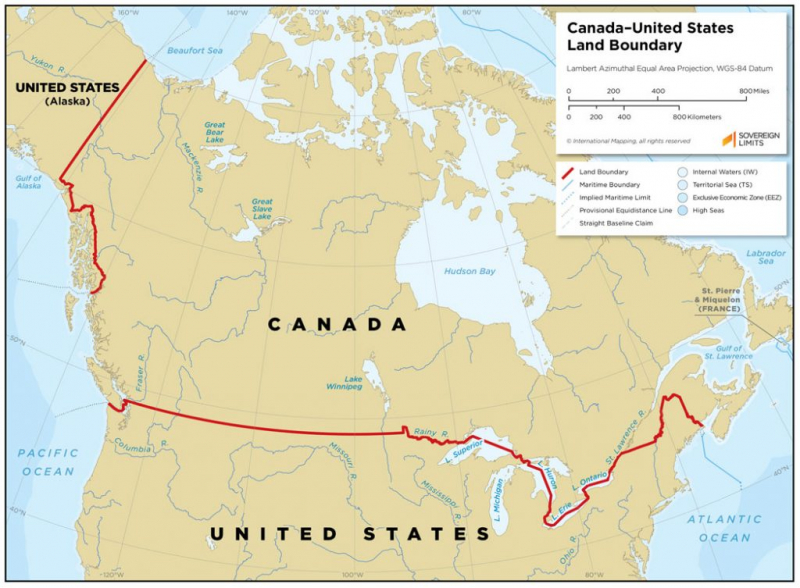
Canada – United States
The longest international border in the world shared by the same two countries is the border between the United States and Canada, also referred to as the International Boundary. The terrestrial boundary is 8,891 kilometers (5,525 miles) long, including 2,475 kilometers (1,538 miles) that are shared with Alaska. It also includes tiny segments of marine boundaries on the Atlantic, Pacific, and Arctic coasts as well as the Great Lakes. It is the sole land border with Canada.
The American Revolutionary War between Great Britain and the United States was put to a conclusion by the Treaty of Paris in 1783. The parties stipulated all of the United States' borders in the second article of the Treaty, including but not limited to the northern border along what was then British North America. The line that connected the northwest corner of Nova Scotia to the Connecticut River's head and continued down the center of the river to the 45th parallel of latitude was included in the mutually agreed-upon boundary.
Even though there is civilian law enforcement present, the International Boundary is sometimes referred to as the "longest undefended border" in the world. Outside of border controls, crossing is prohibited because everyone entering or leaving the country is subject to immigration and customs checks. Contrast this with the United States-Mexico border, which is actively guarded by U.S. Customs and Border Protection agents to stop illegal immigration and drug trafficking and is one-third the length of the Canada-U.S. border.
Length: 8,891 kilometers