Mendel's law of inheritance was developed from his findings
The process by which a kid inherits genetic information from a parent is known as inheritance. The fact that the kids resemble their parents is due to inheritance, which underlies the entire process of heredity. Simply put, this indicates that individuals of the same family share traits as a result of inheritance.
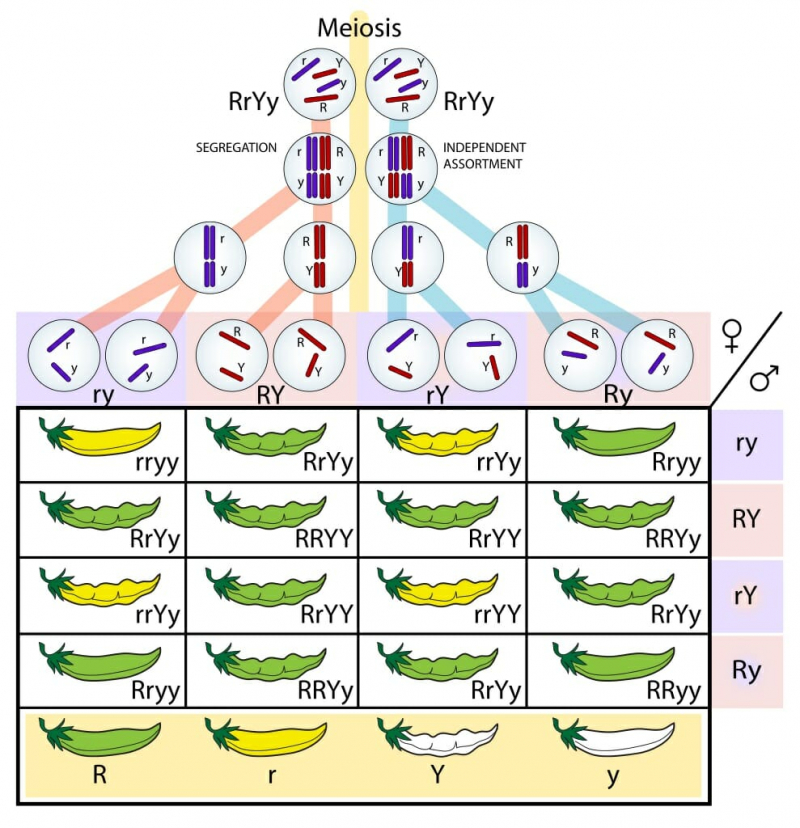
Gregor Mendel uncovered the basic principles of inheritance through his study of pea plants. He concluded that genes are inherited from each parent as separate, paired units. Mendel observed how parental genes separated and if they showed up as dominant or recessive qualities in the children. He was aware of the mathematical patterns passed down from one generation to the following. Typically, Mendel's Laws of Heredity are phrased as follows:
- The Law of Segregation: A gene pair determines each inherited trait. So that each sex cell only contains one of a pair of parental genes, parental genes are arbitrarily distributed to the sex cells. Thus, when sex cells combine to form offspring during fertilization, they receive one genetic allele from each parent.
- The Law of Independent Assortment: Different qualities' genes are grouped independently of one another so that inheriting one trait does not affect inheriting another.
- The Law of Dominance states that an organism with two possible gene variants will express the dominant form.