Top 15 Most Important Historical Figures In France
France is renowned for having an incredible past, one that has been shaped by some of the most extraordinary individuals. Many of these well-known French ... read more...individuals can be found throughout history, adding to the rich fabric of French history and culture. Who are these individuals? What part did they play in the development of France? The most important historical figures in France are listed below.
-
One of France's most well-known residents, Joan of Arc is best recognized for her role in bringing the Hundred Years War to a close. She successfully regained French lands and gave the French the win over the English.
Her religious fervor, particularly her holy visions of Saints Michael and Catherine, which inspired her to take the lead in combat with the divine prophecies that she would save France, served as the inspiration for Joan of Arc's deeds.
Following the guidance of the saints, Joan fought with Dauphin Charles, the heir to the French throne, in a number of wars that helped France retake its lands from the English.
After winning a battle, Charles was proclaimed Charles VII and anointed king of France in the cathedral of Reims in 1429. Joan was sold to the English as a hostage by the Burgundians despite the fact that the French had reclaimed their monarchy due to the ongoing war with them. She was accused of being a heretic and a witch, and she was burned at the stake. She continues to be the patron saint of France, and there are sculptures of her all around the nation as a mark of respect for the young woman who led France to triumph.
Birth - Death: 1412 - 1431

Photo: Today in History - Joan of Arc 
Photo: Toronto Star - Joan of Arc -
The Austrian Archduchess Marie Antoinette was born in Vienna in 1755. She married Louis-Auguste, the future King Louis XVI of France, at the age of fourteen. The last monarchs of France were Queen Marie Antoinette and King Louis the XVI.
The French people initially held Marie Antoinette in great regard throughout her reign as Queen of France, but when the monarchy came under fire for its decadence and extravagant spending, popular opinion of the queen sharply declined. When the enraged Parisians stormed Versailles, the unrest reached a fever pitch.
Marie Antoinette is perhaps most known for the iconic phrase "Let them eat cake," which she uttered after learning that Parisians were no longer able to afford to purchase bread, shortly prior to the French Revolution when the majority of French people were experiencing extreme poverty. She had apparently intended to indicate that they should eat brioche if there was in fact no bread. Many historians contend that there is no solid evidence to support the notion that Marie Antoinette actually made these declarations, despite the fact that it was a baseless myth that spread quickly.
Marie Antoinette's and King Louis XVI's poor reputation among the French people is frequently mentioned as a cause of the French Revolution. At the age of 38, Marie Antoinette would eventually be executed by guillotine at the Place de la Concorde in Paris on October 16, 1793. During her imprisonment and horrific trials, her hair had become entirely white.
Birth - Death: 1755 - 1793
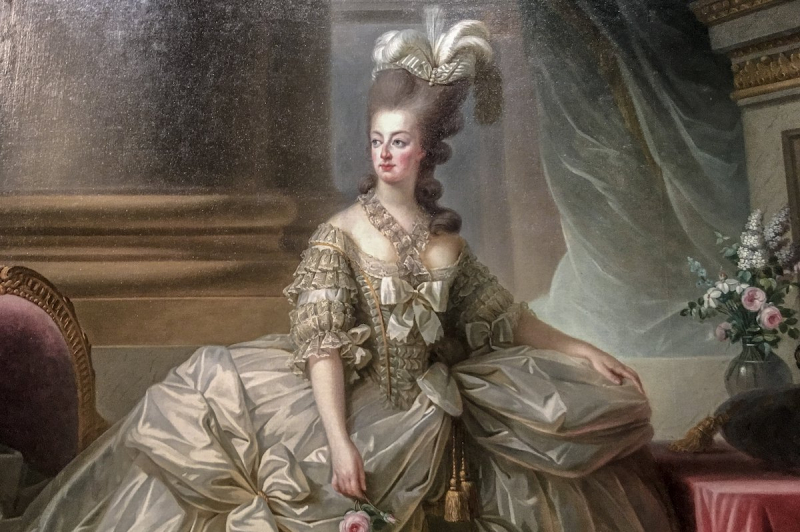
Photo: baotintuc.vn - Marie Antoinette 
Photo: Eva - Marie Antoinette -
Following the passing of his father, King Louis XIV of France was anointed monarch at the young age of 4. His intricate building of the Chateau de Versailles and the splendor of his reign, nicknamed "Le Grand Siecle" of French classicism, are one of the most important historical figures in France.
While Louis was still a kid, Cardinal Mazarin served as King Louis XIV's chief minister and helped to rule the nation. At the age of 23, Louis assumed the role of the absolute and divine monarch following the death of the Cardinal in 1661. He believed he was ruling France directly on behalf of God. Throughout his reign, he fought in numerous conflicts and battles across Europe against the dynasties of Spain, Flanders, and the Habsbourg. The first French colonies in "Nouvelle France" were founded under the reign of King Louis XIV, with the first colony being in Quebec, Canada, and extending to certain regions further south to Louisiana. The Sun King, who ruled for 72 years until passing away at age 76 from gangrene-related complications, would have the longest reign in the history of France and Europe.
Birth - Death: 1638 - 1715
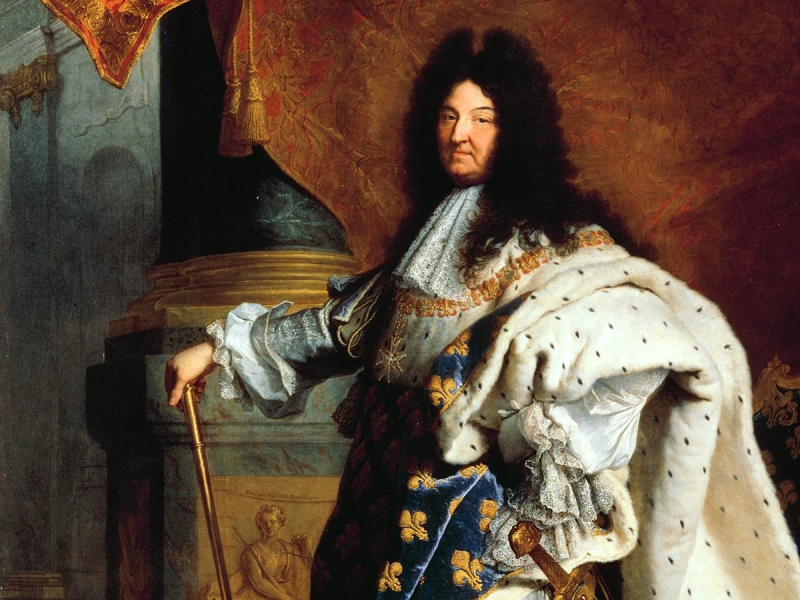

Photo: bio. Biography.com - King Louis XIV 
Photo: www.history.com - Louis XIV -
Victor Hugo, a prominent French author known for his poems, novels, and dramas, is best known for his novels The Hunchback of Notre Dame (1831) and Les Misérables (1862). Hugo was an artist during the Romantic period, which was characterized by a concentration on nature as an inspiration for both literature and art.
Victor Hugo began writing semi-political works with The Hunchback of Notre Dame. The protagonist of the tale was a disfigured orphan who suffered abuse from the locals. Later, it was transformed into a movie, and a 1996 Disney animated picture was produced.
When it was first published in 1862, Les Misérables, which is set in 1845, was a major success, making him very well-known not just in France but also all over the world after it was translated into various languages. It chronicles the activities of a man serving a 19-year sentence for robbing a loaf of bread to feed his hungry niece. It was an excellent book that exposed the numerous problems with post-revolutionary French society and the conflict between good and evil.
Birth - Death: 1802 - 1885

Photo: The Guardian - Victor Hugo 
Photo: CafeBiz- Victor Hugo -
The Eiffel Tower is the most popular landmark in Paris and arguably the most well-known monument in all of France.
Gustave Eiffel, a French engineer with a specialty in metal fabrication, was in charge of building the tower for the Universal Exposition in 1889. The aesthetic elite of his day criticized Eiffel for the tower's "barbaric mass" black structure and construction's viability while it towered over the picturesque city of Paris.
Despite the controversy surrounding its construction, the Eiffel tower has emerged as a recognizable building in Paris. Gustave's amazing career was made possible in part by his contributions to the Statue of Liberty's structural design as well as a number of other brilliant structures around the world, such as bridges, skyscrapers, and railroads. Complete construction of the Statue of Liberty took place in Paris, after which it was disassembled and transported to America. The Eiffel Tower, which came to represent Paris, is his final and longest-lasting legacies.
Birth - Death: 1832 - 1922
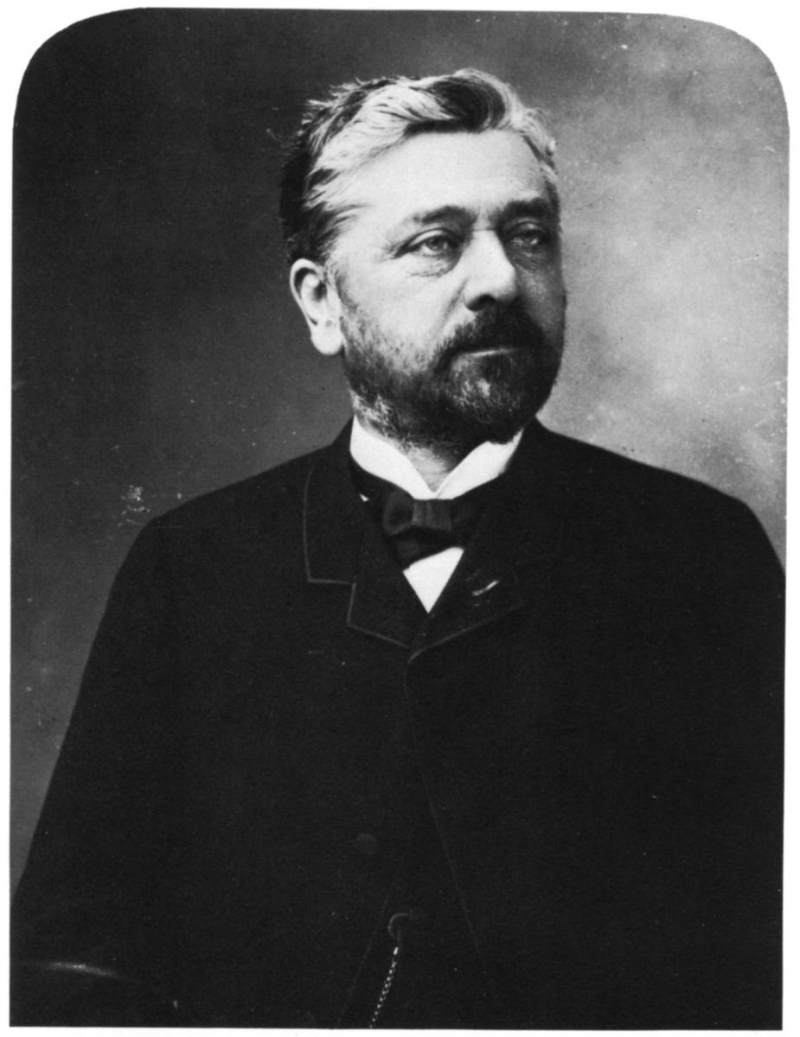

Photo: Structurae - Gustave Eiffel 
Photo: Mairie de Paris - Gustave Eiffel -
The famed French aviator, poet, author, and journalist Antoine de Saint-Exupéry famously described his journeys and thrilling experiences as a pilot in his literary works. He worked as a commercial pilot for the first aero-postal services while concurrently serving in the French Air Force. He fled to America after the German Armistice in 1940, where he authored his most well-known book, Le Petit Prince or The Little Prince, which was first made available there in both English and French. His literary career peaked with the 1943 publication of The Little Prince, a classic that was written while he was in New York arguing for American intervention in the War against the Nazi regime. Although he received numerous literary awards for his works Night Flight (1931) and his memoir Wind, Sand, and Stars (1939), his literary endeavors culminated with the publication of these two works.
Later, in 1943, he would return to France and fight alongside the Allies with a squadron stationed in the Mediterranean. While mapping out German locations in the Rhone valley in his P38 unarmed plane on a reconnaissance mission on July 31, 1944, he vanished. His disappearance would not be solved until 2004 when pieces of his plane were found off the coast of Marseille. The Little Prince is a book that honors Antoine de Saint-Exupéry.
Birth - Death: 1900 - 1944
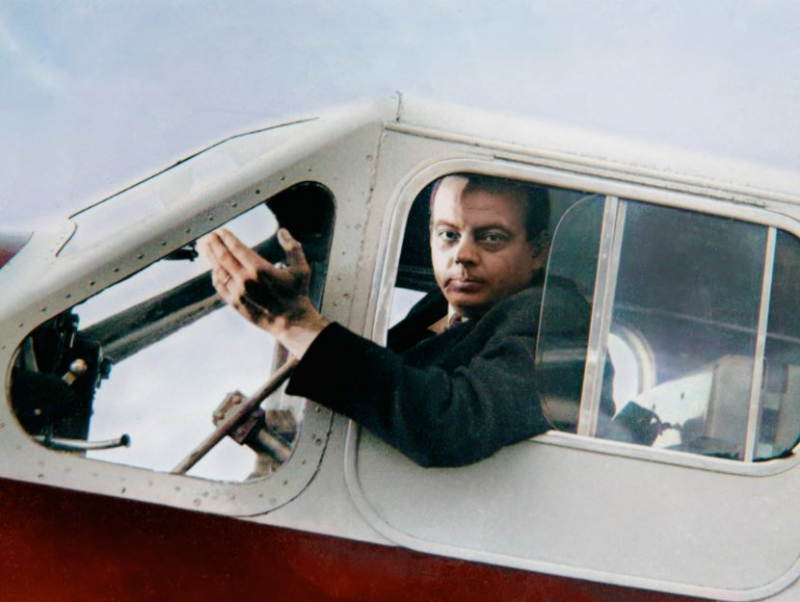

Photo: Pinterest - Antoine de Saint-Exupéry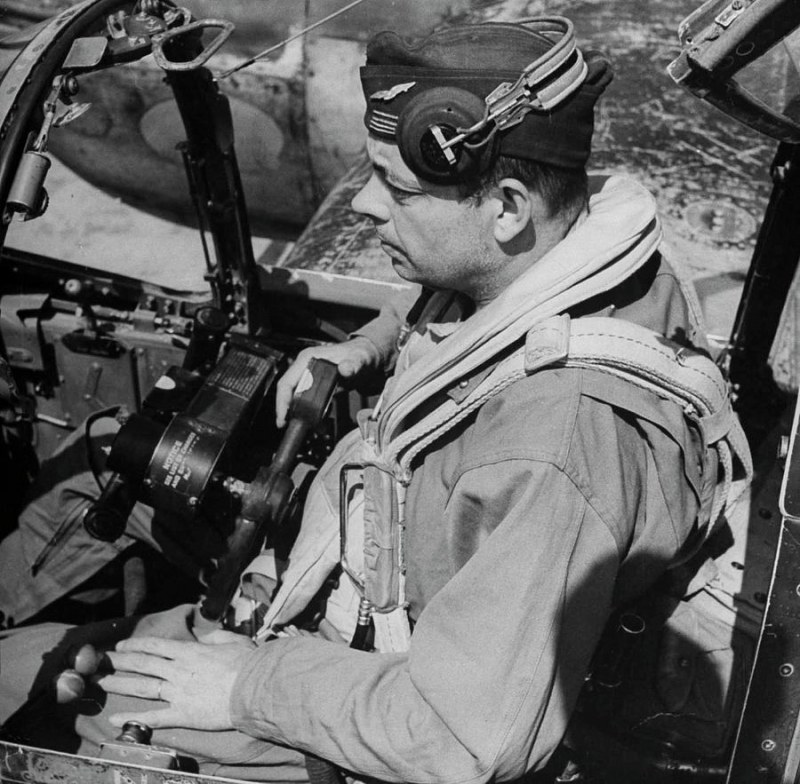 
Photo: This Day in Aviation - Antoine de Saint-Exupéry -
The epitome of French elegance and style is represented by the Chanel fashion house. The little black dress, characteristic suits and dresses, accessories, and perfumes made by Chanel's founder Gabrielle "Coco" Chanel are what make her the most well-known French fashion designer. Chanel would develop into a legendary French brand.
When her mother passed away when she was 12 years old, she became an orphan and spent the next six years in an orphanage. Her signature black and white hues as well as the stain glass windows of the Abby later inspired her to create the intertwined CC brand logo for Chanel. The austere life in the Abby would eventually have a strong influence on her designs. At initially, Chanel catered to the affluent and stylish elites, offering them simple and elegant fashions. Due to the lack of textiles following the First World War, she freed the feminine form by doing away with corsets and waistlines in favor of looser gowns made of jersey fabrics. She was regarded as avant-garde because of her straightforward, more usable forms in manly tones. Despite having a straightforward yet classy appearance and hardly ever appearing in public without her trademark pearls, Chanel would go on to become a global fashion icon.
Birth - Death: 1883 - 1971
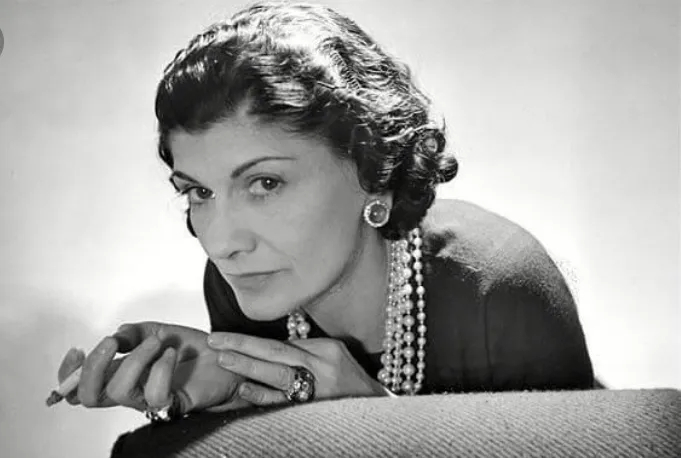

Photo: HistoryColored - Coco Chanel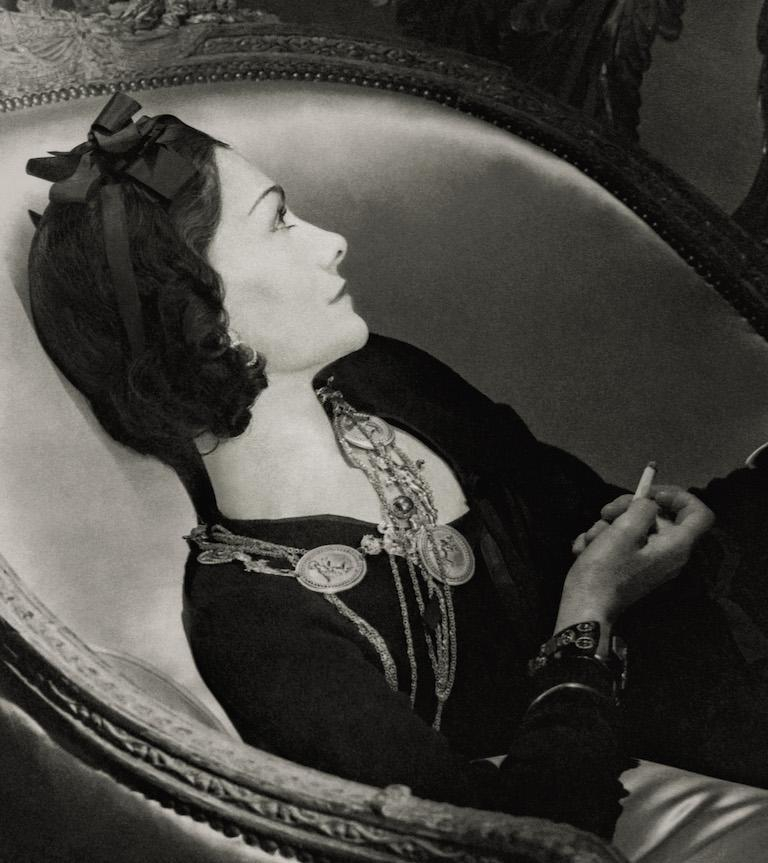 
Photo: Historical babes - Tumblr - Coco Chanel -
The renowned French singer Edith Piaf's "La Vie en Rose" is the most well-known French song in the entire globe. Edith, who was born in Paris in 1915, had a challenging upbringing characterized by illness and deprivation. She started singing in the Great Music Halls, including Moulin Rouge, after being discovered singing in the streets of Paris. She had many close acquaintances in the theater, music, and art worlds, and her songs playing on Radio France helped her gain more notoriety throughout France.
She continued to perform during the German occupation and after the war rose to international fame, performing at Carnegie Hall in New York City. She would return to Paris while dealing with her severe pain, financial difficulties, and drinking. She was acclaimed for her unique musical interpretations and stirring and heartfelt performances, particularly for her most well-known songs like "Mon Dieu," which was written in honor of her lover Marcel Cerdan, who died in an aircraft crash while en route to meet her in New York. She is best known for her iconic French song "La Vie en Rose."
Birth - Death: 1915 - 1963
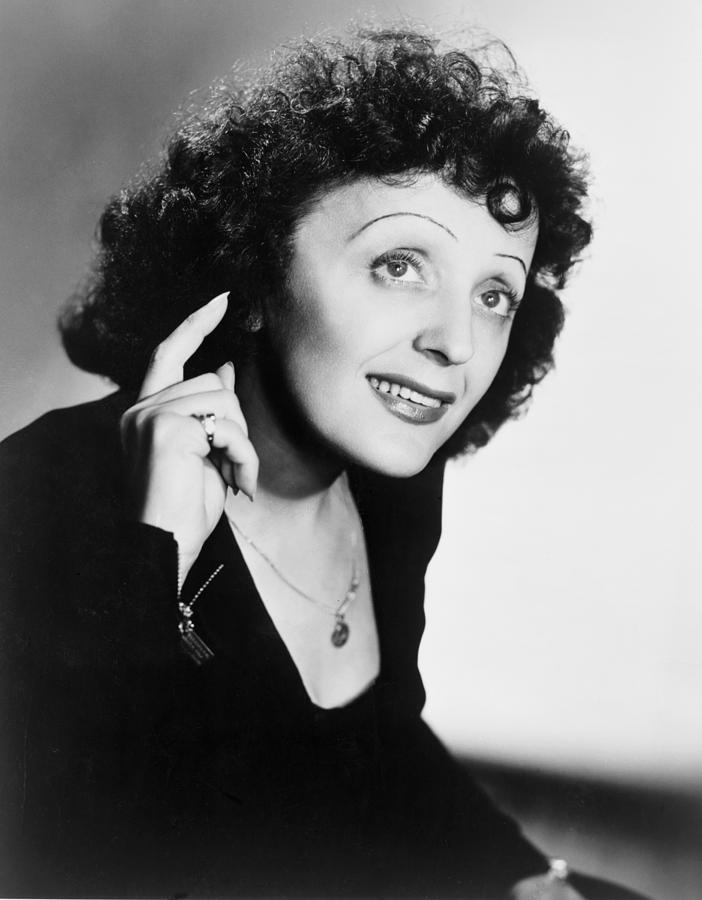

Photo: Fine Art America - Edith Piaf 
Photo: Eskipaper.com - Edith Piaf -
Auguste Rodin's controversial and turbulent love affair with Camille Claudel was just 19 when Rodin first saw her, and he was captivated by her talent, originality, and attractiveness. She was a gifted sculptor who studied at the Academy Colarossi in Paris under the tutelage of Alfred Boucher, her first tutor. The sensuality and fluidity of two lovers caught dancing in an embrace are beautifully depicted in her bronze sculpture "La Valse," which has become famous. The three stages of life and the conflict between youth, old age, and death are shown in her piece "The Mature Age," which is currently on display at the Rodin Museum in Paris.
She was cared for by Rodin until their separation because it was practically difficult for a woman to receive any fame or to make a living as an artist during her lifetime. Many years after her passing, she would finally be acknowledged for her contributions. Her sculptures in marble and bronze, which combine sensuality with strength and poetry, were considered avant-garde, especially for a woman of her day. Because of her financial dependence on Rodin and the fact that he won't marry her, her intense relationship with him would be a major source of frustration. Claudel, regrettably, spent the final 30 years of her life in a mental hospital.
Birth - Death: 1864 - 1943

Photo: Supercurioso - Camille Claudel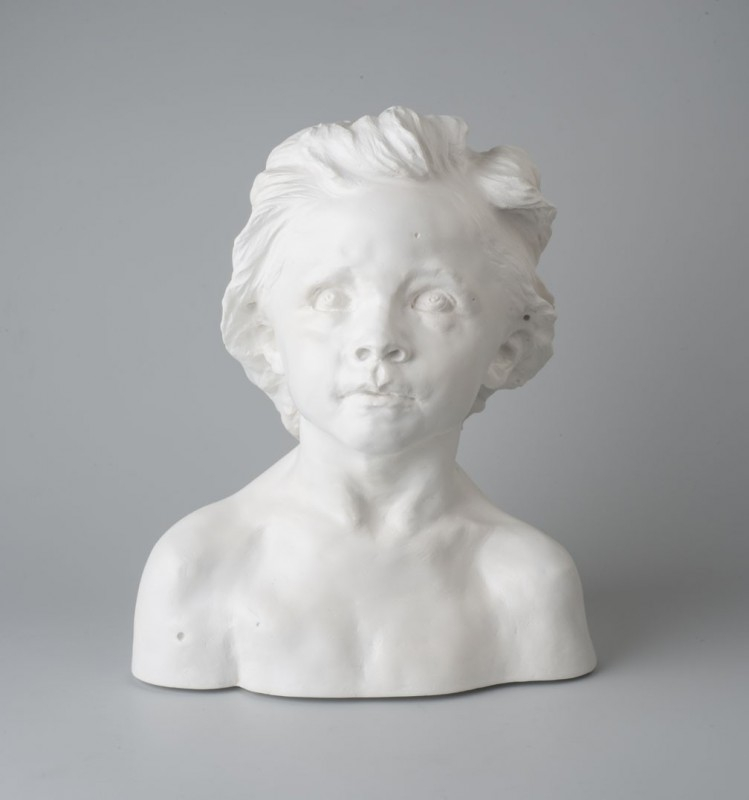 
Photo: Musée Rodin – Boutique - The Little Chatelaine (Camille Claudel) -
The Thinker, one of the most well-known sculptures, was created by French artist Auguste Rodin. Rodin, who was born in Paris in 1940, is regarded as the originator of modern sculpture and one of the most significant artists of the second half of the 19th and 20th centuries. His artwork included elements of impressionism, romanticism, and light and form. His study of the sculptures of Michelangelo and Donatello while living in Italy served as inspiration for him, and his own sensual works in marble and bronze were thought to be avant-garde at the time.
In addition, he owned several notable sculptures, including "The Kiss" and statues of Victor Hugo and Honoré de Balzac, two well-known French writers. He frequently copied Rodin's statues in varied dimensions, including the eerie "Les Bourgeois de Calais" at the Palace of Westminster in London. Camille Claudel, his partner and a fellow sculptor, contributed significantly to the design and composition of his works. The sculpture "L'Eternelle Printemps," which exudes incredible sexuality and sensuality, was allegedly inspired by his decade-long relationship with Claudel. Rodin's sculptures, in all of their sensual and passionate guises, will live on in infamy.
Birth - Death: 1840 - 1917
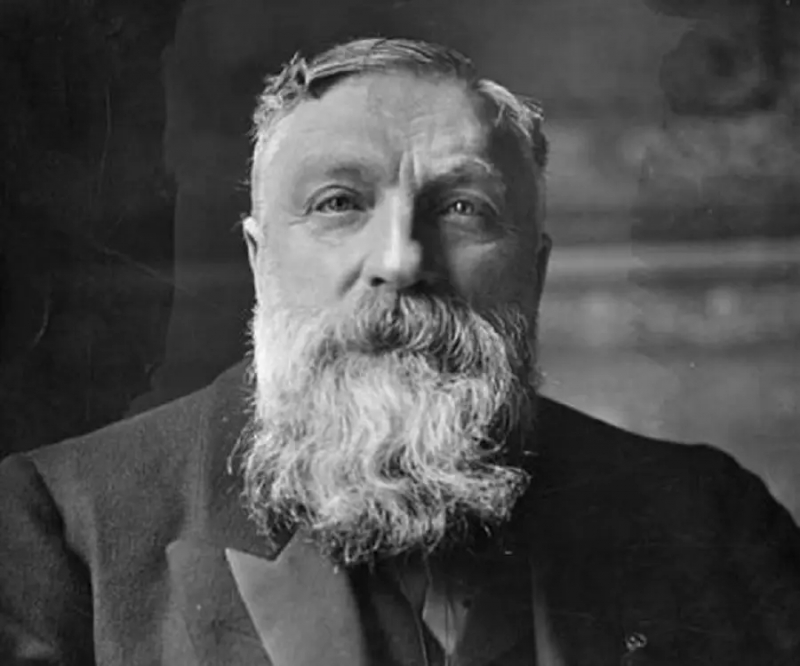

Photo: Famousbio - Auguste Rodin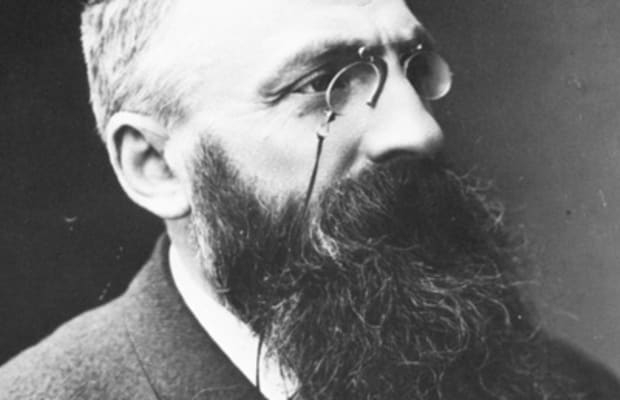 
Photo: bio. Biography.com - Auguste Rodin -
Maximilien Robespierre was a French lawyer and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution as one of the most important historical figures in France. He advocated for the elimination of both clerical celibacy and the Atlantic slave trade while serving as a member of the Estates-General, the Constituent Assembly, and the Jacobin Club. After being chosen as the "public accuser" in 1791, Robespierre became a vocal supporter of male citizens without a political voice, their unequal access to the National Guard, elected positions, and the commissioned ranks of the army, as well as their rights to petition and to keep and bear arms for self-defense. The uprising that resulted in the overthrow of the French monarchy on August 10th, 1792, and the calling of a National Convention was heavily influenced by Robespierre. His objectives included establishing direct democracy, equality before the law, the abolition of prerogatives, and a single, indivisible France. Because of his dedication to high moral standards, he was given the moniker "the incorruptible".
Early in September 1792, Robespierre, one of the key figures in the Paris Commune, was chosen as a delegate to the French Convention. However, he soon came under fire for attempting to establish either a triumvirate or a dictatorship. His adversaries were those who did not vigorously defend France (modérantisme).Birth - Death: 1758 - 1794

Photo: Wikipédia - Maximilien de Robespierre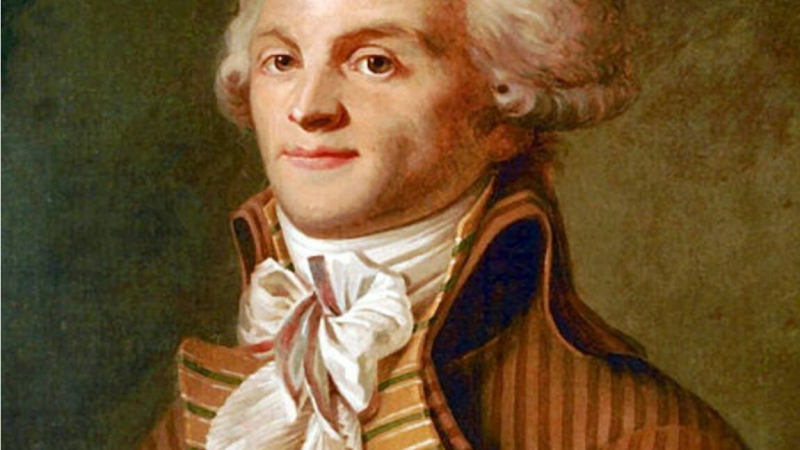 
Photo: Société des Études Robespierristes - Maximilien Robespierre -
French composer Claude Debussy authored music. Although he vehemently disputed the title, he is occasionally regarded as the first Impressionist composer. He was one of the composers who had the largest impact in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Debussy was admitted at the age of eleven to the Conservatoire de Paris, France's top music school, despite coming from a modestly wealthy family with no interest in the arts. Despite the orthodox academics at the Conservatoire's criticism, he initially studied the piano but eventually discovered his passion for creative music. He spent many years honing his mature style, and he was almost 40 years old when Pelléas et Mélisande, his sole opera, brought him international acclaim in 1902.
Prélude à l'après-midi d'un faune (1894), Nocturnes (1897-1899), and Images are some of Debussy's symphonic compositions (1905–1912). Heavily reacting to Wagner and the German musical tradition, his music was in many ways. In his "symphonic sketches," La Mer, he explored an alternative to the classical symphony (1903–1905). In his later years, he concentrated on chamber music, finishing three of the six intended sonatas for various instrumentation.Birth - Death: 1862 - 1918
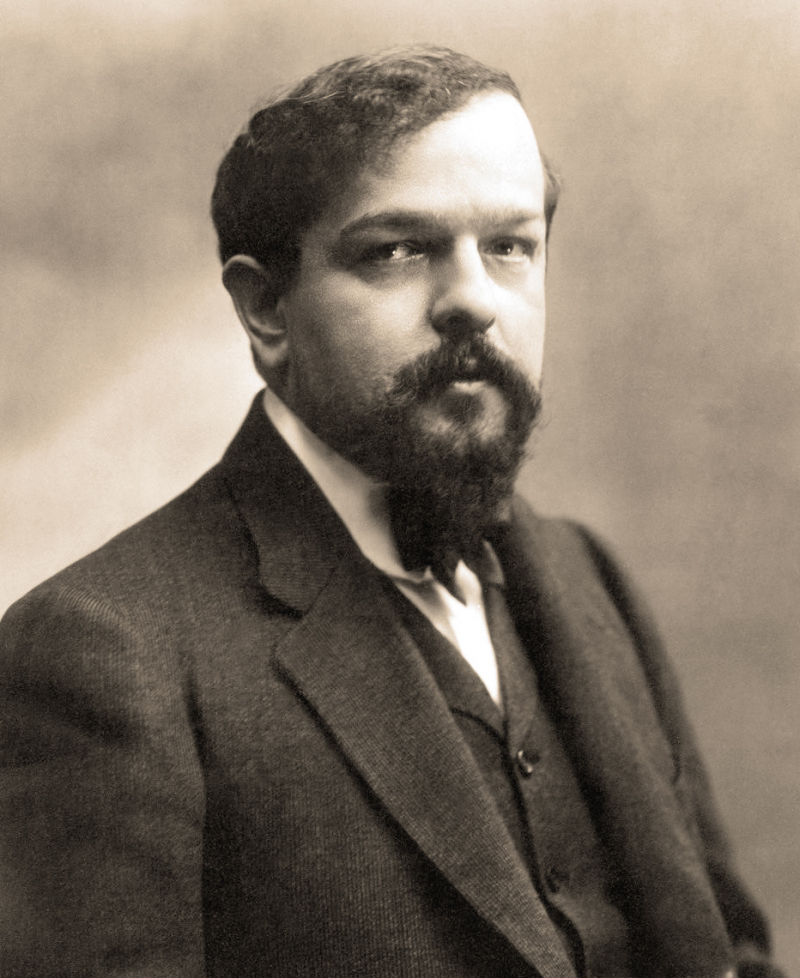

Photo: Wikipedia - Claude Debussy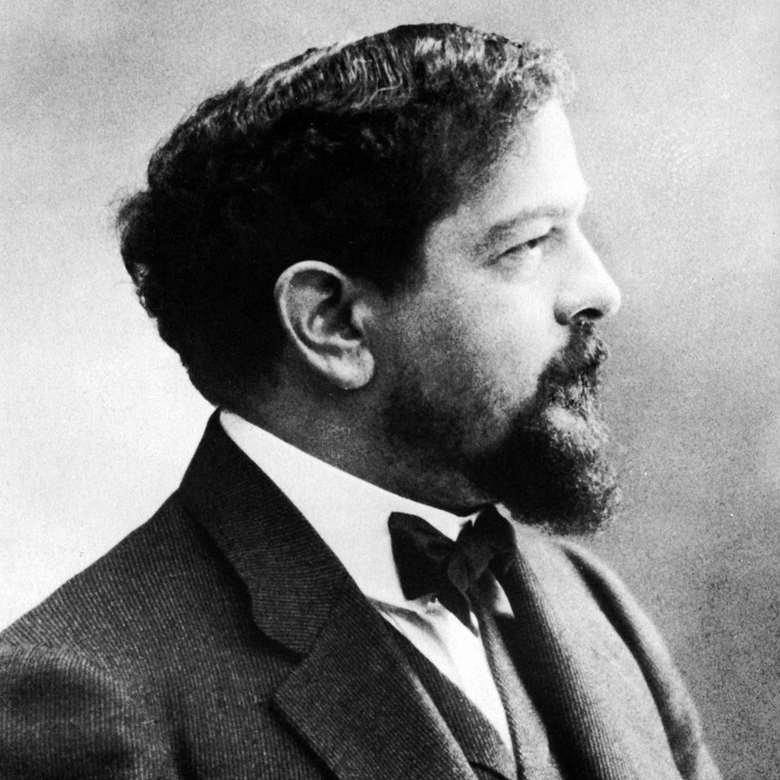 
Photo: Gramophone - Claude Debussy -
Claude Monet, a French painter and the father of impressionist art, is regarded as a significant forerunner of modernism, particularly for his efforts to capture nature as he saw it in his works. He was the most productive and consistent impressionist painter during the course of his lengthy career, especially when it came to plein air (outside) landscape painting, which is the art of expressing one's perceptions before nature. Impression, Soleil levant, a painting by Monet that was displayed in the 1874 "exhibition of rejects," a substitute for the Salon, is where the word "Impressionism" originates.
Monet was up in Le Havre, Normandy, where he developed an early love in the outdoors and in drawing. His father, Claude-Adolphe Monet, disapproved and preferred that he pursue a career in business, despite the fact that his mother, Louise-Justine Aubrée Monet, encouraged his desire to become a painter. He was very close to his mother, but she passed away in January 1857 when he was sixteen. As a result, he was transferred to live with Marie-Jeanne Lecadre, his wealthy, childless aunt. He continued his education at the Académie Suisse, where he studied under academic history painter Charles Gleyre and was a fellow student of Auguste Renoir. Landscapes, seascapes, and portraits were among his early subjects, although they received little attention. Eugène Boudin, who introduced him to the idea of plein air painting, was a significant early influence. Monet settled in Giverny, also in northern France, in 1883, when he bought a home and grounds and started a massive landscaping project that included a water lily pond.
Birth - Death: 1840 - 1926

Photo: Wikimedia Commons - Claude Monet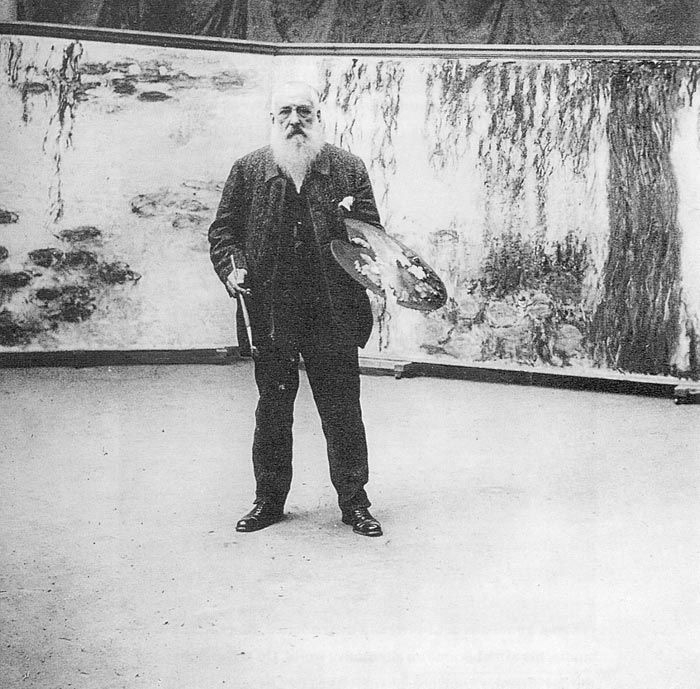 
Photo: Wikipedia - Claude Monet -
The French Enlightenment author, historian, and philosopher François-Marie Arouet, better known by his pen name Voltaire, was renowned for his wit, criticism of Christianity—particularly the Roman Catholic Church—and of slavery, as well as his support for freedom of speech, freedom of religion, and the separation of church and state. He was born in Paris, the youngest of the five children of Marie Marguerite Daumard, a member of the lowest class of French nobility, and François Arouet, a lawyer and minor treasury official.
Writing in nearly every literary genre, including plays, poems, novels, essays, histories, and scientific expositions, Voltaire was a diverse and prolific author. Over 20,000 letters, as well as 2,000 booklets and pamphlets, were written by him. He was one of the first writers to achieve fame and financial success abroad. As a vocal supporter of individual rights, he was always in danger due to the harsh censorship regulations of the Catholic French monarchy. His polemics savagely mocked prejudice, orthodoxy, and the French institutions of his time. His most well-known work and magnum opus, Candide, is a novella that makes fun of, critiques, and comments on a variety of historical events, thinkers, and philosophical ideas.
Birth - Death: 1694 - 1778

Photo: Historia y biografía de - Voltaire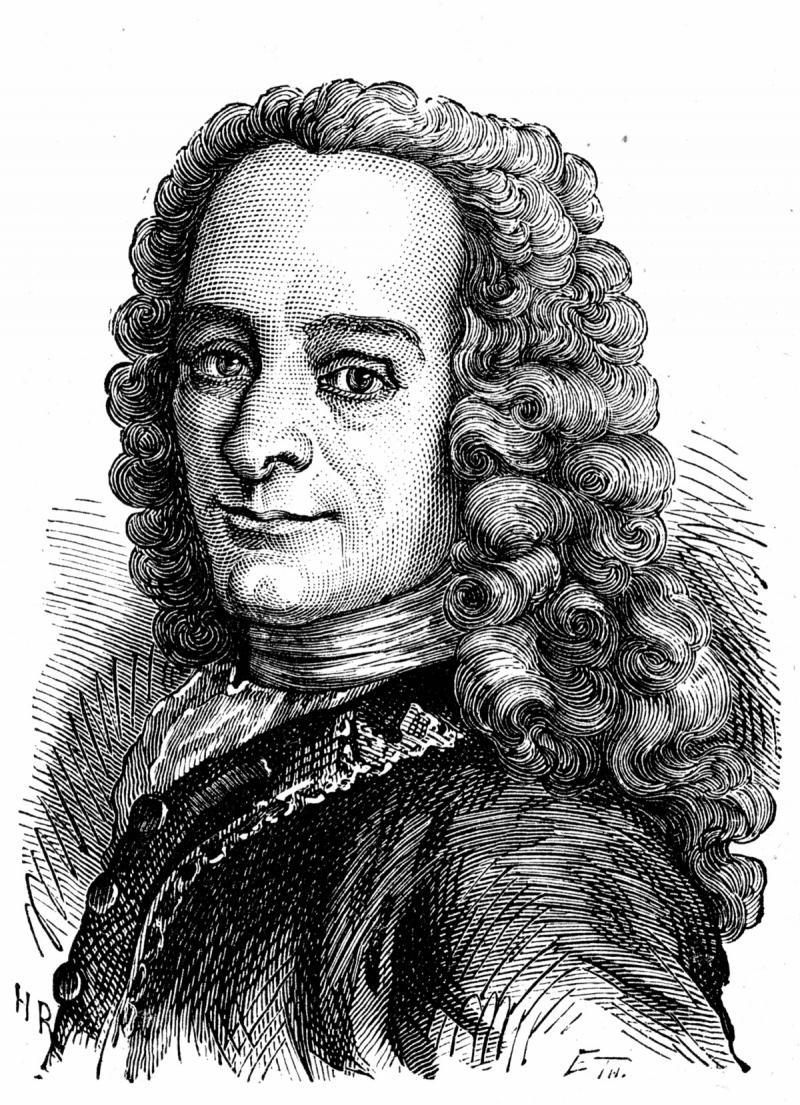 
Photo: Wikimedia Commons - Voltaire -
In order to bring back democracy in France, Charles de Gaulle, a French army officer and statesman, led Free France against Nazi Germany during World War II and presided over the Provisional Government of the French Republic from 1944 to 1946. When President René Coty appointed him Prime Minister and President of the Council of Ministers in 1958, he was forced out of retirement. The Fifth Republic was established by him after the French Constitution was revised and approved by referendum. Later same year, he was elected president of France. He was re-elected in 1965 and served in that capacity until his resignation in 1969.
He was born in Lille and received his education at Saint-Cyr. He was a distinguished officer in the First World War who was wounded numerous times before being captured at Verdun. He was an advocate for mobile armored divisions in the interwar period. He oversaw an armored division that launched a counterattack against the German invaders in May 1940, leading to his appointment as Undersecretary for War. De Gaulle escaped to England after rejecting his government's armistice with Germany and urged the French in his Appeal of June 18 to continue the battle and resist occupation. In opposition to the Axis, he oversaw the Free French Forces and eventually the French National Liberation Committee. He gained Winston Churchill's support despite having tense relations with the United States and became the undeniable head of Free France. In June 1944, after France had been liberated, he was appointed head of the Provisional Government of the French Republic.
The Trente Glorieuses, a period of exceptional growth that began in 1944 as part of de Gaulle's dirigiste economic program, contained significant state-directed supervision over a capitalist sector. He resigned in early 1946 out of frustration with the resurgence of petty partisanship in the Fourth Republic, but remained politically active as the founder of the Rassemblement du Peuple Français (RPF; "Rally of the French People"). His War Memoirs, which swiftly became a mainstay of contemporary French writing, were written when he retired in the early 1950s.
Birth - Death: 1890 - 1970

Photo: bio. Biography.com - Charles de Gaulle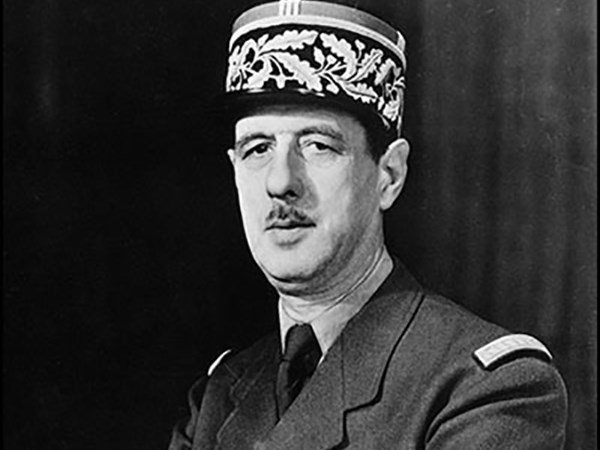 
Photo: bio. Biography.com - Charles de Gaulle