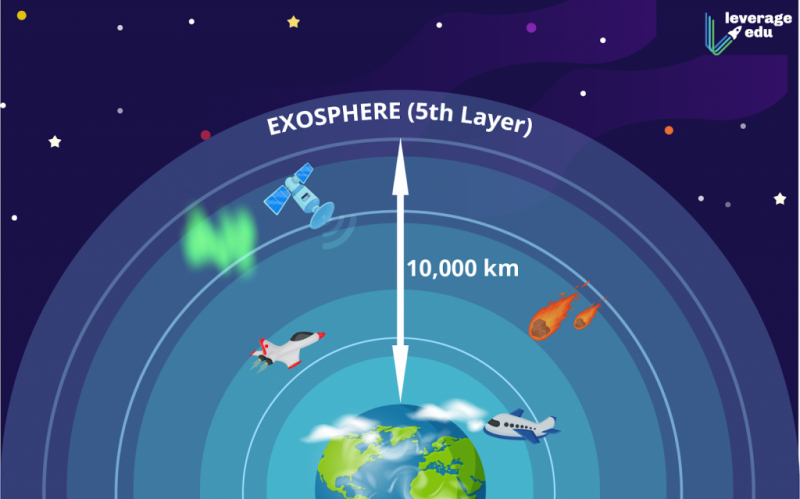
The Earth’s Atmosphere Extends to a Distance of 10,000 km

The Earth's atmosphere is thickest during the first 50 km or so from the surface, although it extends out into space for around 10,000 km. The troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere are its five principal layers. As one ascends higher into the sky and moves away from the surface, air pressure and density often drop.
Near the surface of the Earth, the majority of the atmosphere is located. In actuality, the first 11 km above the planet's surface contain 75% of the atmosphere. The greatest layer is the exosphere, which starts at the base of the top of the thermosphere at an altitude of roughly 700 km above sea level and extends to a distance of about 10,000 km (6,200 mi). Exosphere and empty space in outer space, where there is no atmosphere, converge.
The exosphere is primarily made up of heavier molecules including nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide as well as hydrogen and helium, both of which have extremely low densities. The exosphere no longer functions like gas because the atoms and molecules are so wide apart, and particles are continually escaping into space. These free-moving particles travel in and out of the magnetosphere on ballistic trajectories, and may also move with the solar wind.