Top 10 Most Important Historical Figures In Belgium
Belgium is a country in Northwestern Europe, officially known as the Kingdom of Belgium. The country is bounded to the north by the Netherlands, to the east by ... read more...Germany, to the southeast by Luxembourg, to the southwest by France, and to the northwest by the North Sea. The country is well-known for its people's rich history in fields including politics, art, literature, and philosophy. This article will introduce you to the most important historical figures in Belgium. Look through the list to learn a little bit more about them.
-
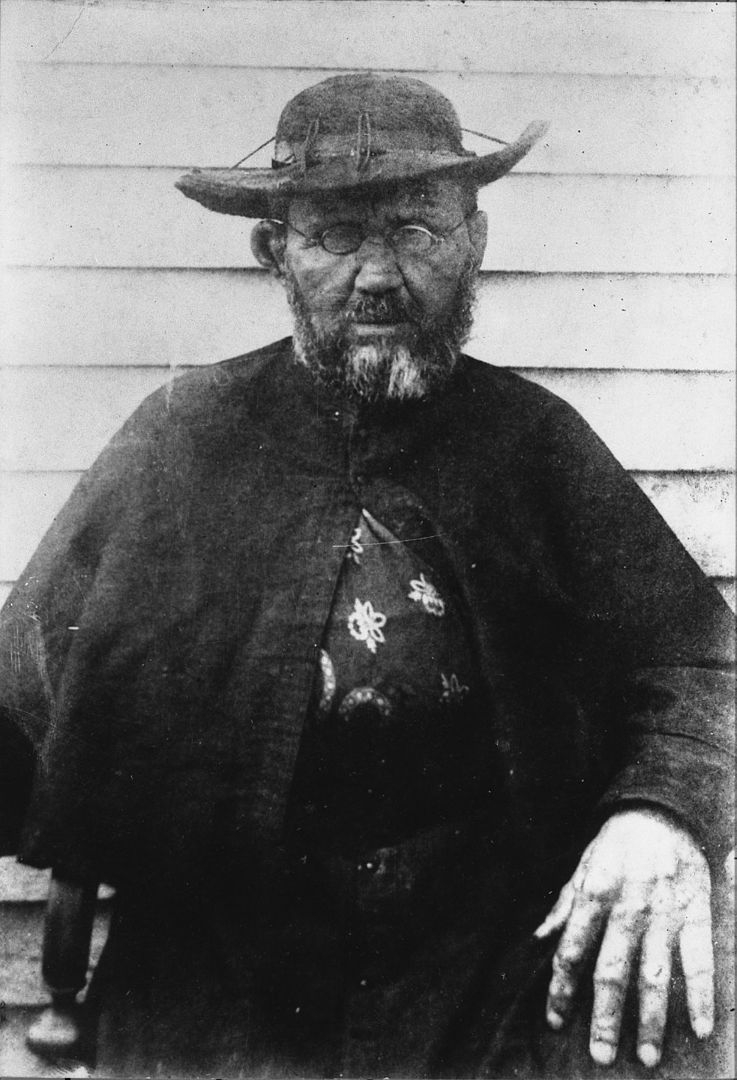
One of the most important historical figures in Belgium is Father Damien. Father Damien or Saint Damien of Molokai, SS.CC. or Saint Damien De Veuster (Dutch: Pater Damiaan or Heilige Damien van Molokai; 3 January 1840 – 15 April 1889), was a Belgian Roman Catholic priest and member of the Congregation of the Sacred Hearts of Jesus and Mary, a missionary religious institute. He was honored for his ministry in the Kingdom of Hawaii for individuals with leprosy (Hansen's disease) who lived in government-mandated medical quarantine in a community on the Kalaupapa Peninsula of Molokai from 1873 until his death in 1889.
During this time, he taught the people of Hawaii about the Catholic faith. Father Damien also cared for the patients and trained community leaders to build houses, schools, roads, hospitals, and churches. He healed the ulcers of the locals, built a reservoir, fashioned coffins, dug graves, shared pipes, and ate poi with them, providing both medical and emotional support.
Father Damien got leprosy after eleven years of caring for the physical, spiritual, and emotional needs of individuals in the leper colony. Despite the sickness, he persisted with his labor until his death on April 15, 1889. Father Damien also had tuberculosis, which worsened his condition, but others believe he volunteered in the first place because of his ailment. Father Damien has been dubbed a "charity martyr." In the Catholic Church, Damien De Veuster is regarded as a saint. Damien is regarded as the spiritual patron of leprosy and outcasts in the Anglican Communion and other Christian religions. Father Damien Day, which falls on April 15, is also a minor statewide holiday in Hawaii. Father Damien is the patron saint of the Diocese of Honolulu as well as the state of Hawaii. On October 11, 2009, Pope Benedict XVI canonized Father Damien. In the Catholic Encyclopedia, Libert H. Boeynaems refers to him as "the Apostle of the Lepers." The feast day of Damien De Veuster is May 10.

en.wikipedia.org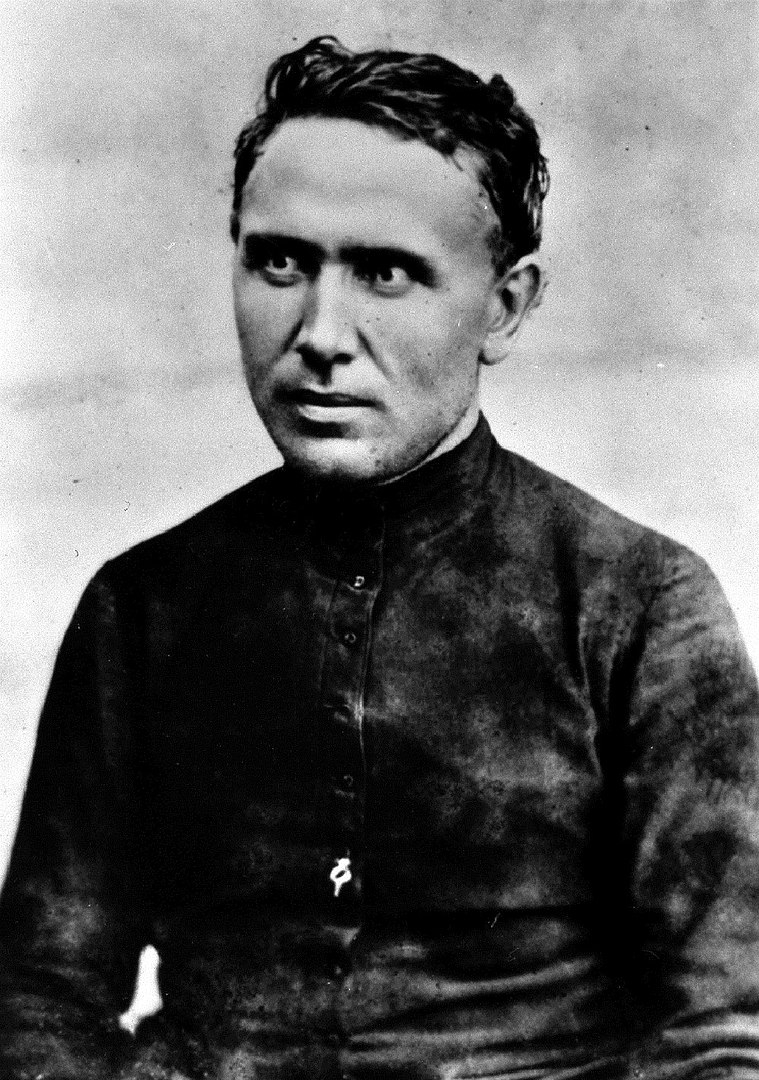 
Father Damien in 1873 -en.wikipedia.org -
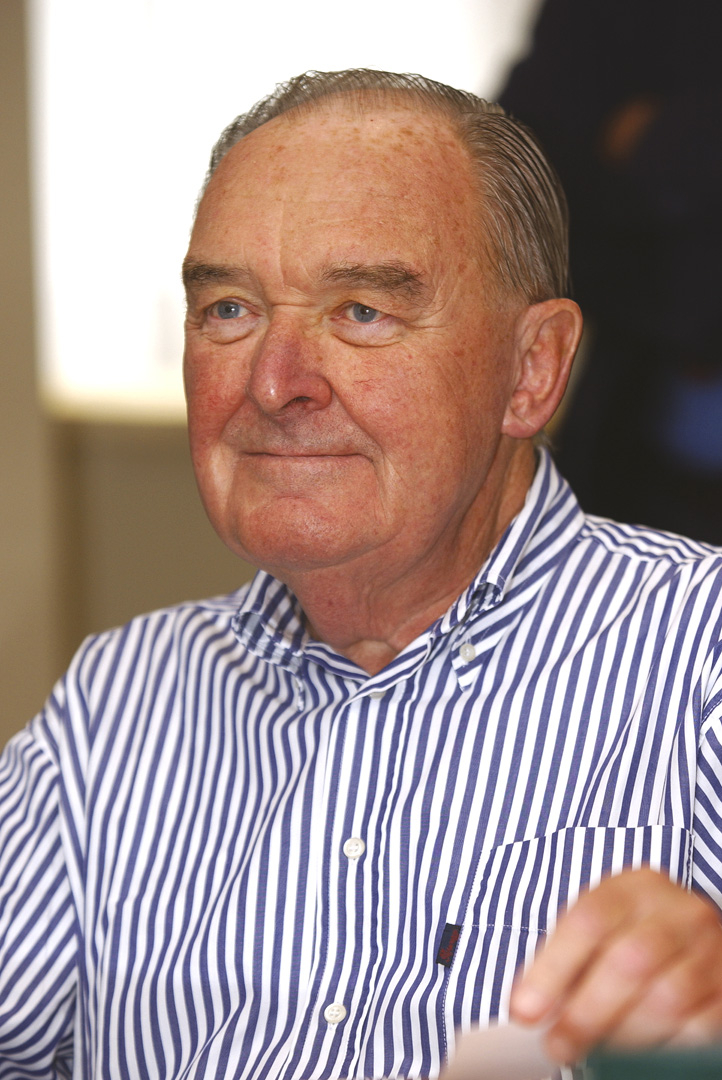
Paul Adriaan Jan, Baron Janssen (12 September 1926 – 11 November 2003) was a Belgian physician. He founded Janssen Pharmaceutica, a pharmaceutical company with approximately 20,000 workers that is now a division of Johnson & Johnson.
Paul Janssen was the son of Constant Janssen and Margriet Fleerackers. He attended secondary school at the Jesuit St Jozef college in Turnhout before deciding to follow in his father's footsteps and become a physician. Janssen studied physics, biology, and chemistry at the Facultés universitaires Notre-Dame de la Paix (FUNDP) in Namur during WWII. He subsequently went on to study medicine at the Catholic University of Leuven and Ghent University. Janssen obtained his magna cum laude medical degree from Ghent University in 1951. In 1956, he received a postdoctoral degree in pharmacology from the same university and studied at the University of Cologne's Institute of Pharmacology.
During his military duty and until 1952, he worked at the University of Cologne's Institute of Pharmacology. Janssen established his own research laboratory in 1953 with a loan from his father of 50,000 Belgian francs. That same year, he discovered ambucetamide, an antispasmodic shown to be especially beneficial for menstrual pain reduction. On February 11, 1958, he discovered haloperidol, which was a key breakthrough in the treatment of schizophrenia. He and his colleagues created the fentanyl family of medications as well as a variety of anesthetic agents such as droperidol and etomidate. Diphenoxylate (Lomotil), one of his anti-diarrheal medications, was utilized in the Apollo program.
Janssen Pharmaceutical was the first Western pharmaceutical business to open a factory in the People's Republic of China in 1985. In 1995, he co-founded the Center for Molecular Design with Paul Lewi, where he and his team used a supercomputer to search for candidate compounds for potential AIDS medicines.
Janssen and his team of scientists discovered approximately eighty new pharmaceuticals in total, four of which are on the WHO list of essential medicines. King Baudouin elevated him to the Belgian nobility and bestowed the title of Baron on him in 1991. Janssen died in 2003 in Rome, Italy, while attending the 400th anniversary of the Pontifical Academy of Sciences, of which he had been a member since 1990.

kaowarsom.be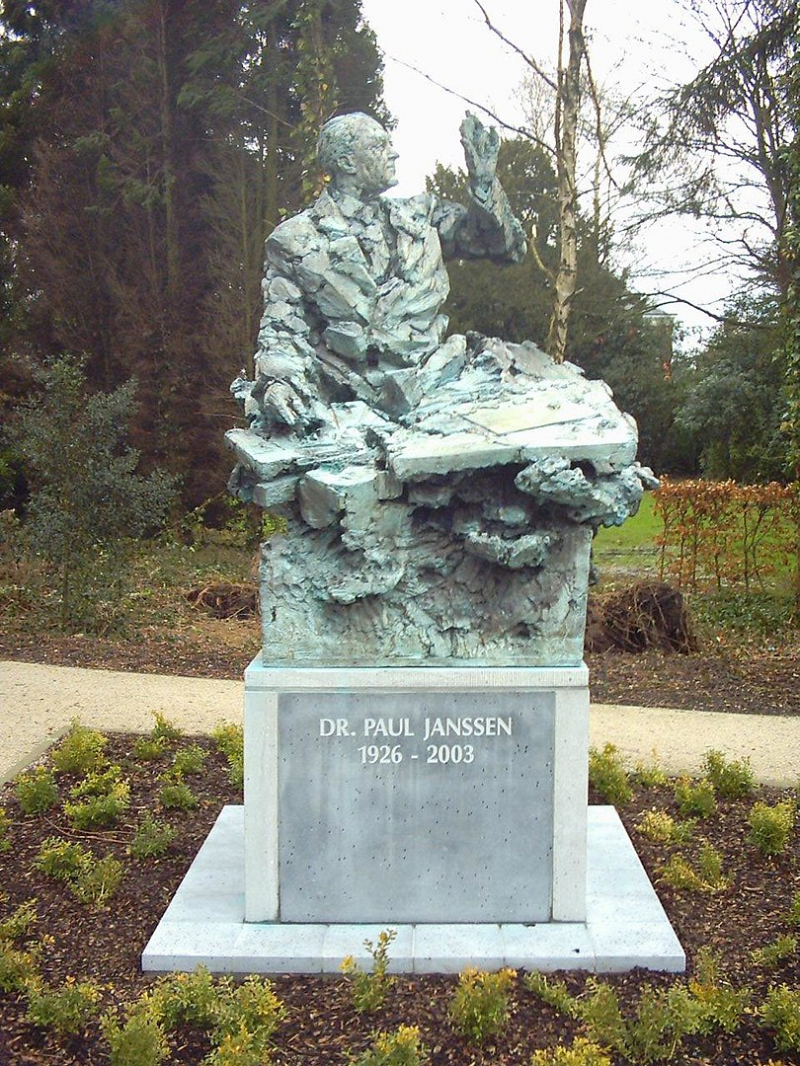 
en.wikipedia.org -
Ambiorix (Gaulish for "king of the surroundings" or "king-protector") (fl. 54-53 BC) was the leader of a Belgic tribe in north-eastern Gaul (Gallia Belgica), where modern Belgium is located, together with Cativolcus, prince of the Eburones. Ambiorix became a Belgian national hero in the nineteenth century as a result of his resistance to Julius Caesar, as described in Caesar's Commentarii de Bello Gallico.
Ambiorix's revolt was a Gallic Wars episode between 54 and 53 BC in which the Eburones tribe, led by Ambiorix, rebelled against the Roman Republic. Dissatisfaction among the subdued Gauls sparked a significant insurrection against Julius Caesar among the Belgae in the winter of 54-53 BC, when the Eburones of north-eastern Gaul rose in rebellion under their commander Ambiorix. Fifteen Roman cohorts were annihilated at Atuatuca Tungrorum (modern Tongeren, Belgium), and a garrison led by Quintus Tullius Cicero narrowly escaped after being rescued by Caesar in time. The remainder of 53 BC was spent on a retaliatory war against the Eburones and their allies, who were claimed to have been nearly destroyed by the Romans.
Until the nineteenth century, Ambiorix was a relatively unknown character. Belgium's independence in 1830 prompted a search for national heroes. Ambiorix and his exploits were rediscovered in Caesar's De Bello Gallico. Joannes Nolet de Brauwere Van Steeland, a Belgian poet, created a lyrical epic about Ambiorix in 1841. Furthermore, on September 5, 1866, a statue of Ambiorix, referred to by Caesar as Atuatuca, i.e. Atuatuca Tungrorum, was constructed on the main market square in Tongeren, Belgium. Ambiorix is now one of the most well-known characters in Belgian history. Many businesses, bars, and fripperies have been named after him, and he appears in many Belgian comics, including Suske en Wiske and Jommeke.
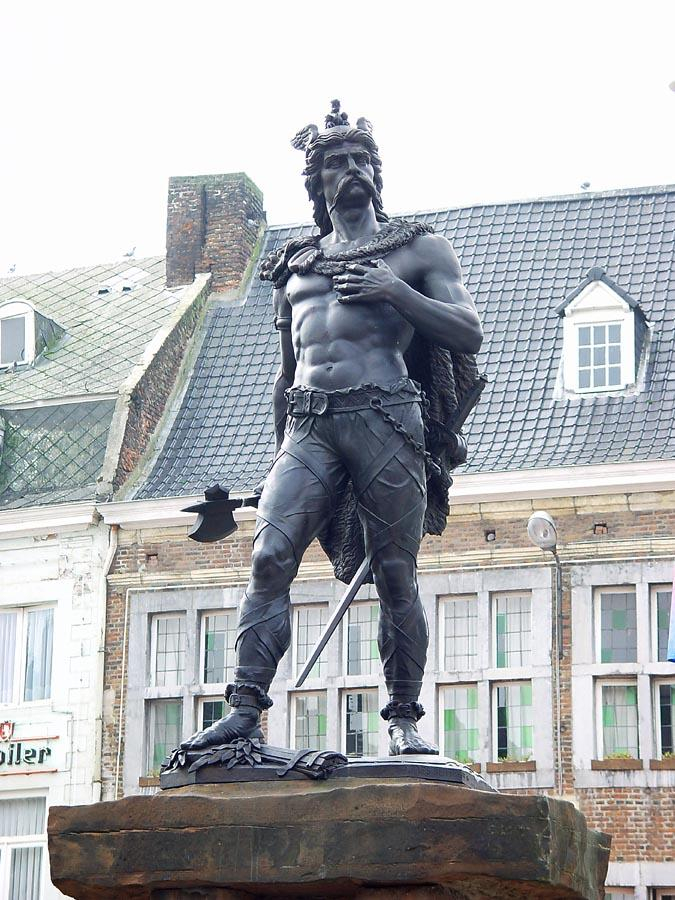

Denkmal of Ambiorix -en.wikipedia.org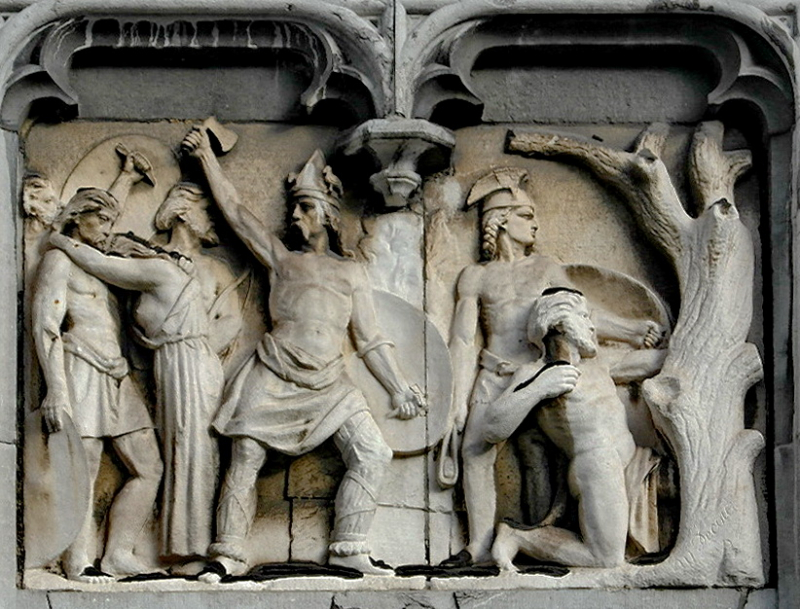 
Ambiorix attacking Roman soldiers -en.wikipedia.org -
One of the most important historical figures in Belgium is Adolf Daens. He (18 December 1839 – 14 June 1907) was an Aalst-born Flemish priest. He entered the Society of Jesus in 1858 but left two years later to become a priest. He is well recognized for his sociopolitical activism after joining the diocesan priesthood. He founded the "Daensist movement," which was inspired by Leo XIII's encyclical Rerum Novarum and began in 1893 with the Christene Volkspartij. The Christene Volkspartij compelled the mainstream Catholic Party to radicalize and democratize.
In 1894, Daens was elected to the Belgian parliament. Right-wing Catholic organizations won his bishop's censure (1898), but this did not prevent him from being re-elected M.P. (1902–1906). He made significant contributions to the developing social awareness among Belgian Catholics and is a pivotal figure in the Flemish movement as well as the history of Belgian trade unions. His bishop, Antoon Stillemans, suspended him. He passed away in Aalst.
Adolf's brother Pieter Daens is the narrator in Louis Paul Boon's novel Daens (Pieter Daens of hoe in de negentiende eeuw de arbeiders van Aalst vochten tegen armoede en onrecht, i.e., "Pieter Daens or How the workers of Aalst fought poverty and injustice in the nineteenth century"). In 2005, he ended fifth place in the Flemish version of the De Grootste Belg election ("The Greatest Belgian"). Daens was ultimately rehabilitated by the church on June 6, 2015, 108 years after his death. Monsignor André-Joseph Léonard, Archbishop of Mechelen-Brussels, presided over the yearly Mass in his honor.
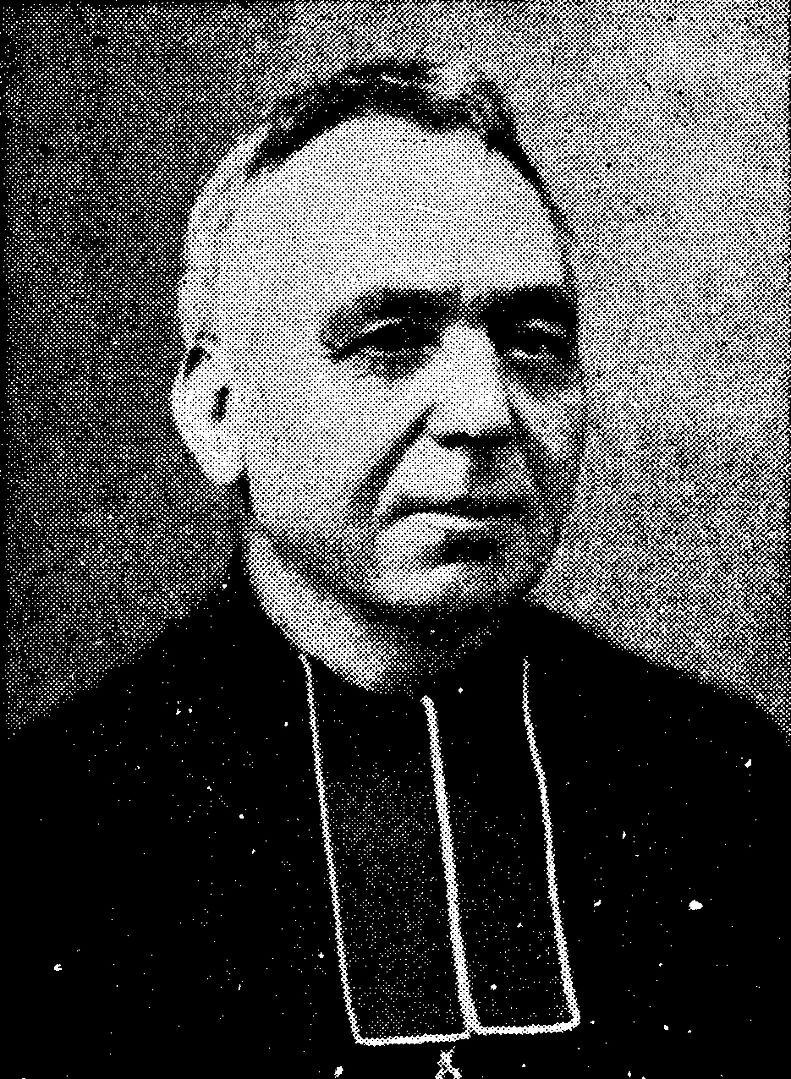

en.wikipedia.org 
Statue of Priest Daens in Haaltert -en.wikipedia.org -
Andreas Vesalius (31 December 1514 – 15 October 1564) was a 16th-century anatomist, physician, and author of De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem (On the fabric of the human body in seven books). Vesalius is widely regarded as the father of modern human anatomy.
On December 31, 1514, Vesalius was born Andries van Wesel to his father Anders van Wesel and mother Isabel Crabbe in Brussels, which was then part of the Habsburg Netherlands. Jan van Wesel, his great-grandfather, was probably born in Wesel and got a medical degree from the University of Pavia before teaching medicine at the University of Leuven. His grandfather, Everard van Wesel, was Emperor Maximilian's Royal Physician, and his father, Anders van Wesel, was Maximilian's apothecary and afterward valet de chambre to his successor, Charles V.
He taught at the University of Padua from 1537 until 1542 and then served as an Imperial physician at Emperor Charles V's court. After Emperor Charles V abdicated, he remained at court and enjoyed the Emperor's son Philip II's favor. Andreas Vesalius is the Latinized version of Andries van Wesel. Latinizing one's name was a frequent practice among European academicians during his time. Andrea Vesalius, André Vésale, Andrea Vesalio, Andreas Vesal, Andrés Vesalio, and Andre Vesale are all variations on his name.
Anatomies had already been published, but Vesalius's were in a different class. They were based on actual human body dissections (after death). And the drawings were of the finest caliber. For many centuries, dissections of cadavers (dead human bodies) were prohibited, which constrained earlier work on anatomy. Galen provided the majority of information about the human body prior to Vesalius. Vesalius demonstrated that many of the things Galen wrote about were incorrect by dissecting human bodies. Galen's primary misconceptions included the human heart, liver, and lower jaw bones. Galen's work was discovered to be based on Barbary apes, but he also dissected pigs, which resulted in more incorrect observations.
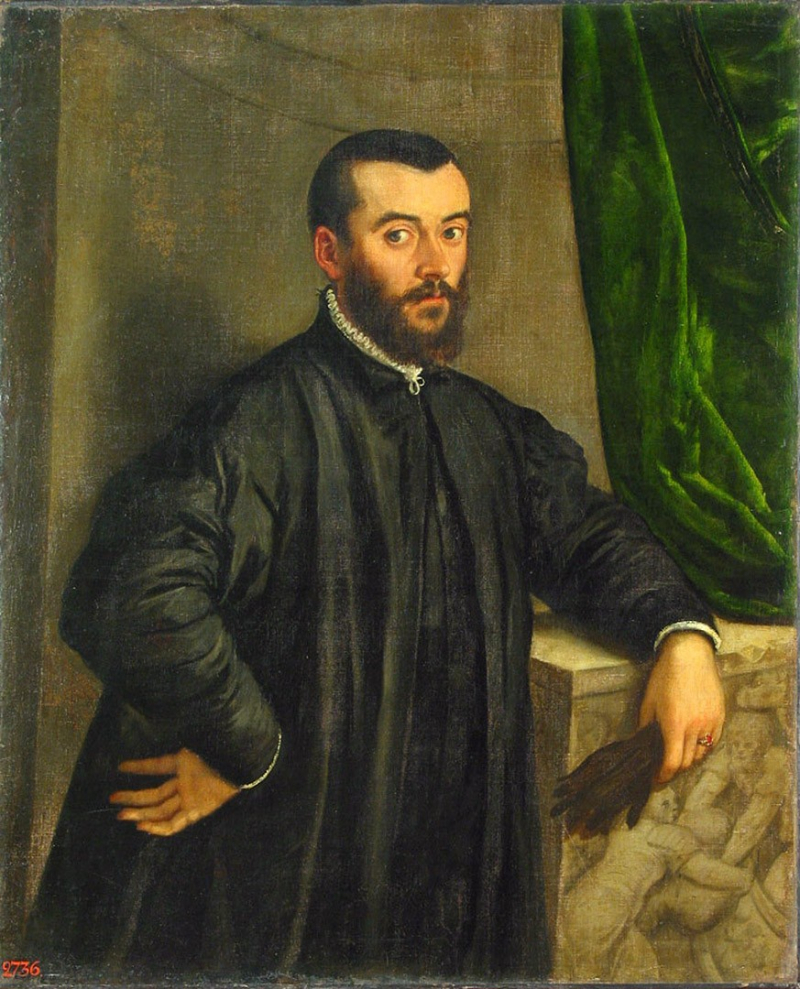

en.wikipedia.org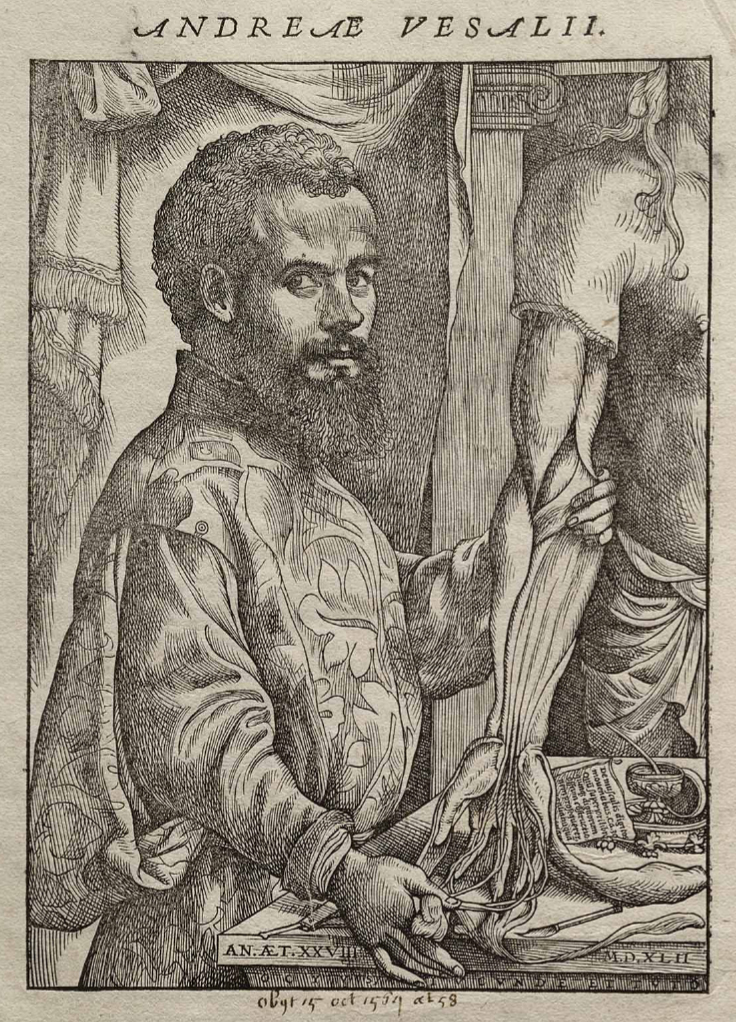 
en.wikipedia.org -
One of the most important historical figures in Belgium is Jacques Romain Georges Brel. He (April 8, 1929 – October 9, 1978) was a Belgian singer and actor who wrote and performed literary, intellectual, and theatrical songs that drew a big, devoted following, primarily in Belgium and France, but later worldwide. He is regarded as a modern chanson master.
Despite the fact that he recorded the majority of his songs in French and rarely in Dutch, he influenced English-language composers and singers such as Scott Walker, David Bowie, Alex Harvey, Marc Almond, Neil Hannon, and Rod McKuen. Many artists, including Bowie, Walker, Ray Charles, Judy Collins, John Denver, The Kingston Trio, Nina Simone, Shirley Bassey, James Dean Bradfield, Frank Sinatra, and Andy Williams, recorded English adaptations of his compositions.
Brel was a well-known actor who appeared in ten films. He directed two films, one of which, Le Far West, won the Palme d'Or at the 1973 Cannes Film Festival. Brel is the third-best-selling Belgian recording artist of all time, having sold over 25 million records worldwide. In 1950, Brel married Thérèse "Miche" Michielsen, with whom he had three children. From 1972 until his death in 1978, he was also in a romantic connection with actress and dancer Maddly Bamy.
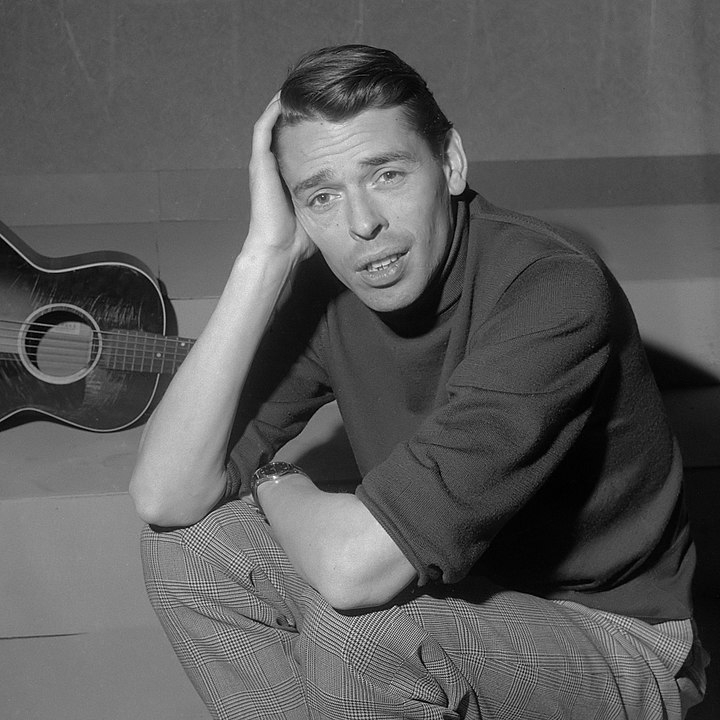

en.wikipedia.org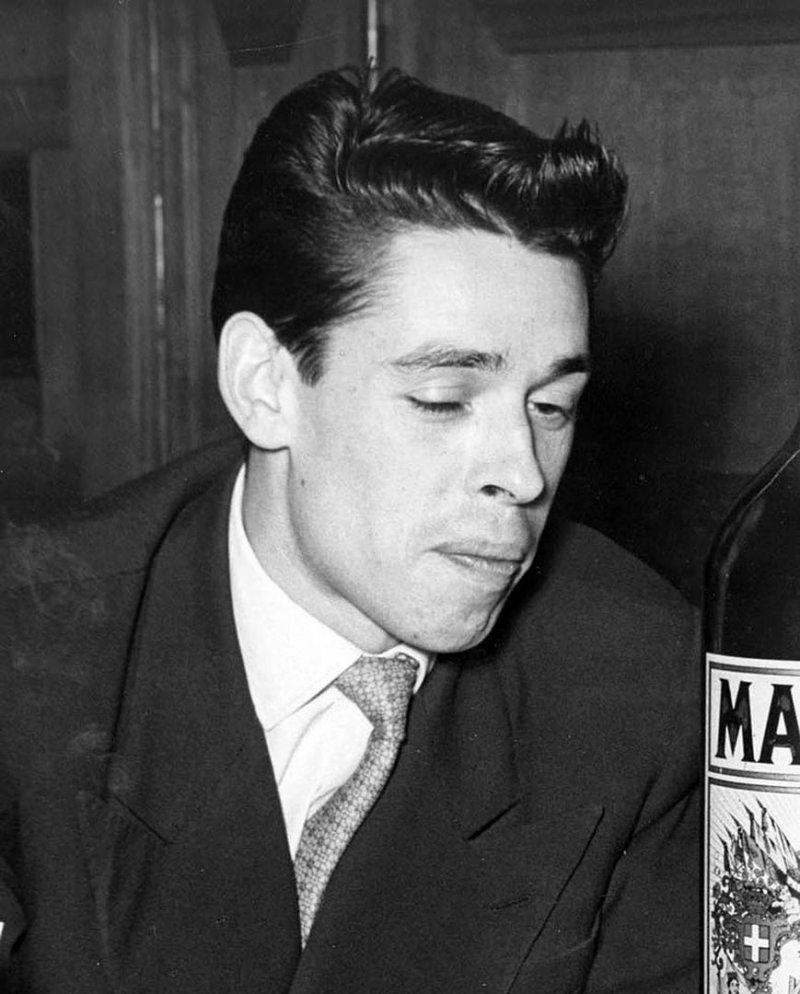 
en.wikipedia.org -
Charlemagne (Charles the Great, 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, and the first Holy Roman Emperor from 800. Charlemagne was the first recognized emperor to rule in Western Europe following the fall of the Western Roman Empire some three centuries earlier. The Carolingian Empire was Charlemagne's extended Frankish empire. He was canonized by Antipope Paschal III, an act that was later declared invalid, and he is today considered by some to be beatified (a step on the way to sainthood) in the Catholic Church.
Charlemagne was Pepin the Short's and Bertrada of Laon's eldest son. He was born prior to their official marriage. Following his father's death in 768, he ascended to the throne of the Franks, initially ruling alongside his brother Carloman I until the latter's death in 771. As sole king, he carried on his father's policy of papal protection and became its sole defender, driving the Lombards from northern Italy and conducting an assault on Muslim Spain. He also battled against the Saxons to his east, Christianizing them (under penalty of death), which resulted in tragedies such as the Verden Massacre. He reached the pinnacle of his power in 800 when Pope Leo III crowned him Emperor of the Romans on Christmas Day in Old St. Peter's Basilica in Rome.
Charlemagne was dubbed the "Father of Europe" (Pater Europae) because he united most of Western Europe for the first time since the Roman Empire's classical age, as well as portions of Europe that had never been under Frankish or Roman dominion. His reign ushered in the Carolingian Renaissance, a flurry of cultural and intellectual activity within the Western Church. The Eastern Orthodox Church disliked Charlemagne because of his filioque backing and the Pope's preference for him as emperor over the Byzantine Empire's first female monarch, Irene of Athens. These and other disagreements eventually led to the division of Rome and Constantinople in the Great Schism of 1054.
Charlemagne died in 814 from an infectious lung illness. In his imperial capital city of Aachen, he was laid to rest in the Aachen Cathedral. He was married at least four times and had three legitimate boys who grew up. Only Louis the Pious, the youngest, lived to succeed him. Many of Europe's royal houses have direct forebears in Charlemagne and his predecessors, notably the Capetian dynasty, the Ottonian dynasty, the House of Luxembourg, and the House of Ivrea.

Emperor Charlemagne -en.wikipedia.org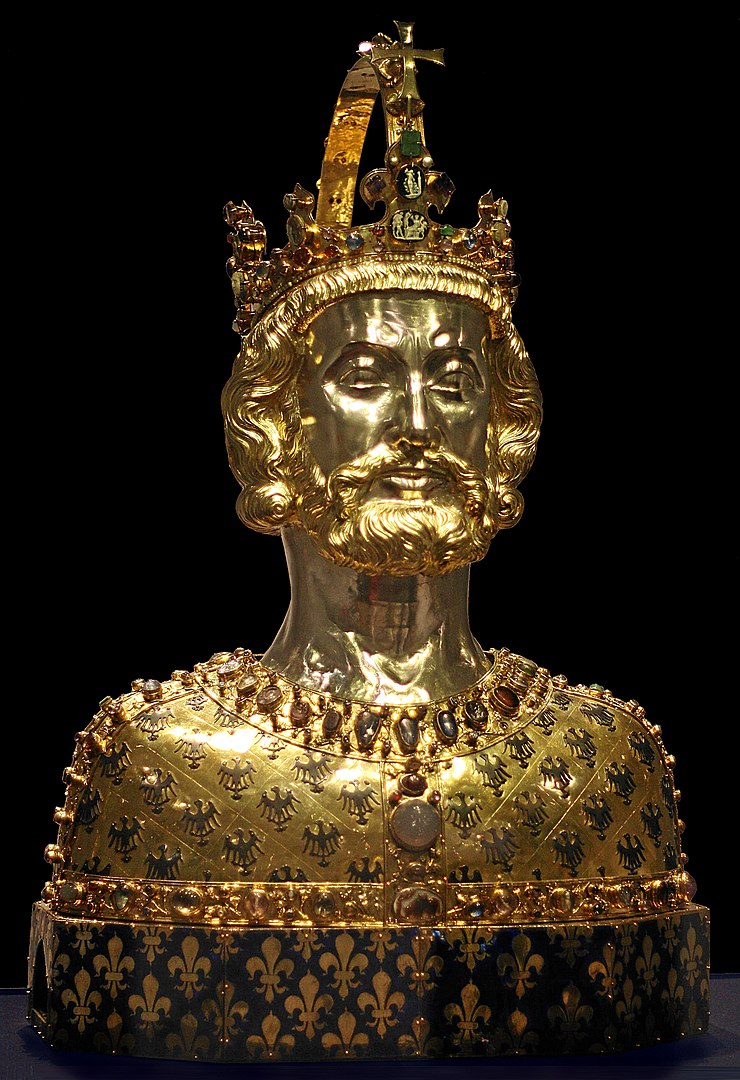 
The Bust of Charlemagne -en.wikipedia.org -
Gerardus Mercator (5 March 1512 – 2 December 1594) was a Flanders-born 16th-century geographer, cosmographer, and cartographer. He is most known for designing the 1569 globe map, which used a novel projection to portray sailing paths with constant bearing (rhumb lines) as straight lines, an innovation that is still used in nautical charts today.
Mercator was a pivotal figure in the history of cartography. He is widely regarded as one of the founders of the Netherlandish school of mapping and geography, with Gemma Frisius and Abraham Ortelius. He is also commonly regarded as the school's most renowned person. He was a well-known producer of globes and scientific instruments in his day. He was also interested in theology, philosophy, history, mathematics, and geomagnetism. He was also skilled calligraphy and engraver. Unlike other famous intellectuals of the period, he traveled infrequently, and his understanding of geography came from his collection of over a thousand volumes and maps, guests, and his extensive communication (in six languages) with other scholars, statesmen, travelers, merchants, and seafarers.
Mercator's early maps were large enough for wall installation, but in the second half of his life, he created over 100 new regional maps on a smaller scale suited for binding into his Atlas of 1595. This was the first time the word Atlas was used to refer to a map book. Mercator, on the other hand, used it as a neologism for a dissertation (Cosmologia) on the origin, history, and description of the cosmos, rather than just a collection of maps. He picked the name to honor the Titan Atlas, "King of Mauretania," whom he regarded as the first great geographer.
The sale of terrestrial and celestial globes provided a significant portion of Mercator's income. For sixty years, they were regarded as the finest in the world, and so many were sold that there are several surviving examples. This was a large-scale operation that included manufacturing the spheres, printing the gores, constructing large stands, and packing and delivering them around Europe. He was well known for his scientific tools, particularly his astrolabes and astronomical rings, which were used to research astronomy and astrology geometry.
Mercator published on geography, philosophy, chronology, and theology, among other topics. All of the wall maps were etched with extensive text about the place in question. The famous world map of 1569, for example, is etched with approximately 5,000 words in fifteen legends. His chronology chart was 400 pages long, and it fixed the dates (from the beginning of time) of earthly dynasties, key political and military events, volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and eclipses. He also published works on the gospels and the Old Testament.

en.wikipedia.org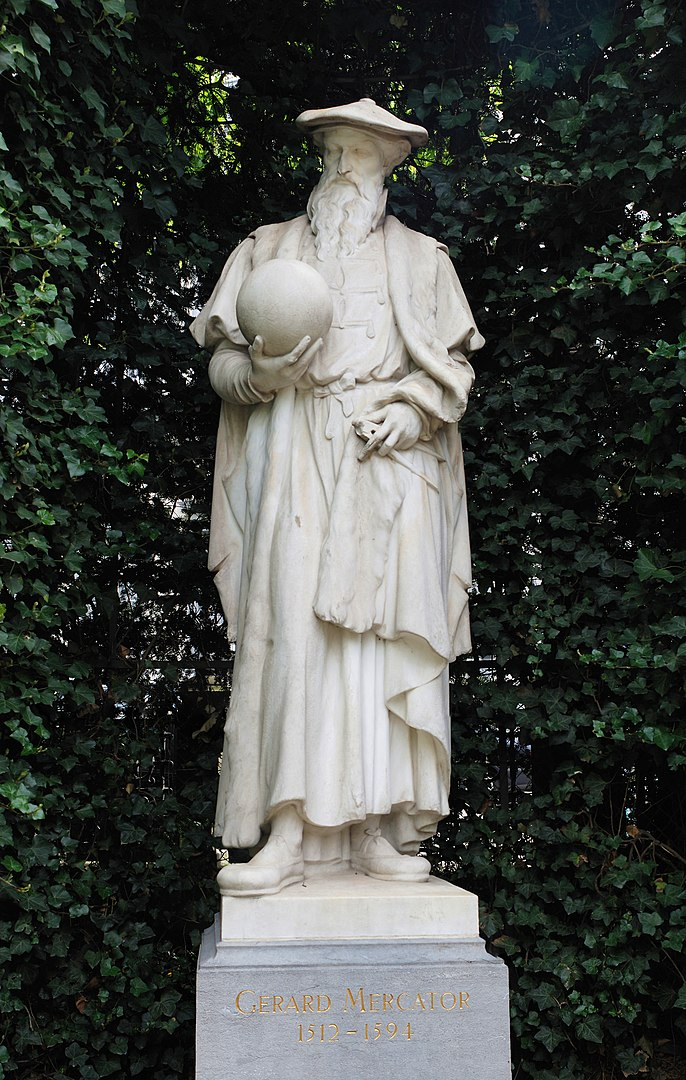 
Statue of Mercator -en.wikipedia.org -
Sir Peter Paul Rubens (28 June 1577 – 30 May 1640) was a Flemish artist and diplomat from the Southern Netherlands' Duchy of Brabant (modern-day Belgium). He is often regarded as the most prominent Flemish Baroque artist. Rubens' highly heated compositions allude to learned aspects of classical and Christian history. His distinct and extremely popular Baroque style stressed movement, color, and sensuality, following the Counter-direct, Reformation's dramatic aesthetic style. Rubens was a painter who created altarpieces, portraits, landscapes, and historical works depicting mythological and allegorical subjects. He was also a prolific designer of cartoons for Flemish tapestry factories as well as frontispieces for Antwerp publishers.
Rubens was a classically educated humanist scholar and diplomat who was knighted by both Philip IV of Spain and Charles I of England, in addition to having a huge workshop in Antwerp that produced paintings popular with nobles and art collectors throughout Europe. Rubens was an extremely productive artist. Michael Jaffé's catalog of his works lists 1,403 items, minus countless replicas prepared in his studio.
His commissioned works were largely history paintings with religious and mythical themes, as well as hunt scenes. He created portraits, particularly of friends, and self-portraits, as well as landscapes later in life. Rubens created tapestries, prints, and his own home. He also managed the ephemeral decorations for Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand of Austria's royal arrival in Antwerp in 1635. In 1622, he released Palazzi di Genova, a book illustrated with drawings of Genoa's palaces. The book had a significant impact on the dissemination of the Genoese palace style in Northern Europe. Rubens was an ardent art collector who amassed one of Antwerp's largest collections of art and books. He was also an art dealer, selling a large number of art artifacts to George Villiers, the 1st Duke of Buckingham.
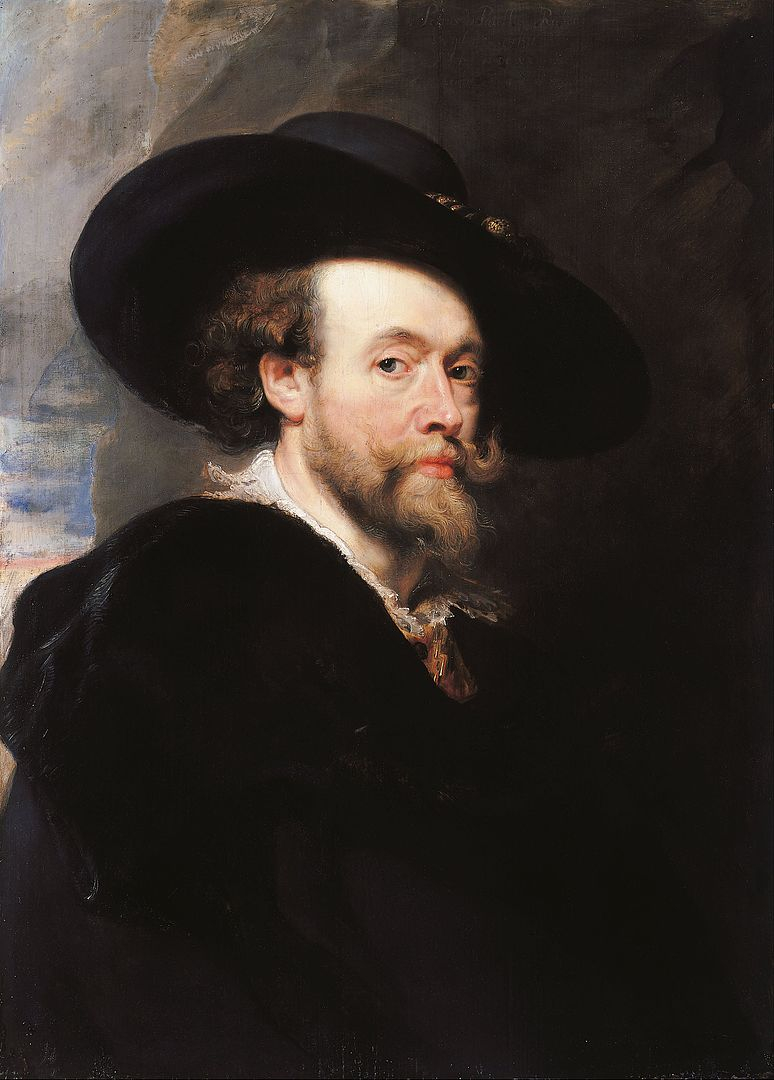

en.wikipedia.org 
caphesuada.net -
Hendrik Conscience was a Belgian author who lived from 3 December 1812 to 10 September 1883. He is regarded as the forefather of Dutch-language literature in Flanders, working during a time when the French language dominated the upper classes in literature and governance in Belgium. Conscience fought as a Belgian revolutionary in 1830 and was a renowned Romanticist writer of the early nineteenth century. He is most known for his romantic nationalist novel The Lion of Flanders (1838), which was inspired by the triumph of a Flemish peasant militia over French knights during the Franco-Flemish War in 1302 at the Battle of the Golden Spurs.
Hendrik was the son of a Frenchman, Pierre Conscience, from Besançon, who had been chef de timonerie in Napoleon Bonaparte's navy and had been appointed under-harbourmaster at Antwerp when it became part of France in 1811. Cornelia Balieu, Hendrik's mother, was a Fleming who was illiterate. Pierre Conscience remained in Antwerp after the French left following the Congress of Vienna in 1815. He started buying and breaking up worn-out ships, which were plenty in Antwerp after the peace.
Over the course of his career, he authored over 100 books and novellas and rose to prominence. With the decline of romanticism after his death, his writings fell out of favor, yet they are still considered classics of Flemish literature. At King Leopold's request, the job of the keeper of the Royal Belgian museums was formed and assigned to him in 1867. He continued to publish novels on a regular basis, with approximately eighty books published in total. He was the most prominent citizen of Antwerp. His 70th birthday was marked by public celebrations. He died at his home in Antwerp after a protracted illness. He was given a proper burial and buried at Antwerp's Schoonselhof cemetery, where his tomb is now a memorial to the famous writer.

en.wikipedia.org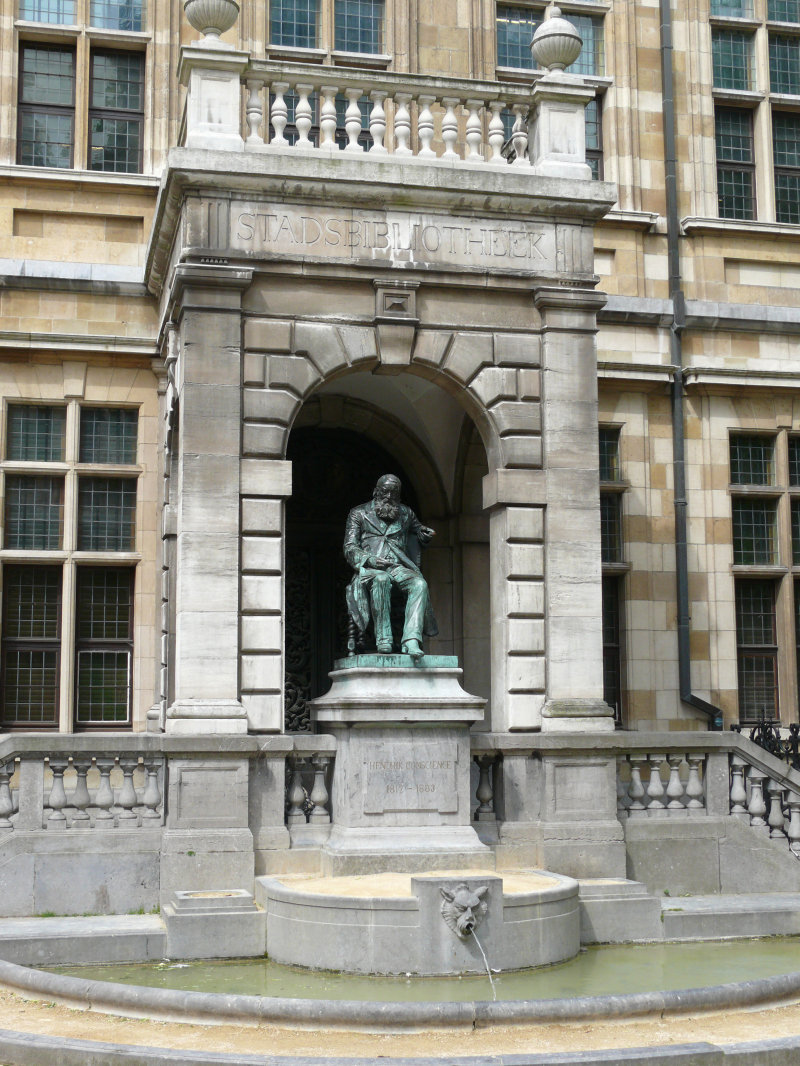 
Statue of Conscience outside the Hendrik Conscience Heritage Library -en.wikipedia.org