How do germs spread between animals and people?
Because of the intimate relationship between humans and animals, it is critical to be aware of the frequent ways in which people can become infected with microorganisms that cause zoonotic illnesses. These can include:
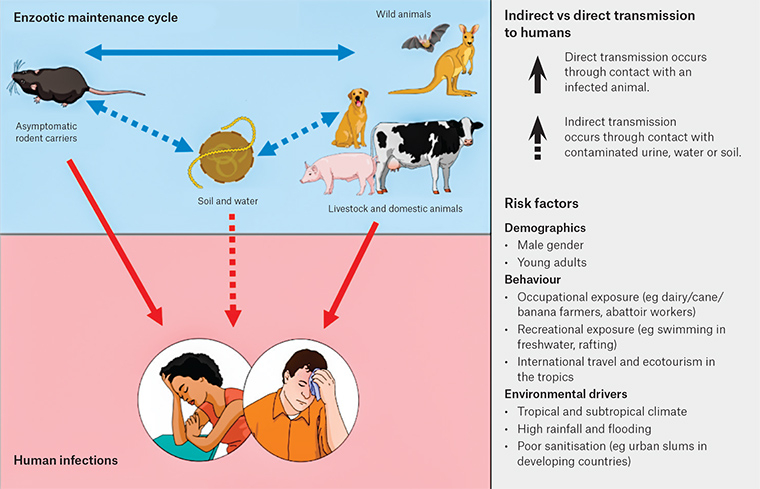
- Direct contact: Coming into contact with the saliva, blood, urine, mucous, feces, or other body fluids of an infected animal. Examples include petting or touching animals, and bites or scratches.
- Indirect contact: Coming into contact with areas where animals live and roam, or objects or surfaces that have been contaminated with germs. Examples include aquarium tank water, pet habitats, chicken coops, barns, plants, and soil, as well as pet food and water dishes.
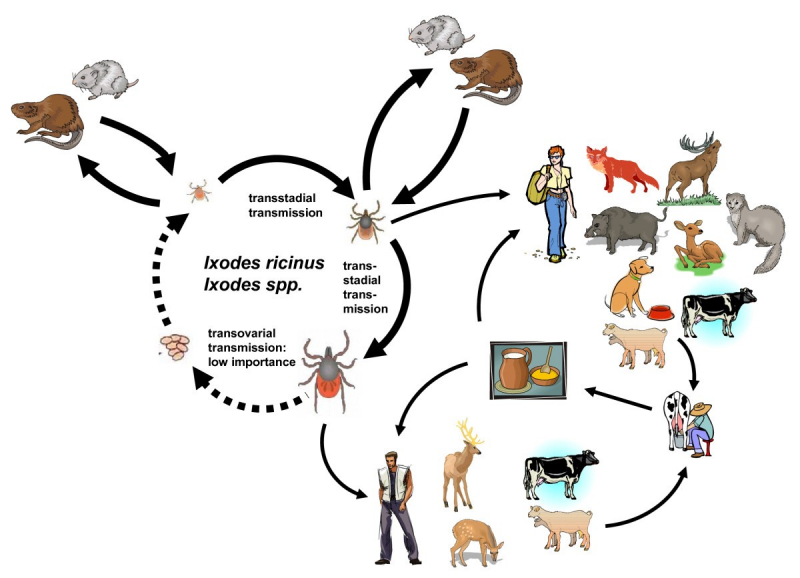
- Vector-borne: Being bitten by a tick, or an insect like a mosquito or a flea.
- Foodborne: Each year, 1 in 6 Americans get sick from eating contaminated food. Eating or drinking something unsafe, such as unpasteurized (raw) milk, undercooked meat or eggs, or raw fruits and vegetables that are contaminated with feces from an infected animal. Contaminated food can cause illness in people and animals, including pets.
- Waterborne: Drinking or coming in contact with water that has been contaminated with feces from an infected animal.