Interactions
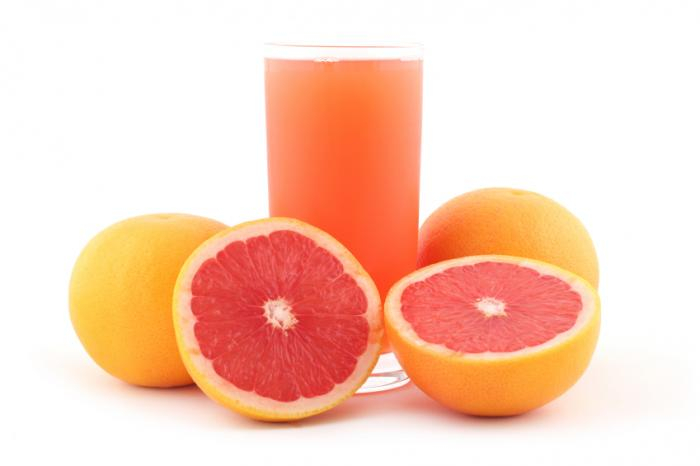
Intestinal CYP3A4 inhibitors are well-known to exist in grapefruit juice components. Cmax and area under the curve may rise when grapefruit juice and atorvastatin are combined (AUC). This discovery first raised questions about potential toxicity, and in 2000 it was advised that atorvastatin users avoid consuming grapefruit juice "in an unsupervised manner." Research on the effects of grapefruit juice consumption on primarily lower doses of atorvastatin have shown that grapefruit juice increases blood levels of atorvastatin, which could increase the risk of adverse effects. These studies primarily involved young people.
Fibrates are a class of medications that can be used alone or in conjunction with statins to treat severe or resistant mixed hyperlipidemia. A higher risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis can result from using atorvastatin at the same time as medications in the fibrate medicine class (such as gemfibrozil and fenofibrate).
Typical drugs with which Atorvastatin may interact are:
- amiodarone
- antibiotics, such as erythromycin
- antidepressants, such as nefazodone
- antifungals, such as itraconazole, ketoconazole, posaconazole, or voriconazole
- bezafibrate
- calcium channel blockers such as amlodipine, diltiazem, or verapamil
- colchicine
- cyclosporine
- digoxin
- HIV medications such as tipranavir, ritonavir or pibrentasvir
- niacin
- oral contraceptives
- strong CYP3A4 inducers such as efavirenz or rifampin
- strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, such as clarithromycin or cyclosporine
- warfarin.