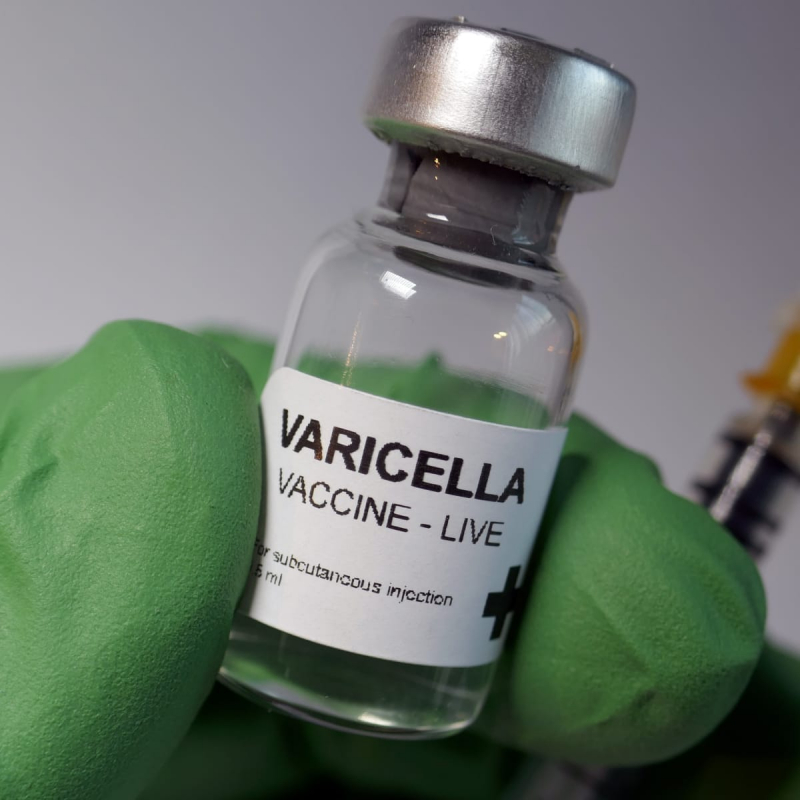
Varicella zoster virus (VZV) vaccine
Many women of childbearing age have experienced chickenpox (varicella) or got the varicella vaccination as a child. Because chickenpox can affect a pregnant woman and her fetus, testing your immunity to chickenpox before conceiving is a smart idea. If you aren't immune, now is a good time to be vaccinated. The VZV vaccination, like the MMR booster, is a live-attenuated virus vaccine. Due to the theoretical risk of prenatal exposure, a woman should receive this vaccine at least four weeks before attempting to conceive.
Chickenpox is contagious and can cause itching skin, a rash, and fever. If you acquire chickenpox while pregnant, it can result in birth abnormalities. Birth defects are medical abnormalities that occur at birth. They alter the shape or function of one or more body parts. Birth defects can affect overall health, how the body develops, and how the body functions. Tell your provider if you're thinking about getting pregnant and haven't had chickenpox or been vaccinated against it. This immunization is not safe to receive while pregnant. If you require it, obtain it before you become pregnant. Wait one month after receiving this immunization before attempting to become pregnant.