Top 7 Things to Know About Ativan
Ativan or Lorazepam is a benzodiazepine medication. It is used to treat alcohol withdrawal, anxiety disorders, extreme agitation, difficulty sleeping, active ... read more...seizures, including status epilepticus, and chemotherapy-related nausea and vomiting. Don't miss this post because it will give you some things to know about Ativan.
-
The way Ativan works is the first thing to know about Ativan.
- The drug lorazepam is sold under the trade name Ativan, which has sedative, anticonvulsant, and anxiety-relieving properties.
- However, they believe that Ativan's (lorazepam) effects are caused by its capacity to form a strong bond with the GABA-benzodiazepine receptor complex, which increases the affinity for GABA (a neurotransmitter that blocks impulses between nerve cells in the brain). Anxiety, mood problems, seizure disorders, and pain have all been connected to low GABA levels.
- The group of drugs known as benzodiazepines includes Ativan.
Photo: M Care Exports 
Photo: Ark Behavioral Health -
- May be used to treat anxiety disorders or to relieve short-term anxiety (for example, before surgery) (although studies have not documented use beyond 4 months).
- Additionally offered as an injectable form, which may be used to treat protracted seizures.
- Can be used for some other indications, such as lower back pain, even though they have not been FDA-approved. This is known as using medication off-label.
- Lorazepam is the brand name for generic Ativan.
- In the first instance, ativan or intravenous diazepam are used to treat convulsive status epilepticus. In the treatment of status epilepticus, lorazepam is more effective than diazepam and intravenous phenytoin and carries a decreased risk of persistent seizures that would necessitate further therapy. But at least for the elderly, phenobarbital is more effective than lorazepam and other medications.
- When someone is having mechanical ventilation, ativan may be administered. However, it has been discovered that propofol is more efficient and affordable than lorazepam in critically sick patients; as a result, the use of propofol for this indication is now recommended whereas lorazepam is contraindicated.
- Ativan is effective in treating catatonia with a speech impediment. The need for treatment for a few days may be necessary if the symptoms return. As part of the benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome, catatonia brought on by abrupt or too rapid withdrawal from benzodiazepines should also respond to therapy with ativan. Haloperidol is occasionally administered concurrently with lorazepam due to the drug's potential for paradoxical effects.
- It is occasionally used in chemotherapy in addition to drugs to relieve nausea and vomiting, specifically those brought on or made worse by psychological sensitivity to the idea of being ill

Photo: Drugs.com 
Photo: Drugsdb.com -
- The most frequently reported side effects are drowsiness, tiredness, or dizziness. Any one of these adverse consequences may reduce a person's ability to react quickly, decrease their ability to drive or operate machinery, or raise their risk of falling. Alcohol should be avoided because it may intensify these effects.
- There have also been reports of amnesia, forgetfulness, unsteadiness, visual issues (blurred or double vision), sexual dysfunction, nausea, constipation, and a number of other side effects.
- May infrequently result in respiratory depression (unusually slow and shallow breathing). Larger Ativan doses, those who already have respiratory issues, or the use of Ativan in conjunction with other drugs that also cause respiratory depression increase the risk (such as opioids).
- The use of ativan may raise the likelihood of depression, reveal depression, or trigger suicidal thoughts. Keep an eye out for a change in mood.
- Ativan has the potential to cause both physical and emotional dependence. The shortest amount of time at the lowest dose is ideal. The availability of ativan may be sought after by drug users.
- With sudden discontinuance, withdrawal symptoms (such as convulsions, tremors, cramping, vomiting, sweating, or sleeplessness) may develop; taper down gradually under a doctor's care.
- Paradoxical reactions, or those that go against expectations, can occasionally happen. Anxiety, agitation, wrath, disturbed sleep, sexual disinhibition, or hallucinations are some of the symptoms.
- After receiving Ativan intravenously, those over the age of 50 may be more susceptible to experiencing intense and protracted sedation.
- Several other drugs, including as opioids, sedatives (such as alcohol, antipsychotics, antidepressants, or sedative antihistamines), clozapine, probenecid, and valproate, may interact with it.
- Some persons, such as those with pre-existing respiratory conditions (including COPD or sleep apnea), a history of drug or alcohol misuse, those at high risk of falling, pregnant or nursing women, or those with kidney or liver problems, may not be a good fit. The effects of Ativan may be more noticeable in the elderly or the weak.
The most common adverse effect associated with Ativan use is sedation. The most frequently reported side effects with lorazepam were drowsiness (15.9%), dizziness (6.9%), weakness (4.2%), and unsteadiness (3.4%) in a cohort of approximately 3,500 patients receiving treatment for anxiety. With aging came more side effects, like drowsiness and unsteadiness. Hypotension, respiratory depression, behavioral disinhibition, and cognitive impairment may also manifest. That's all about the third thing to know about Ativan we want to mention.
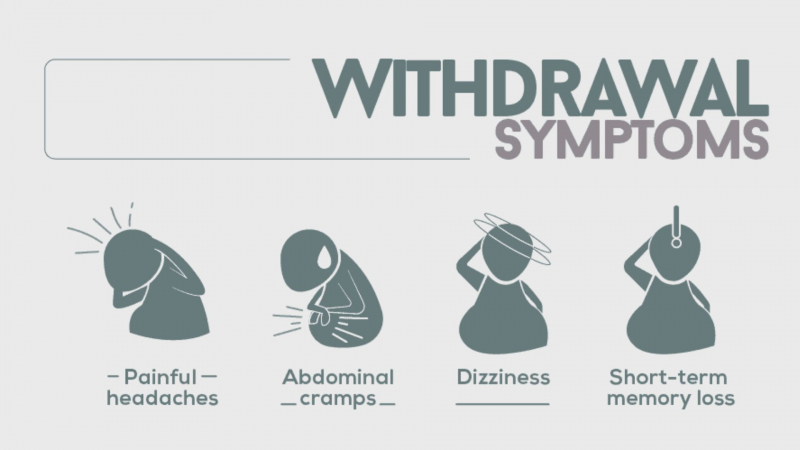
Photo: Northpoint Washington 
Photo: Ark Behavioral Health -
The following thing to know about Ativan is tips for using it. Every day at set times, or on a "PRN" basis, Ativan can be taken. The maximum amount of dosages you should take in a day will often be prescribed by your healthcare professional. Liquid Ativan should be measured with an oral syringe or dosage spoon, both of which are available from your pharmacist.
- Both with and without meals are acceptable. When used to treat anxiety, it is possible to administer two doses, the largest being administered right before nigh
- Precisely as prescribed by your doctor. Do not alter the dosage without consulting your doctor first. Don't stop taking Ativan abruptly if you've been taking it for a while since withdrawal symptoms (such as impaired vision, sleeplessness, sweating, and, very occasionally, seizures) could occur. On how to gradually reduce the dose, your doctor will provide you advice. Keep away from any possible drug users.
- Taking Ativan may make you drowsy and impair your ability to drive or handle other difficult jobs. If Ativan has this impact on you, avoid engaging in these activities.
- When using Ativan, avoid consuming alcohol as it may intensify the sedative and respiratory depression adverse effects.
- Your risk of falling may increase if you take Ativan since it can make you feel lightheaded. After lying down, take caution when getting up or sitting down.
- Consult your doctor if you believe you have developed an Ativan dependence or addiction.
- Without first confirming that they are compatible with Ativan with your pharmacist or doctor, do not take any additional drugs, including those purchased over-the-counter.

Photo: Pine Grove 
Photo: Medical News Today -
When used with Ativan, certain medications may have a reduced impact, shorten the duration of action, cause more side effects, or have no effect at all. Even while it is not always necessary to cease taking one of the drugs, sometimes there is an interaction between two drugs. Consult your doctor to learn how to handle drug interactions.
Typical drugs with which Ativan may interact are:
- anti-anxiety medications, including other benzodiazepines, such as diazepam and oxazepam
- anticonvulsants such as valproate
- antidepressants, such as amitriptyline, imipramine, nortriptyline
- antihistamines that cause sedation, such as diphenhydramine
- barbiturates
- duloxetine
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors, such as selegiline, isocarboxazid, or phenelzine
- opioid analgesics such as codeine, oxycodone and morphine
- oral contraceptives
- muscle relaxants such as cyclobenzaprine
- probenecid
- scopolamine
- sleeping pills, such as zolpidem
- some medications used to treat mental illness, such as clozapine and thioridazine
- theophylline.
Photo: Vinmec 
Photo: Daily Mail -
- Depending on the Ativan formulation utilized, certain effects take longer to reach their peak. Within two hours of intramuscular (IM) administration and 15-20 minutes after intravenous (IV) administration, optimal effects when administered preoperatively (including lack of recall or recognition) are visible. After oral treatment, peak concentrations happen in less than two hours.
- The intended benefits typically last six to eight hours, however some people may experience them for longer.
Photo: VipVorobjev 
Photo: Speeds Healthcare -
- People who have previously had hypersensitivity or allergy to Ativan, any benzodiazepine, or any of the components in lorazepam tablets or injections should avoid taking lorazepam.
- Benzodiazepines, such as Ativan, may reduce the respiratory drive of the central nervous system and are therefore contraindicated in cases of acute respiratory failure. An improper example would be the treatment of anxiety caused by acute, severe asthma. The ability and willingness of a person to fight for air may suffer from the anxiolytic effects. However, Ativan may be given to provide profound sedation if mechanical ventilation is required.
- Acute intoxication: Ativan and the effects of alcohol, drugs, or other psychoactive substances may work in concert. Therefore, it shouldn't be given to someone who is intoxicated or drunk.
- Ataxia is a neurological clinical symptom that manifests as unstable and awkward movement of the limbs and torso as a result of a breakdown in the coordination of large muscle movements. This is especially noticeable when standing and walking. It is the typical way that someone who is acutely intoxicated by alcohol may be affected. Ataxic individuals should not be given benzodiazepines.
- Acute narrow-angle glaucoma - Ativan dilates pupils, which may further obstruct the drainage of aqueous humor from the eye's anterior chamber, exacerbating narrow-angle glaucoma.
- The central nervous system depressive effects of lorazepam may make sleep apnea worse. The person's capacity to safeguard his or her airway while sleeping may be further diminished.
- Ativan is under the Food and Drug Administration's (FDA) pregnancy category D, which implies that if taken during the first trimester of pregnancy, it is likely to harm the developing fetus. Prenatal Ativan administration to pregnant women may result in floppy infant syndrome or respiratory depression in the newborn that requires care. Regular Ativan use in the third trimester of pregnancy increases the probability that the baby will develop benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome. Hypotonia, refusal to suckle, apneic fits, cyanosis, and altered metabolic reactions to cold stress are only a few symptoms of neonatal benzodiazepine withdrawal. It has been documented that the signs of newborn benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome and floppy infant syndrome can last for weeks or even months after birth.

Photo: Insider 
Photo: GoodRx