Top 10 Possible Heart Symptoms You Shouldn't Ignore
Cardiovascular disease is likened to a "silent killer", which can take a patient's life if it is not detected early and intervened in time. Therefore, being ... read more...equipped with knowledge about cardiovascular symptoms is a prerequisite to helping you and your family avoid danger. Cardiovascular disease is seen as a serious threat that has a direct impact on quality of life. Not all heart problems have clear symptoms. Some heart clinical signs may not appear in the chest and aren't always easily recognizable. If you are at high risk of heart disease, you must pay attention to all of the indicators that are not normal for your heart that is included in the article below.
-
The most typical symptom of heart disease is chest pain, which can appear as pressure, tightness, or agony. The patient feels pressure above the navel in the left chest. It may show up as chest stiffness that spreads to the chin, shoulder, or back. These pain expressions are frequently cyclical, arise during periods of exertion or stress, and go away during rest. Chest pain attacks can last between five and ten minutes and are frequently recurrent.
Everybody experiences chest discomfort differently. It's probably not a heart attack if the pain is only momentary or the area feels more when you touch or press on it. Also keep in mind that you might experience heart issues, including a heart problem, without experiencing chest pain. In particular, that happens a lot to women. It is advised that people who have persistent chest pain should relax and see a medical institution immediately for a prompt diagnosis and treatment because this might possibly be an indication of hazardous heart disease.
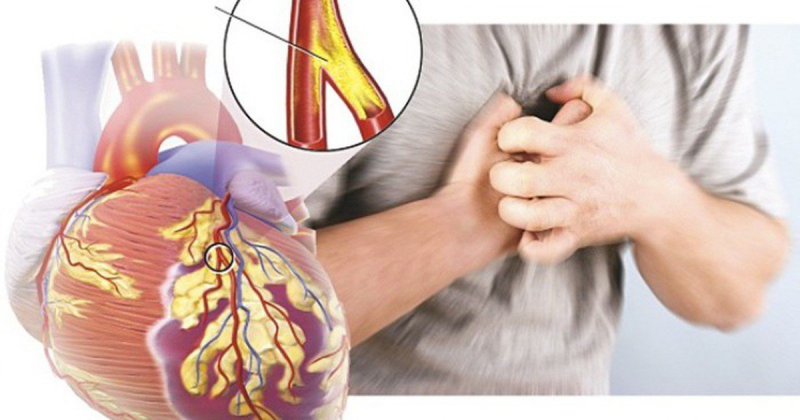
Chest pain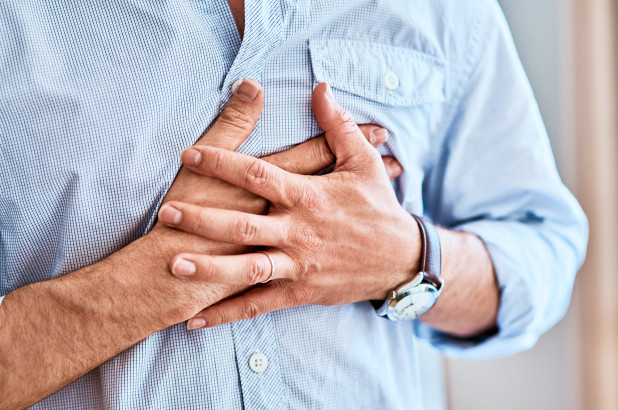 
Chest pain -
Blood stasis in the liver and digestive organs causes patients to frequently feel bloated and full of the stomach. The patient has nausea and loss of appetite as a result of this disease, which also affects the liver and digestive system. These signs and symptoms can occur in some persons who have heart-related diseases. It even makes them vomit. Women experience this symptom more often than men do. Of course, there are a variety of causes of nausea that are unrelated to the heart. You may have eaten anything that was the cause of those symptoms. You must nevertheless be mindful that these symptoms might possibly be signs of heart disease.
In general, the majority of persons with cardiovascular disease do not typically experience nausea. In actuality, the signs and symptoms of cardiovascular disease can be subtle and function as early warning signs of more serious cardiac issues. As a result, patients may find it challenging to identify whether they are experiencing cardiac issues or not, which might delay the start of therapy. Additionally, the condition may occasionally cause certain unusually linked symptoms.
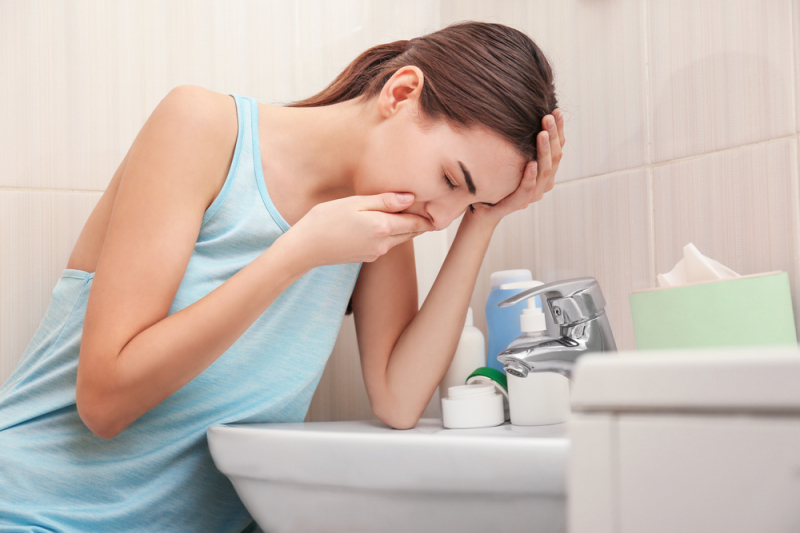

Nausea 
Nausea -
Fainting is an instantaneous loss of consciousness that is quickly followed by a full recovery on its own. Generally speaking, this lasts anything from a few seconds to a few minutes. This results from a momentary reduction in blood flow to the brain. Fainting occurs due to very common cardiovascular diseases due to sudden decrease in cardiac output causing cerebral ischemia, or due to cardiac diseases: aortic valve stenosis, left atrial mucinous tumor, cardiomyopathy hypertrophy,...
Anyone, regardless of age or health status, has the potential to faint. Although fainting is often not a matter of alarm, it can occasionally be a symptom of a serious disease. To determine the reason for your frequent fainting episodes, talk to your doctor. A physical examination, a review of your medical history, and questions regarding the symptoms you had before fainting will be used by your doctor to diagnose you. By evaluating the quantity of blood and the speed at which it moves through various body parts, tests will look for cardiac abnormalities.
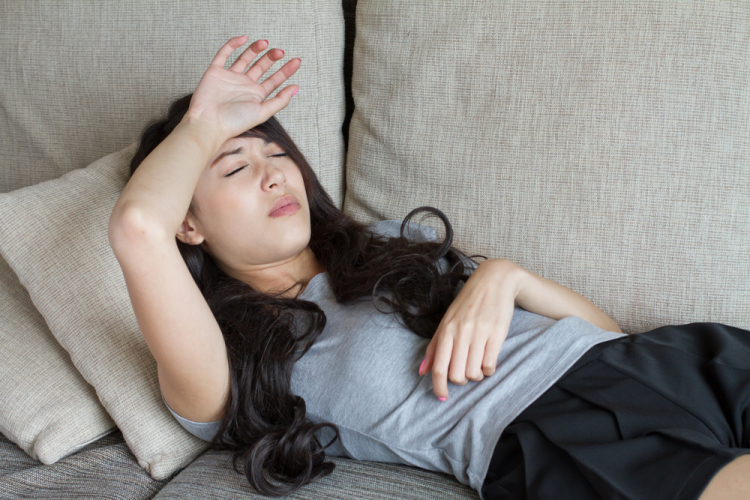

Dizziness and fainting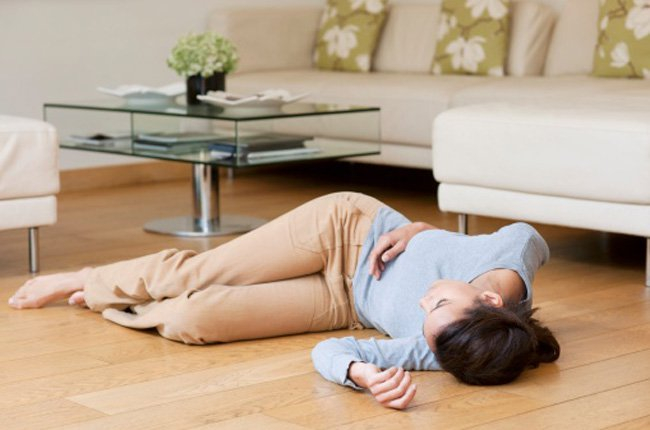 
Dizziness and fainting -
The average heart rate of any individual might vary depending on factors including age, gender, and physical condition. The normal heart rate of an adult ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute while they are at rest and not moving over. Fast heart rate is the term for a condition when the heart rate is more than 100 beats per minute. Heart palpitations frequently result in a worrying sensation and a racing heart. Fast heart rate is typically alarming, although it can sometimes be unimportant. In fewer cases, a fast heart rate may be a sign of a serious cardiac disease requiring specialized cardiology care.
There is often no need to consult a professional because this experience will typically be rare and brief, even if it lasts only a few seconds. You should consult a professional if you have a history of heart disease, this fast heart rate happens regularly, or it is growing worse. Your doctor may conduct imaging or laboratory experiments to assess what is causing this behavior.
Fast heart rate 
Fast heart rate -
People with cardiovascular disease often feel tired and exhausted many times a day, even when they just wake up. This is because the heart is not working efficiently, so it cannot supply enough oxygen to the body, making you tired and sluggish. Fatigue can be viewed as the inability to continue to function at the level of a normal healthy person. One of the cardiovascular causes of this phenomenon is heart failure.
In addition, patients may also experience sleep disturbances and always feel sleepy during the day. This condition is often caused by difficulty sleeping, insomnia, or sleep apnea at night. Frequent feelings of fatigue or sleepiness are not typically associated with cardiovascular disease and may be present in many other conditions. So, if you have these symptoms, contact your doctor to get tested and determine the specific cause.

Tired and sleepy during the day 
Tired and sleepy during the day -
Sweating is a typical physiological occurrence that controls body temperature, particularly after strenuous exercise or labor-intensive tasks. When it's heated outside, the body frequently perspires to lower heat, cool down, and get rid of some extra pollutants. However, even if many people feel cold, their bodies continue to perspire; this is not a typical bodily reaction.
People with heart disease often sweat because the blood is pumped through blocked arteries, causing the heart to spend more energy ejecting blood. In order to reduce body temperature when exerting oneself, the body will sweat more, resulting in a cold sweat from the sufferer. It may be a sign of heart disease if you constantly perspire for no apparent cause, particularly if you also have other symptoms including dizziness, nausea, and shortness of breath. It is necessary to find out the cause to be able to eliminate this disease effectively. It is necessary to find out the cause to be able to eliminate this disease effectively.


Sweating -
A persistent cough typically results from a respiratory condition rather than a cardiovascular problem. However, if you have a history of cardiovascular disease, you should pay close attention to this symptom, particularly if the cough is persistent, frequently happens at night or while you're sleeping, or if it lasts longer than a week. An ongoing cough that won't go away might be brought on by hazardous cardiac conditions or by external stressors.
Cough is a physiological response of the body to a pathological stimulus. Coughing is beneficial because it helps eliminate foreign objects and fluids that obstruct the airways. However, when a persistent cough does not go away for a long time, it can cause damage to the respiratory tract leading to coughing up blood. Heart failure is the primary cause of cardiovascular illnesses that result in a cough. Blood pools in the lungs as a result of decreased cardiac output, or the amount of blood being delivered to the body. The patient experiences a painful and protracted cough that gets worse when they lie down as a result of the blood and fluid in the blood vessels leaking out and into the alveoli.

Persistent cough 
Persistent cough -
Particularly in cases of heart problems, swelling in the lower limbs is a classic indication that the heart is not pumping blood effectively. Heart-related illnesses cause the heart muscle to lose its ability to contract and evacuate blood to other organs while simultaneously reducing the muscle's capacity to draw blood back to the heart. Blood in the peripheral venous system will be sluggish during this time, allowing fluid to leak into neighboring tissues and create edema, especially in the lower extremities.
Additionally, because there is less blood flowing to the kidneys, less urine is being filtered out, which results in water retention and worsening of the edema. Edema frequently affects the lower extremities, such as the feet, ankles, and legs, but it can occasionally affect other organs as well. However, edema can happen together with cardiac disease and may be brought on by renal illness, liver failure, a high salt diet, hypovolemia, or a drug side effect.
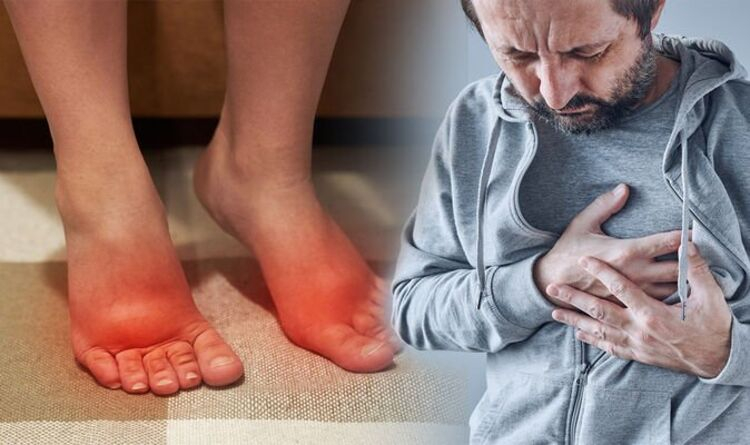
Edema phenomenon 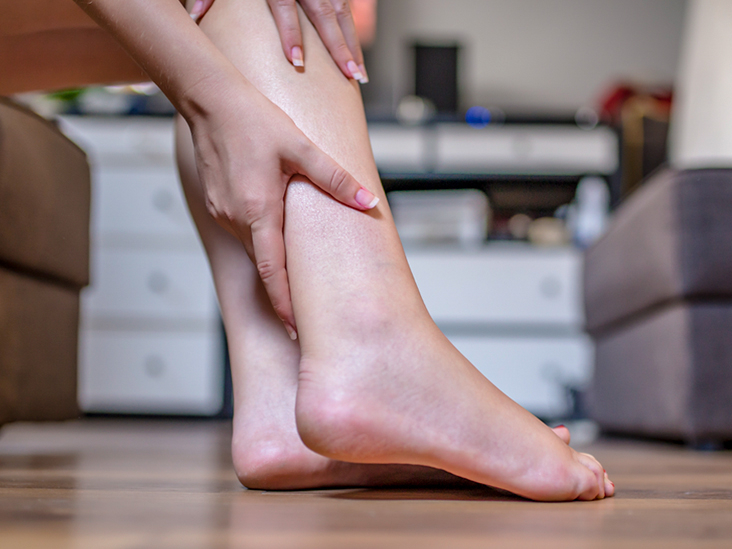
Edema phenomenon -
Shortness of breath is often a typical symptom of heart or lung disease. Heart disease and coronary artery disease are two cardiovascular diseases that often cause shortness of breath. In the human body, the heart and lungs are closely related. For instance, breathing difficulties are frequently brought on by fluid buildup in the right heart or lungs. To offset the strain, the heart must beat more quickly. In order to ensure that the blood traveling to the lungs receives adequate oxygen before returning to the heart to be pumped around the body, the lungs must work harder when the heart beats more quickly than usual.
Shortness of breath is a common symptom of heart failure patients and it usually worsens after exercise or during severe activity. Patients with heart failure often have more difficulty breathing when lying down and must sit up to breathe. Due to a rapid decline in the heart's capacity to contract, which interferes with the process of pumping blood from the heart to the lungs and makes breathing difficult, this shortness of breath usually happens at night while you are asleep.

Shortness of breath 
Shortness of breath -
Radiating pain down the left side of the body is another common sign of heart disease. Many patients wrongly believe they have bone and joint problems when they experience discomfort in the shoulder and left hand. However, pain is a common indication of heart disease. Particularly, the discomfort typically starts in the chest and moves to the arms, back, neck, and shoulder blades. Due to this, many people are often oblivious and delay seeking medical attention until the patient's symptoms are severe enough to significantly impact their quality of life.
Sometimes you will experience left arm pain that worsens with exercise and goes away with rest so this might be a symptom of heart disease. An unstable cardiac condition may also be to blame for left arm discomfort that strikes out of nowhere while doing nothing, such as watching television. Last but not least, contact the doctor immediately soon if your left arm pain is accompanied by symptoms like chest pain, nausea, vomiting, disorientation, unconsciousness, shortness of breath, unusual sweating, stomach bloating, coughing, or wheezing.

Pain spreading to left arm 
Pain spreading to left arm































