Top 7 Things to Know About Atorvastatin
Atorvastatin is a statin drug used to treat abnormal cholesterol levels and prevent cardiovascular disease in people at high risk. Statins are the first line ... read more...of defense against cardiovascular disease. It is listed as one of the Essential Medicines by the World Health Organization. It is accessible as a generic drug. And here are some things to know about Atorvastatin.
-
- It is possible to treat elevated cholesterol with atorvastatin.
- Atorvastatin acts by inhibiting the production of various lipids by the liver's HMG-CoA reductase enzyme (this is the collective term for fats and cholesterol). Additionally, atorvastatin speeds up the breakdown of lipids.
- The group of drugs known as statins includes atorvastatin. Another name for atorvastatin is HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor.
Photo: DOMESCO 
Photo: Wellona Pharma -
Benefits of Atorvastatin is the next thing to know about Atorvastatin.
- If initial dietary strategies are unsuccessful in lowering cholesterol, atorvastatin may be used to treat high cholesterol in those who are at an elevated risk of cardiovascular disease.
- In patients who are at high risk for these events, atorvastatin is also used to reduce the risk of coronary events (such as a heart attack, stroke, or angina). Those who already have coronary heart disease, diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, a history of stroke or occurrences similar to a stroke or a heart attack, or who have numerous risk factors include those with these conditions (such as older age, smoking, high blood pressure, low HDL-C, or a family history of heart disease).
- Compared to other statins, rosuvastatin may be more effective.
- There is a generic form of atorvastatin.
- In individuals with established coronary artery disease, secondary prevention of myocardial infarction, stroke, unstable angina, and revascularization is necessary.
- There is evidence from systematic reviews and meta-analyses that statins, especially atorvastatin, lessen the severity of protein excretion in urine and the loss in kidney function (eGFR), with higher doses having a bigger impact. Data on whether statins lower the risk of renal failure are contradictory. Acute renal injury is not prevented by taking statins, including atorvastatin, prior to heart surgery.

Photo: Vinmec 
Photo: Vinmec -
You are more likely to have the following side effects if you are between the ages of 18 and 60, do not take any other medications, or have any other medical conditions:
- Infections of the urinary tract, arthralgia (joint pain), diarrhea, dyspepsia, discomfort, and nasopharyngitis (swelling of the nasal passages and back of the neck).
- Pain, soreness, or weakening in the muscles. First, more research is required to rule out more severe muscular damage (such as rhabdomyolysis - the destruction of muscle cells). People over the age of 65, those using specific drugs (such as cyclosporine, itraconazole, and HIV antivirals), those who consume more than two alcoholic beverages daily, and those who have kidney disease appear to be at higher risk of experiencing major adverse effects.
- Like other statins, atorvastatin may have an adverse effect on liver function, manifested as changes in liver function tests or jaundice (yellowing of the skin), necessitating a dosage adjustment or stopping the drug altogether.
- Could also have an impact on some diabetes markers (including HbA1c or fasting glucose), and it might not be appropriate for people with liver or kidney illness, stroke or TIA survivors, or those with liver or kidney disease (transient ischemic attack).
- Occasionally has been linked to confusion, cognitive impairment, amnesia, and memory loss. When these symptoms are stopped, they usually go away.
- May interact with a number of other drugs, including digoxin, clarithromycin, protease inhibitors, cyclosporine, gemfibrozil, oral contraceptives, and drugs metabolized by the liver enzyme CYP 3A4.
- Atorvastatin should not be taken during pregnancy, and women who are taking it shouldn't breastfeed. If taken while pregnant, atorvastatin may impede the fetus's ability to synthesize cell membranes and hormones.
- There is proof that people who take atorvastatin in higher doses and for a longer period of time may be more susceptible to adverse effects such myopathy and myalgia. When statins are taken long-term with other concurrent medications, there is also a potential increased risk of statin-induced rhabdomyolysis. As previously said, if this happens, atorvastatin should be stopped very away.
Photo: MyMed.com 
Myopathy (Photo: Premier Neurology & Wellness Center) -
Next up in the list of things to know about Atorvastatin is tips for using this drug.
- One dose every day. Can be taken at any time of day, whether morning or night, although it's recommended to stick to the same schedule each time.
- The dosage of atorvastatin must be customized for each patient, although it should initially range from 10 to 20 mg per day and be determined by the outcomes of cholesterol tests performed two to four weeks later. Follow your doctor's prescription for atorvastatin precisely. Do not alter the dosage without consulting your doctor first.
- While taking atorvastatin, avoid consuming significant amounts of grapefruit juice or grapefruit or grapefruit-related goods.
- Avoid exceeding two glasses of alcohol per day when taking atorvastatin, and keep your consumption to a minimum.
- If you experience any sudden, severe muscle pain or another condition that could increase your risk of kidney failure or serious muscle damage, such as a severe infection, recent major surgery, trauma, unexplained seizures, or serious electrolyte or metabolic disorders, seek immediate medical attention and think about temporarily stopping taking atorvastatin.
- While using atorvastatin, follow the TLC diet created by the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) or a comparable diet.
- Plan to exercise frequently and, if you smoke, give it up. Try to stay away from passive smoking.
- If you have any skin discoloration, shortness of breath, an unexplained cough, or general fatigue, call your doctor right once.
- Both nursing and taking atorvastatin during these times are not recommended. If you are a woman of reproductive age taking atorvastatin, make sure you use reliable contraception, and if you plan to get pregnant, talk to your doctor before you do.
Photo: Healthline 
Photo: GoodRx -
Intestinal CYP3A4 inhibitors are well-known to exist in grapefruit juice components. Cmax and area under the curve may rise when grapefruit juice and atorvastatin are combined (AUC). This discovery first raised questions about potential toxicity, and in 2000 it was advised that atorvastatin users avoid consuming grapefruit juice "in an unsupervised manner." Research on the effects of grapefruit juice consumption on primarily lower doses of atorvastatin have shown that grapefruit juice increases blood levels of atorvastatin, which could increase the risk of adverse effects. These studies primarily involved young people.
Fibrates are a class of medications that can be used alone or in conjunction with statins to treat severe or resistant mixed hyperlipidemia. A higher risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis can result from using atorvastatin at the same time as medications in the fibrate medicine class (such as gemfibrozil and fenofibrate).
Typical drugs with which Atorvastatin may interact are:
- amiodarone
- antibiotics, such as erythromycin
- antidepressants, such as nefazodone
- antifungals, such as itraconazole, ketoconazole, posaconazole, or voriconazole
- bezafibrate
- calcium channel blockers such as amlodipine, diltiazem, or verapamil
- colchicine
- cyclosporine
- digoxin
- HIV medications such as tipranavir, ritonavir or pibrentasvir
- niacin
- oral contraceptives
- strong CYP3A4 inducers such as efavirenz or rifampin
- strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, such as clarithromycin or cyclosporine
- warfarin.
Photo: Vinmec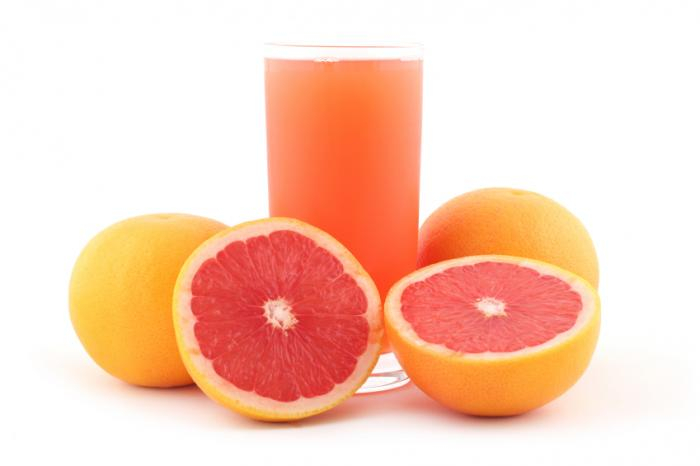 
Photo: Medical News Today -
Response and effectiveness is not be missed when talking about things to know about Atorvastatin.
- Within one to two hours of administration, atorvastatin reaches its peak levels; however, it may take one to two weeks of consistent dose before changes in your cholesterol levels are noticed and up to four weeks before atorvastatin's maximum cholesterol-lowering benefits are noticeable.
- May reduce triglycerides by 30-56% and total cholesterol by 30-46%, with varying increases in HDL.
- More efficient than other statins, perhaps.

Photo: Science Times 
Photo: Alodokter -
When compared to other prescription pharmaceuticals that might cause addiction, such as opiate painkillers, benzodiazepines, and prescription stimulants, atorvastatin and other statin medications do not induce feelings of euphoria or relaxation. But the medication can be abused by taking higher amounts than recommended, obtaining it without a prescription, or stealing it from a friend's or family member's medicine cabinet.
Atorvastatin overdose is a possibility. The following are symptoms of this drug overdose:
- Trouble breathing due to allergic reaction
- Passing out
- Jaundice, indicating liver damage
- Dark urine and muscle pain, indicating rhabdomyolysis and kidney damage
- Seizures
Photo: Everyday Health 
Photo: Freepik