Top 14 Most Famous Tribes in India
Explore the 'Top 14 Most Famous Tribes in India' in this post. Discover their diverse traditions, languages, festivals, and cultural richness. These indigenous ... read more...communities play a vital role in India's cultural tapestry.
-
The first tribe on the list of the top 14 most famous tribes in India is the Gond, primarily residing in central India. They have a rich cultural heritage deeply rooted in their connection to nature and a vibrant tradition of art. They speak the Gondi language, which is central to preserving their oral traditions.
Agriculture is their main livelihood, focusing on crops like rice and millet, with rituals and festivals celebrating the land and its seasons. Traditional attire is practical, adorned with silver and bead jewelry for special occasions. Godly culture combines animistic beliefs with Hinduism. They venerate deities, spirits, and ancestors through rituals and festivals featuring music, dance, and ceremonies. Gond art is renowned for its intricate depictions of nature and daily life. Environmental conservation and sustainable land management are integral to their practices.
In a changing world, the Gond community maintains its cultural richness while adapting to modern challenges and opportunities. Their distinct way of life, which is deeply rooted in nature and artistic expression, adds to India's rich cultural tapestry.

Screenshot of https://www.flickr.com/photos/ramesh_lalwani/3311958260 Video by Prasar Bharati Archives -
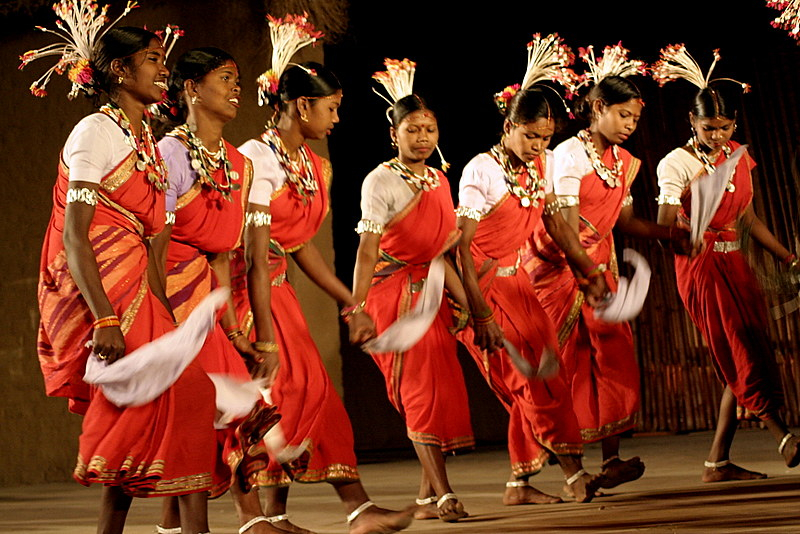
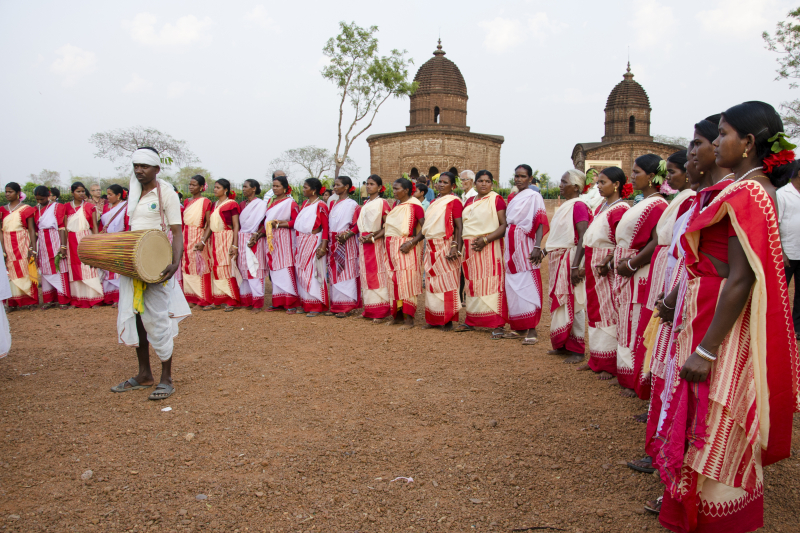
The Santhal people, primarily residing in eastern India, have a rich cultural heritage rooted in their strong community bonds and connection to the land. Their language, Santhali, plays a pivotal role in preserving their oral traditions and values. Agriculture is central to their livelihood, with crops like rice and millet sustaining them. Traditional attire is simple and practical, adorned with silver ornaments and bead necklaces during special occasions.
Santhal culture is deeply spiritual, blending nature worship with ancestor reverence. Their rituals and festivals, including "Baha" and "Sohrai," involve song, dance, and music, celebrating life and seeking blessings. The Santhal people are known for their art, particularly "Sohrai" and "Khovar" paintings that depict daily life and nature.
Socially, Santhal society revolves around clans, known as "parhas" or "kulhis," each with its own customs. Their environmental practices focus on land conservation and sustainable management.
In an ever-changing world, the Santhal community maintains its cultural richness while adapting to new challenges and opportunities. Their distinct way of life, deeply rooted in the land and communal traditions, contributes to India's rich cultural tapestry.

Screenshot of https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Santhal_Dance.jpg Video by Santhal Samaj -
One of the biggest and most dispersed indigenous tribal groups in India, the Bhil people have a rich cultural history that is firmly ingrained in the central and western parts of the nation, which include states like Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra. Their unique identity is a tapestry of traditions, language, and a profound connection to their natural surroundings.
The Bhil people follow a unique blend of indigenous animistic beliefs and influences from Hinduism. Their faith revolves around the worship of nature, ancestors, and spirits, which forms an integral part of their spiritual life. Rituals and festivals, such as "Bhagoria" and "Bhagwana," take center stage in celebrating their cultural values and connecting them to the natural world. These festivals often feature traditional dance, music, and ceremonies.
The Bhil community values environmental conservation and sustainable land use in addition to their cultural traditions. Their traditional practices are intended to protect the natural world they cherish, reflecting their reverence for the environment.
While the Bhil people adapt to the changing dynamics of the modern world, their rich cultural heritage continues to be a source of pride and identity. Their story forms an essential thread in the fabric of India's tribal diversity, contributing to the nation's cultural richness and offering a fascinating window into a way of life deeply connected to the land and its traditions.

Screenshot of https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bhils.jpg Video by Prasar Bharati Archives -
Originating in the state of Meghalaya in northeastern India, the Khasi people are a vibrant and unique tribal community with a rich cultural legacy. Their homeland's lush, hilly terrain is deeply ingrained in their way of life.
The primary source of income for the Khasi community is agriculture. On the Meghalayan hills' slopes, they engage in terraced farming, raising a range of crops such as vegetables, rice, millet, and maize. Customary rites and festivities commemorate the yearly cycle of farming and harvest.
The Khasi people follow a unique matrilineal system of inheritance and descent, where lineage and property are passed through the mother's line. This cultural practice sets them apart and has a profound influence on their social structure and family dynamics.
The Khasi people celebrate many festivals, one of which is "Shad Suk Mynsiem," which is marked by traditional music, dance, and ceremonies. Their cultural heritage continues to sustain them as they seize educational and economic opportunities while retaining their unique identity.
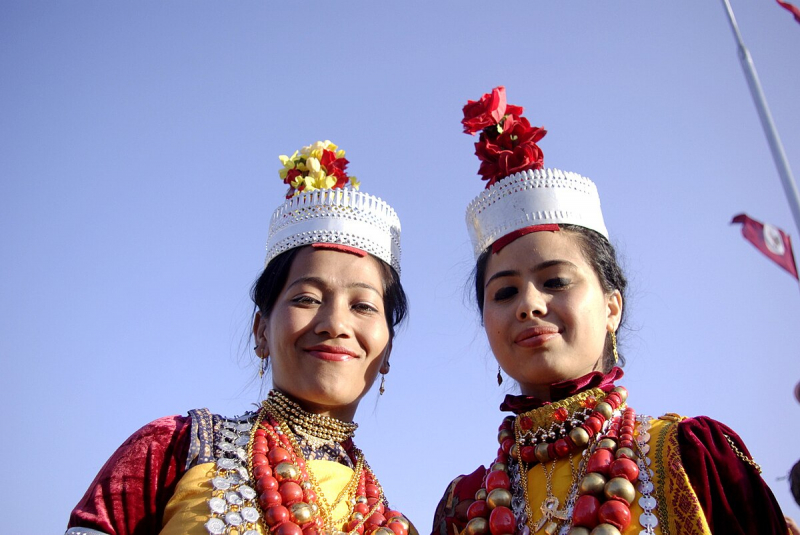

Screenshot of https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Khasi_Girls.jpg Video by The EPIC Channel -
The Warli people are an indigenous tribal community mainly residing in the western Indian states of Maharashtra and Gujarat. They have a distinct and rich cultural heritage that is deeply rooted in their connection to the land and nature.
Central to Warli culture is their unique art form known as "Warli painting." This traditional art features intricate, monochromatic depictions of nature, daily life, and rituals, often painted on mud walls. Warli paintings are not just decorative; they convey their community's stories, values, and cultural identity.
Most Warli people identify as animistic in their religion and beliefs. They honor the elements, their ancestors, and spirits. They gather as a community to celebrate life and ask for blessings for their undertakings, and their rituals are characterized by song and dance.
While preserving their cultural traditions, the Warli people have also adapted to modern life, embracing opportunities for education and employment. Yet, their unique art form, agricultural practices, and deep spiritual connection to nature continue to be the pillars of their cultural identity, and their story is an important thread in the rich tapestry of India's tribal diversity.
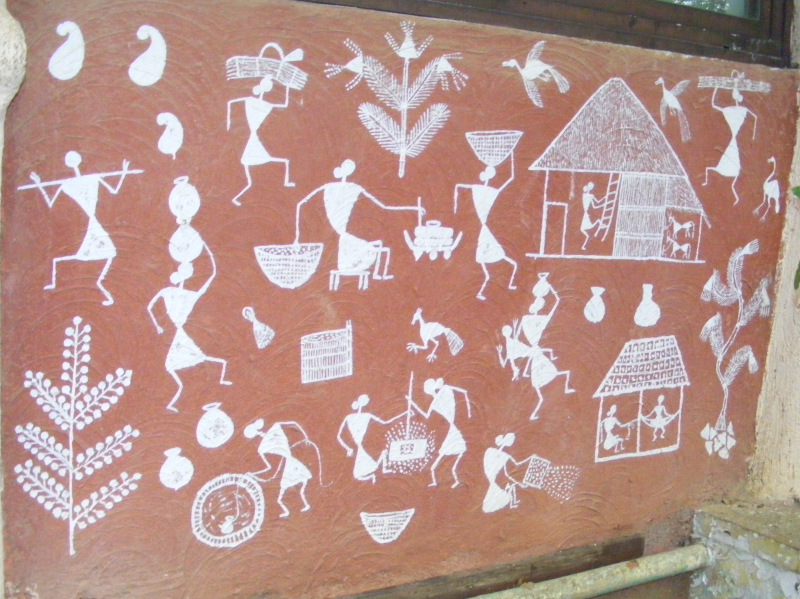

Screenshot of https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Warli_Paintings_SGNP_by_Raju_Kasambe_DSCF0200_%281%29_04.jpg Video by Prasar Bharati Archives -
Ranked 5th in the list of the top 10 most famous tribes in India, Munda, indigenous to the eastern and central regions of India, forms a captivating cultural mosaic within the country's tribal landscape. Their way of life is deeply rooted in their ancestral traditions and closely connected to the land they call home.
The Munda people's beliefs and practices are a fascinating blend of traditional animistic faith and the influence of Christianity, introduced through missionary activities. They venerate various deities and spirits deeply connected to the natural world. Their festivals, such as "Sarhul," "Karam," and "Maghe Parab," are vibrant expressions of their cultural and spiritual values, featuring traditional dances, music, rituals, and elaborate ceremonies that pay homage to their agricultural cycles.
Munda society is structured around clans known as "kilis," each with its own customs and traditions. These kilis serve as not only social units but also mechanisms for resolving disputes and maintaining harmony within their communities.
The Munda people's unique matrilineal society, respect for nature, and rich cultural traditions make them a distinct and intriguing community within India. Their way of life is deeply rooted in their cultural values, respect for women, and harmonious coexistence with the natural environment, marking them as an integral and invaluable part of India's tribal tapestry.
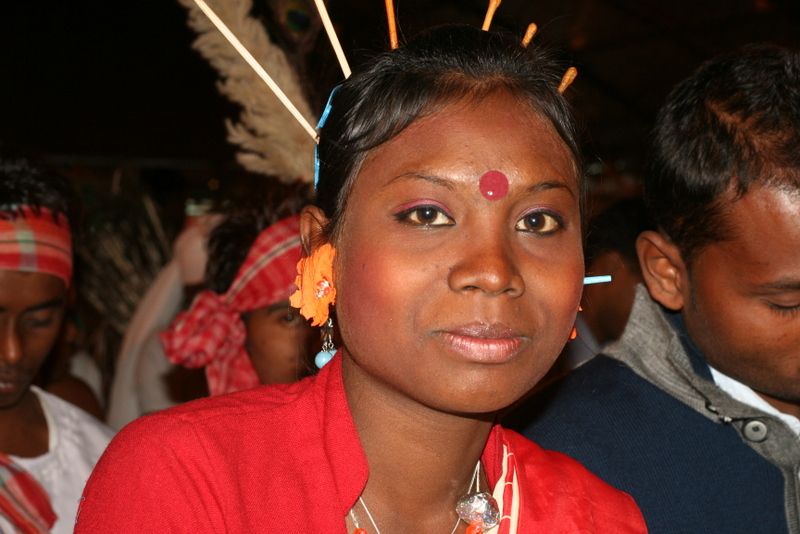

Screenshot of https://www.flickr.com/photos/ramesh_lalwani/8234516415 Video by Prasar Bharati Archives -
The Oraon people, also known as Kurukh, are indigenous to eastern and central India. They have a distinct culture characterized by their language, Kurukh, and their agricultural practices.
The community primarily relies on shifting cultivation and grows crops such as rice, maize, millet, and vegetables. Their traditional attire is simple yet functional, with men wearing dhotis and shirts and women wearing sarongs and blouses. The Oraon people follow a mix of traditional Kurukh religion, which involves the worship of nature, spirits, and ancestors, and elements of Hinduism. They celebrate various festivals like "Sarhul" and "Karam," featuring traditional dances and rituals often tied to agriculture and nature.
The Oraon society is organized into clans called "parha," each with its own customs and traditions. Their artistic skills include bamboo work and jewelry-making, which play a significant role in their culture. Environmental conservation is also vital to them, as they aim to protect their surroundings and practice sustainable land management. The Oraon people contribute to India's diverse tribal culture, and their traditions continue to thrive as they adapt to modern challenges.

Screenshot of https://jharkhandculture.com/node/53 Video by Prasar Bharati Archives -
Mostly living in the hilly areas of northeastern India, especially in the state of Nagaland, are the diverse indigenous tribal communities known as the Naga people. Like the country they live in, their culture and customs are diverse. The primary source of income for the Naga people is agriculture. They grow a variety of crops, such as vegetables, rice, millet, and maize. Their cultural practices and agriculture are closely linked, with numerous festivals and rituals centered around the planting and harvesting cycles.
The Naga community is well known for its unique artistic expressions, which include vivid textiles, elaborate jewelry, and traditional bamboo and wood craftsmanship. They are skilled and creative artists, and their work is a tribute to the natural world, animals, and mythological creatures.
Festivals are a significant aspect of Naga culture, celebrating the changing seasons, harvests, and communal bonds. The Hornbill Festival, in particular, is a well-known celebration that highlights the diverse Naga tribes' cultures through traditional dances, songs, and displays of traditional arts.
While Naga culture is deeply rooted in tradition, it is also evolving as the community adapts to modern challenges and opportunities. The Naga people's cultural diversity, linguistic richness, and vibrant traditions make them an essential and fascinating part of India's multicultural tapestry.

Screenshot of https://huffington1855.rssing.com/chan-40917384/article8332.html Video by WildFilmsIndia -
Offering a fascinating window into the rich diversity of the area's customs and culture, the Bodo people are an indigenous tribal group that is mainly found in the state of Assam in northeastern India. Their rich cultural history is ingrained in the verdant surroundings, and they have developed a strong bond with their homeland, language, and traditions.
Central to Bodo culture is their language, Bodo, which holds a special place in their identity. This Tibeto-Burman language is spoken among the community, and they have developed their script, known as "Bodo script." Through their language, they express their unique stories, beliefs, and way of life.
The Bodo people's religion combines aspects of Hinduism with their traditional Bodo faith. Their festivals and rituals are centered around their reverence for the natural world, their ancestors, and their belief in spirits. Bodo festivals, such as "Magh Bihu" and "Bwisagu," are distinguished by joyful celebrations, traditional dance, music, and rituals.
Traditional attire, including the "Dokhna" and "Arwon" for men and women, as well as intricate jewelry, is an essential part of their cultural identity. The Bodo people's rich cultural heritage is deeply intertwined with their environment, agricultural practices, and spiritual beliefs, making them a vibrant and essential part of the cultural tapestry of northeastern India.
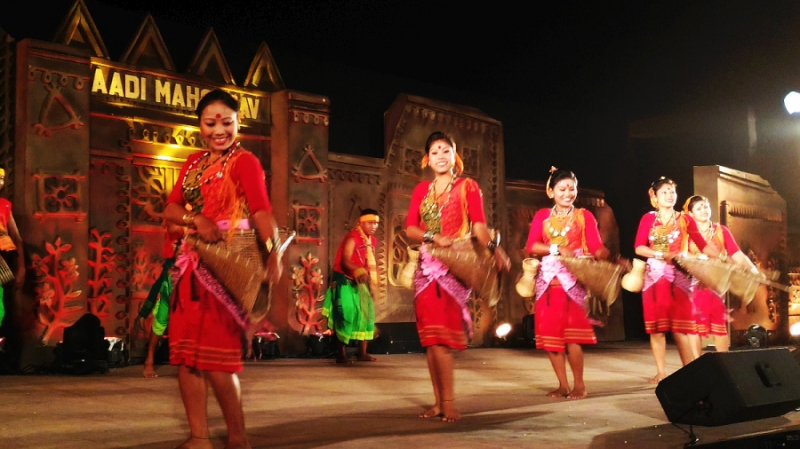

Screenshot of https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Na_%E2%80%93_Gurnai_Dance_of_Bodo,_Assam_P_20171117_181045_08.jpg Video by Ministry of Tribal Affairs -
Located at the bottom of the list of the Top 10 Most Famous Tribes in India, the Adivasis, comprising India's indigenous and tribal communities, offer a vibrant tapestry of diversity and cultural richness. Spread across remote, hilly, and forested regions, these communities maintain a profound connection with their land, often relying on subsistence agriculture and respecting their environment. Their linguistic diversity, which includes a wide range of languages, customs, and belief systems firmly based in rituals and nature worship, defines their identity.
Despite their unique cultural heritage, Adivasis have faced challenges, including land rights issues, displacement due to development projects, and limited access to education and healthcare. Many Adivasi groups actively advocate for their rights, seeking to preserve their cultural heritage and promote sustainable development.
In essence, Adivasis are an integral part of India's social fabric, bringing diversity and resilience to the nation. They embody a deep connection to the land and offer invaluable cultural richness, enhancing the wider tapestry of Indian society. Efforts are ongoing to protect their rights, empower their communities, and ensure the preservation of their unique cultural heritage.

Screenshot of https://www.flickr.com/photos/ramesh_lalwani/5558445852 Video by newslaundry -
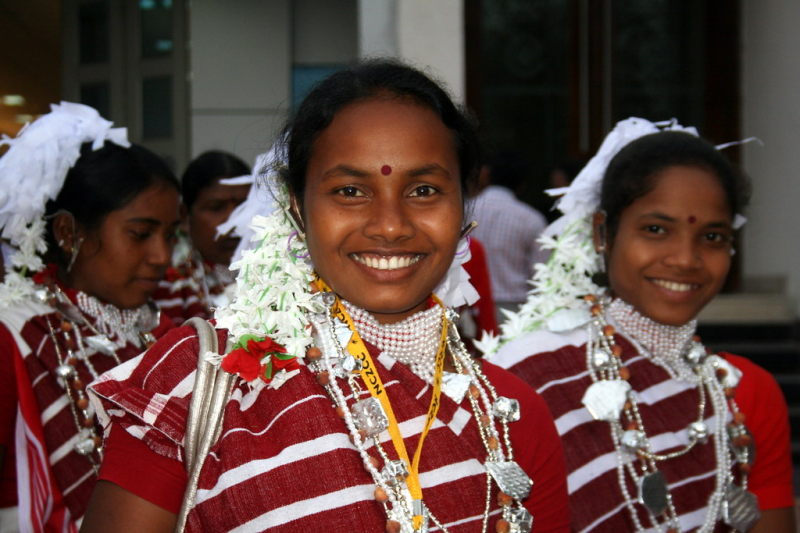
Nestled in the northeastern state of Assam, India, the Rabha tribe stands as a testament to the rich tapestry of indigenous cultures that adorn this diverse nation. Comprising a population of approximately 1.5 million people, the Rabha community carries a unique legacy of traditions, customs, and a way of life that is deeply rooted in their ancestral lands.
The Rabha people are celebrated for their vibrant cultural heritage, which finds expression through their traditional dances, such as the captivating 'Bahi,' performed during various festivities. Their attire is a visual feast, adorned with intricate patterns and jewelry that reflect the vibrant spirit of their culture. However, the true essence of Rabha life lies in their harmonious relationship with the natural world.
Agriculture forms the crux of the Rabha tribe's livelihood, and their expertise in cultivating crops like rice and jute is renowned. Through their agricultural practices, they demonstrate a profound understanding of the environment and a commitment to sustainable living. Their agricultural rituals and celebrations are deeply intertwined with nature, reinforcing their close bond with the land they call home.
As we delve deeper into the world of the Rabha tribe, we discover a people who exemplify the beauty of coexistence with nature, celebrate their identity through age-old customs, and contribute significantly to India's rich indigenous heritage. In this article, we will explore the history, culture, and traditions of the Rabha tribe, shedding light on the lesser-known aspects of their remarkable existence.

Screenshot of https://www.flickr.com/photos/bezoire/12878308814/ Video by Honiya Dakpe -
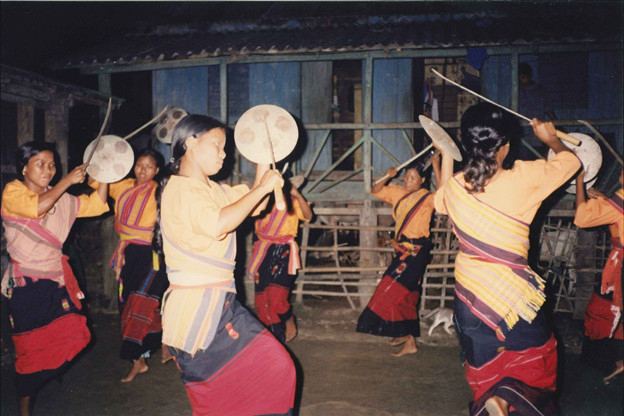
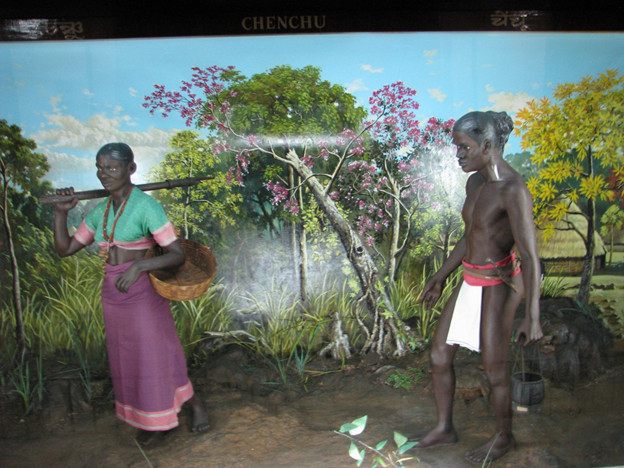
In the heart of southern India, within the states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, there is a remarkable indigenous community known as the Chenchu tribe. Comprising a population that has long maintained a close relationship with the verdant forests surrounding them, the Chenchu people embody a way of life intimately intertwined with nature's rhythms.
The Chenchu tribe is celebrated for their profound knowledge of the wilderness, which sets them apart as expert hunters and gatherers. Their traditional lifestyle revolves around the forest's abundant resources, and their understanding of the diverse flora and fauna that grace their surroundings is nothing short of exceptional. They are renowned for their skill in herbal medicine, which they draw from the natural pharmacy of their forest home.
Despite their modest numbers, the Chenchu people have preserved their unique cultural practices and rituals. Their spiritual beliefs are deeply rooted in the natural world, emphasizing the importance of living in harmony with the environment. The Chenchu community serves as both stewards and protectors of the forest, nurturing a connection with the wilderness that is becoming increasingly rare in the modern world.

Screenshot of https://www.flickr.com/photos/bezoire/12878308814/ Video by Vineet Kumar -
The Mishing tribe is a vibrant indigenous community whose history and customs are as rich as the fertile lands they call home. They are located along the picturesque Brahmaputra Valley in Assam, India.
The Mishing tribe subsists through agriculture, with rice cultivation being their forte. Their traditional agriculture practices exemplify a deep understanding of the fertile land that lines the Brahmaputra's banks. Yet, it's not just their agricultural expertise that distinguishes the Mishing people; it's their cultural heritage and eco-friendly lifestyle that paint a vivid portrait of their identity.
One of the most striking aspects of the Mishing tribe is their unique stilt houses, known as 'Chang Ghar.' These structures are more than just homes; they symbolize the Mishing way of life and their intricate bond with the natural world. The Mishing people's clothing, particularly their traditional Mekhela-Chadar attire made from Muga silk, is a testament to their commitment to preserving their cultural identity.
The Mishing community is characterized by its vibrant culture, replete with traditional songs, dances, and rituals. The 'Ali Ai Ligang' festival marks the beginning of the agricultural season and is one of the most significant celebrations in their calendar. During this festival, they perform various cultural performances, reinforcing their rich heritage.

Screenshot of https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mising_people Video by DesiGirl Traveller -
In the rugged landscapes of Nagaland, India, there exists a tribal community with a heritage as fierce as the terrain they inhabit: the Konyak tribe. Hailing predominantly from the Mon district, the Konyak people have earned a reputation for their warrior traditions, headhunting history, and distinct cultural practices that have fascinated anthropologists and travelers for generations.
The Konyak tribe's history is steeped in stories of valor and resilience. Renowned for their headhunting practices, which have long been abandoned, they were once known as formidable warriors in the region. Their traditional attire, adorned with boar's teeth, hornbill feathers, and intricate tattoos, is a striking reflection of their fierce identity.
However, the Konyak people have not only preserved their warrior legacy; they have also become celebrated artisans, crafting remarkable wood carvings, beads, and jewelry. The intricate craftsmanship of their creations serves as a testament to their artistic prowess and cultural heritage.
The heartbeat of the Konyak community is the annual Aoling festival, celebrating the arrival of spring. During this event, they engage in various traditional dances and rituals, offering an insight into their rich cultural tapestry. As we embark on an exploration of the Konyak tribe, we will delve into their captivating history, their artistic talents, and the resilient spirit that defines this indigenous community, reaffirming the unique and enduring cultural heritage of Nagaland's enigmatic Konyak tribe.

Screenshot of https://www.flickr.com/photos/bezoire/12878308814/ Video by Sansad TV