Jung Typology Test
The Jung Typology Test, or the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI), is a widely recognized psychological assessment tool for categorizing an individual's personality traits and preferences. Rooted in the theories of Carl Gustav Jung, this assessment was developed by Katharine Cook Briggs and her daughter Isabel Briggs Myers.
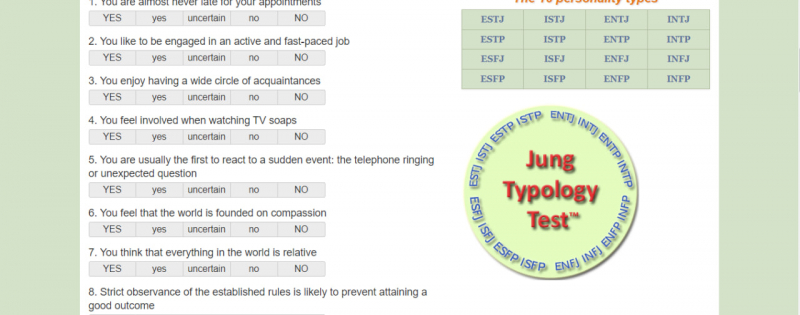
Its primary purpose is identifying an individual's psychological preferences in perceiving the world and making decisions. Participants will respond to over 60 statements on a five-point scale from yes to no. The test classifies people into one of 16 personality types, determined by their position on four dichotomies: Extraversion/Introversion, Sensing/Intuition, Thinking/Feeling, and Judging/Perceiving.
Extraversion versus Introversion examines how individuals gain energy, Sensing versus Intuition assesses information-gathering preferences, Thinking versus Feeling examines decision-making processes, and Judging versus Perceiving reflects how individuals approach the external world. The resulting 16 personality types are represented by a four-letter code: INTJ and ESFP, each associated with specific traits and tendencies.
The Jung Typology Test finds applications in personal development, career counseling, team dynamics, and relationship counseling. It aids individuals in gaining self-awareness, understanding their communication styles, and navigating interpersonal relationships.
Official website: https://www.humanmetrics.com/personality