon," is 5 km across. It has a coordinated orbit with Earth, but does not really orbit it. It also has an orbit that gives the impression that it is moving in the same direction as the Earth, but it is actually traveling in a different direction around the Sun.
In contrast, 2002 AA29, which is only 60 meters across and orbits the Earth in a horseshoe shape, passes within 95 years of the planet. It will seem to circle Earth in a resemblance to a satellite orbit in around 600 years. It might be a good target for a space exploration expedition, according to scientists.
Photo: universetoday Source: lil info youtube chanel -
Scientists have found historical evidence of organic molecules and water on Mars, as well as the basis for life on Saturn's moon Titan. Deep space nebulae can be seen to contain amino acids. Additionally, researchers have made assumptions regarding the potential for life to live below the ice surfaces of Titan and Europa, moons of Saturn. However, only Earth has really been found to have life.
However, scientists are developing experiments that will help find out if there is life in other worlds. The Nexus for Exoplanet System Science (NExSS), for instance, was newly established by NASA and will spend the ensuing years searching through the data returned by the Kepler satellite telescope (and other missions that have not yet been launched) for indications of life on extrasolar planets.
Massive radio dishes are now searching for the telltale signs of intelligent life stretching out across intergalactic space by examining distant stars. And more recent space observatories, including the James Webb Telescope from NASA, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), and the Darwin project from the European Space Agency, may just have the power to detect the presence of life on distant planets.

Photo: wallpaperup 
Photo; rojgaraurnirman -
Contrary to what you may instantly think, the gravitational field of the Earth does not even extend across the entire planet. The gravitational field of Earth has very rough terrain, just like the surface of the planet, which has a variety of terrain.
This is due to a number of factors but is principally determined by the separation between the Earth's surface and its center. As a result, the Earth's gravity will actually somewhat decrease at the peak of a mountain because it is a little farther from the planet's center.
Mountain ranges, on the other hand, will typically have a higher gravitational field over a larger region because of the increased mass.
Additionally, as we already learned, the Earth is not perfectly spherical. If it were, the gravitational field would be roughly uniform everywhere. Due to centrifugal forces generated by the planet's rotation, gravity is also weaker at the planet's equator.
Photo: phys.org 
Photo: wealthtechtoday -
The tilt of the Earth does, one of the interesting facts about Earth, change through time, despite popular belief. Oblivion, also known as obliquity, has changed during the past million years between 22.1 and 24.5 degrees in relation to Earth's orbital plane. Since each hemisphere receives greater solar energy throughout its summers, this has a significant impact on the Earth's temperature and seasons. The opposite is true of its winters.
This was shown to be one of the primary factors influencing changes in Earth's climate over time by the late Serbian mathematician, astronomer, climatologist, and geophysicist Milutin Milankovitch (the melting and retreat of glaciers and ice sheets).
The tilt of the Earth's axis is currently 23.4 degrees. That falls about in the middle of its two historical extremes. In a roughly 41,000-year cycle, this angle is progressively decreasing. Although its occurrence is well known in the planetary and climatic sciences, scientists still don't fully understand why it occurs.
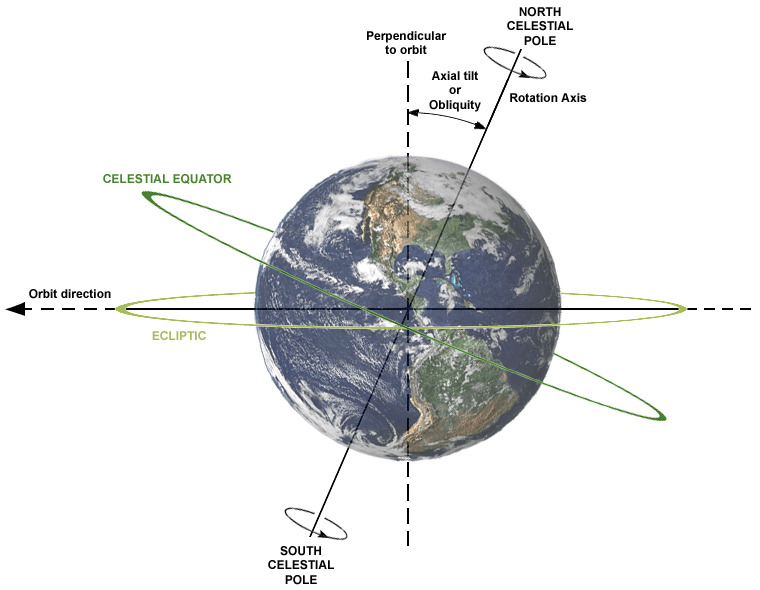
Photo: universetoday Source: MITK12Videos youtube chanel






























