Top 8 Health Benefits of Fasting
Intermittent fasting is an eating pattern in which you alternate between eating and fasting intervals. There are many different types of intermittent fasting, ... read more...such as the 16/8 and 5:2 methods. Numerous studies have shown that it can have significant health and cognitive benefits. Here are some health benefits of intermittent fasting that have been scientifically proven.
-
Fasting has been shown in several studies to improve blood sugar control, which might be especially beneficial for those at risk of diabetes. In fact, a study of ten people with type 2 diabetes found that short-term intermittent fasting reduced blood sugar levels considerably.
In the meanwhile, another study found that intermittent fasting and alternate-day fasting were just as efficient at lowering insulin resistance as calorie restriction. Insulin resistance can be reduced by increasing your body's sensitivity to insulin, allowing glucose to be transported more efficiently from your bloodstream to your cells. This, combined with the potential blood sugar-lowering benefits of fasting, might help keep your blood sugar steady, preventing blood sugar spikes and crashes. However, keep in mind that fasting may affect blood sugar levels differently in men and women, according to some research. For example, one three-week research found that alternate-day fasting worsened women's blood sugar control while having no effect on men.
Promotes blood sugar control by reducing insulin resistance 
Promotes blood sugar control by reducing insulin resistance -
While acute inflammation is a natural immune response that helps in the fight against infection, chronic inflammation can have serious health consequences. Inflammation has been linked to the development of chronic diseases like heart disease, cancer, and rheumatoid arthritis, according to research.
Fasting has been shown in some studies to help reduce inflammation and promote improved health. Intermittent fasting for one month reduced levels of inflammatory markers in 50 healthy people, according to one research. When they fasted for 12 hours a day for a month, the same effect was discovered in another small study. Furthermore, one animal research discovered that consuming a very low-calorie diet to mimic the effects of fasting reduced inflammation and was helpful in the treatment of multiple sclerosis, a chronic inflammatory disease.

Promotes better health by fighting inflammation 
Promotes better health by fighting inflammation -
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the world, accounting for around 31.5% of all deaths. One of the most effective methods to lower your risk of heart disease is to change your diet and lifestyle.
According to some studies, including fasting in your daily routine may be beneficial to your heart health. One small research found that fasting on alternate days for eight weeks lowered "bad" LDL cholesterol and blood triglycerides by 25% and 32%, respectively. Another research of 110 obese people found that fasting for three weeks under medical supervision reduced blood pressure, blood triglycerides, total cholesterol, and "bad" LDL cholesterol levels considerably. In addition, one research of 4,629 adults found that fasting was linked to a decreased risk of coronary artery disease and diabetes, which is a major risk factor for heart disease.

May enhance heart health by improving blood pressure, triglycerides and cholesterol levels 
May enhance heart health by improving blood pressure, triglycerides and cholesterol levels -
Some studies have found that fasting may have a powerful effect on brain function, even though most research is limited to animal studies. Intermittent fasting for 11 months increased both brain function and structure in mice, according to one research.
Other animal research has found that fasting can help enhance cognitive function by protecting brain health and increasing nerve cell production. Fasting may benefit in the prevention of neurodegenerative disorders since it can help reduce inflammation. Fasting may protect against and enhance outcomes for conditions including Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, according to animal research. However, more studies are needed to evaluate the effects of fasting on brain function in humans

May boost brain function and prevent neurodegenerative disorders 
May Boost Brain Function and prevent neurodegenerative disorders -
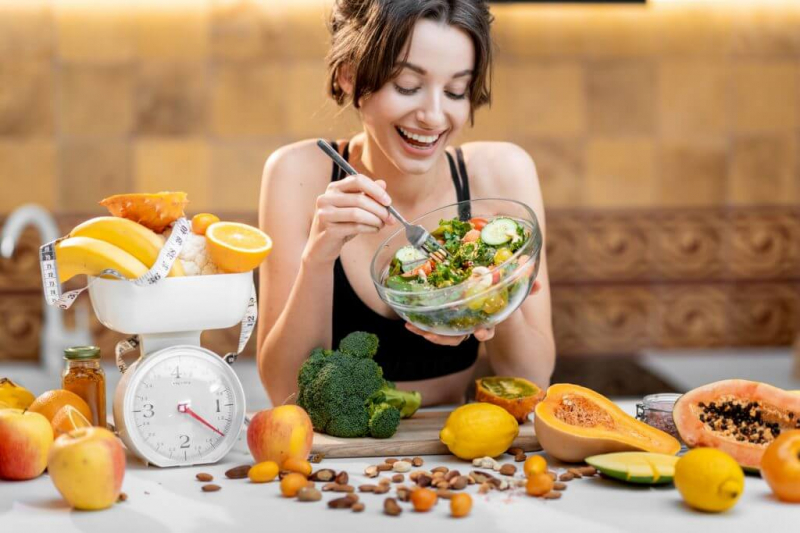
Many dieters pick up fasting as a way to lose weight quickly and easily. Abstaining from all or certain foods and beverages should theoretically reduce your overall calorie consumption, resulting in greater weight loss over time.
Short-term fasting has also been shown to boost metabolism by increasing levels of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine, which may help with weight loss. Over the course of 12–24 weeks, one study found that whole-day fasting might reduce body weight by up to 9% and considerably reduce body fat. Another study found that intermittent fasting for 3–12 weeks was as successful as continuous calorie restriction in terms of weight reduction, with body weight and fat mass dropping by up to 8% and 16%, respectively. Fasting was also found to be more effective than calorie restriction in increasing fat reduction while preserving muscle tissue undamaged.

Aids weight loss by limiting calorie intake and boosting metabolism 
Aids weight loss by limiting calorie intake and boosting metabolism -
Human growth hormone (HGH) is a protein hormone that affects a number of body processes. According to studies, this important hormone is involved in growth, metabolism, weight loss, and muscular strength.
Fasting has been shown in several studies to increase HGH levels naturally. Fasting for 24 hours significantly increased HGH levels in 11 healthy people, according to one research. Another small research of 9 men found that fasting for two days increased HGH production by five times. Fasting may also help maintain consistent blood sugar and insulin levels throughout the day, which may help to optimize HGH levels since some research shows that maintaining high insulin levels can lower HGH levels.

Increases growth hormone secretion, which is vital for growth, metabolism, weight loss and muscle strength 
Increases growth hormone secretion, which is vital for growth, metabolism, weight loss and muscle strength -
A great way to increase your lifespan, promote better health, and assist in weight loss is to reduce your calorie or protein intake. Researchers discovered that restricting calories increased energy production and reduced the risk of chronic diseases including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Besides, intermittent fasting also causes a number of physiological changes that help to slow down the aging process by keeping cells and DNA healthy.
Several animal studies have found positive outcomes when it comes to fasting's possible longevity-extending benefits. In one study, rats who fasted every other day had a slower rate of aging and lived 83% longer than rats who did not fast. Other animal studies have come to the same conclusion, claiming that fasting can improve lifespan and survival rates. However, current research is still restricted to animal studies. More research is necessary to confirm how fasting affects the human lifespan and aging.

Could delay aging and extend longevity 
Could delay aging and extend longevity -
Fasting may help in the treatment and prevention of cancer, according to animal and test-tube research. In fact, one rat research discovered that fasting on alternate days helped to prevent tumor growth.
A small study suggests that a certain type of intermittent fasting is safe and effective for people who have been diagnosed with cancer and that it may help cancer treatments like chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and hormonal therapy work better. A test-tube study found that exposing cancer cells to several cycles of fasting was as effective as chemotherapy at slowing tumor growth and increasing the impact of chemotherapy drugs on cancer formation. Unfortunately, the majority of study focuses on the effects of fasting on the growth of cancer in animals and cells. Despite these promising findings, further research is needed to see how fasting affects cancer growth and treatment in humans.

May aid in cancer prevention and increase the effectiveness of chemotherapy 
May aid in cancer prevention and increase the effectiveness of chemotherapy





























