Top 9 Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 is a vitamin that your body need for activities such as DNA synthesis, energy production, and the proper functioning of your central nervous ... read more...system. Even though the vitamin may be found in a variety of foods, B12 deficiency and insufficiency are rather common. Limited food intake, malabsorption, certain medical conditions, or the use of B12-depleting medications are all common causes. Below are some of the Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency!
-
Everybody gets fatigued from time to time. Getting enough sleep, eating a healthy diet, and exercising frequently, on the other hand, will help most people feel more energized. Constant fatigue and weakness, even after resting, may indicate an underlying health problem or imbalance. Fatigue is one of the signs and symptoms of a B12 deficiency.
You'll probably feel fatigued if your B12 levels are low or deficient. B12 is required for the normal functioning of your body's cells. As a result, low B12 levels can reduce normal red blood cell production, limiting oxygen delivery. Megaloblastic anemia can be caused by a B12 or folate deficiency. Large, abnormal, and immature red blood cells occur as a result of this condition, as does impaired DNA synthesis. You'll feel weak and exhausted if your body doesn't have enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen to your tissues. Even if your B12 levels are regarded within range or only borderline low, you might experience fatigue and other symptoms associated with B12 deficiency.

Fatigue 
Fatigue -
Vitamin B12 deficiency might show up as pale skin or skin with a little yellow tinge. Vitamin B12 is required for the formation of red blood cells and the maintenance of a healthy nervous system.
Anemia caused by a lack of matured, healthy red blood cells in the body, similar to iron deficiency anemia, can cause your skin to become pale. Jaundice is a disorder in which your skin and the whites of your eyes get a yellowish color due to a B12 deficiency. High amounts of bilirubin, a waste product produced when your body breaks down red blood cells, cause the color. Besides, vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to pigmentation problems and patchy skin, as a result of not eating enough veggies and fresh fruits, your skin may seem dull and dark.

Pale or yellow skin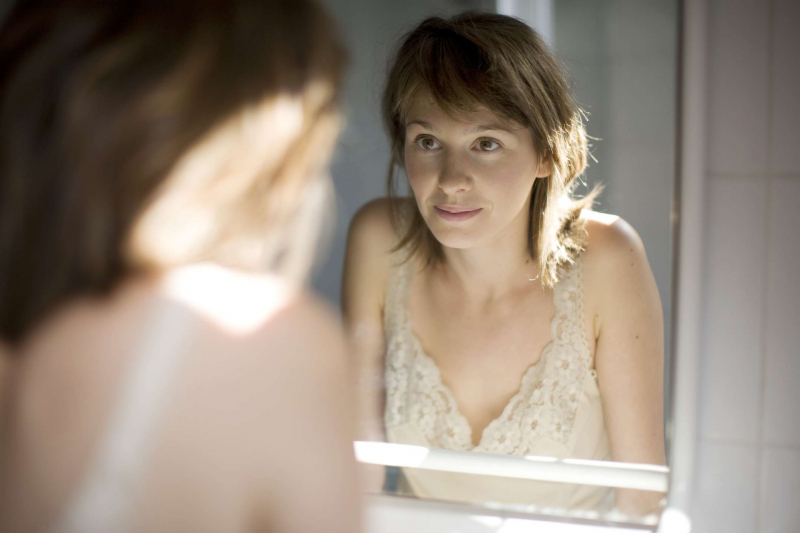 
Pale or yellow skin -
B12 deficiency and insufficiency can cause neurological symptoms such as headaches. Headaches are one of the most common symptoms of B12 deficiency in both adults and children.
According to some research, those who suffer from certain types of headaches often are more likely to have low B12 levels. In a 2019 study of 140 people, half of whom had migraines, researchers discovered that blood levels of B12 were considerably lower in migraine patients than in non-migraine patients. In addition, those with the greatest B12 levels were 80% less likely to suffer from migraines than those with the lowest B12 levels, according to the study. Therefore, treatment with B12 may relieve migraine headache symptoms in some people.

Headaches 
Headaches -
Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause hematological problems, as well as neurological and psychological problems, such as irritability, personality changes, depression, and memory loss. Excitotoxic reactions induced by the accumulation of homocysteine are also known to worsen depression.
B12 is necessary for the proper functioning of your central nervous system, and a lack of it can have negative consequences for your mental health. B12 deficiency, in particular, has been linked to an increased risk of depression. Low amounts of B12 can lead to an increase in homocysteine, a sulfur-containing amino acid. As a result, increased oxidative stress, DNA damage, and cell death in the body may contribute to the development of depression. In a 2020 study of 132 children and teenagers, 89 with depression and 43 without, researchers discovered that those with depression had lower B12 levels and higher homocysteine levels than those without depression.

Depressive symptoms 
Depressive symptoms -
Vitamin B-12 may have a role in other aspects of human health, such as the composition and function of the gastrointestinal (gut) microbiome, according to some studies. Vitamin B-12 is necessary for over a dozen enzymes in bacteria and is synthesized and used by bacteria in the human gut microbiome.
Diarrhea, nausea, constipation, bloating, gas, and other gastrointestinal symptoms can all be signs of a B12 deficiency. Both adults and children might be affected by these issues. However, keep in mind that many of these symptoms are non-specific and might be caused by a variety of different things. Food intolerances, medications, and infections, for example, can all cause diarrhea.
Gastrointestinal issues 
Gastrointestinal issues -
People with low or deficient B12 levels may feel foggy-headed and have trouble concentrating and completing tasks, as a deficiency in B12 has a negative impact on the central nervous system.
Because the risk of B12 deficiency grows with age, older adults are more susceptible to these adverse effects. In fact, low B12 levels have been linked to decreased mental function in older adults in some studies. Fortunately, studies demonstrate that B12 medication helps alleviate mental impairment caused by low B12 levels. For example, 202 people with mild mental impairment, low or low-normal B12 levels, and high homocysteine levels were given B12 replacement therapy for three months in a 2020 research. 84% of those reported significant improvements in symptoms such as poor attention, memory problems, and forgetfulness after the treatment.

Difficulty concentrating and mental impairment 
Difficulty concentrating and mental impairment -
If you experience mouth ulcers on a regular basis, it might be an indication of a vitamin B12 shortage. This vitamin is essential for the functioning of your nervous system, the formation of red blood cells, and the release of energy from food.
A medical term for an inflamed, red, and painful tongue is glossitis, and a B12 deficiency may be the cause. Glossitis can appear alongside stomatitis, which is characterized by sores and inflammation in the mouth, in people who have this deficiency. Glossitis and stomatitis are common in people who have B12 deficiency-related anemia, but they can also occur without anemia and be a symptom of early B12 insufficiency. Glossitis, on the other hand, can be caused by dietary deficits such as folate, riboflavin (B2), and niacin (B3).

Pain and inflammation of the mouth and tongue 
Pain and inflammation of the mouth and tongue -
A prolonged vitamin B12 deficiency can cause nerve damage, resulting in a pins-and-needles feeling in your hands or feet. Dr. Sarah Baker, an internist of CHI Memorial Chattanooga Internal Medicine Group, explains, "Vitamin B12 is essential to help neurons function. When B12 levels are too low, neurons are unable to function properly, resulting in symptoms such as numbness and tingling in the hands and feet".
This numbness or tingling is known as paresthesia, and if left untreated, it can become permanent. Many adults and kids who have B12 deficiency report experiencing paresthesia. Insufficient levels of the vitamin can cause nerve damage, which can affect your balance and ability to walk. If not addressed, this can become permanent, so let your doctor know if you have any issues.
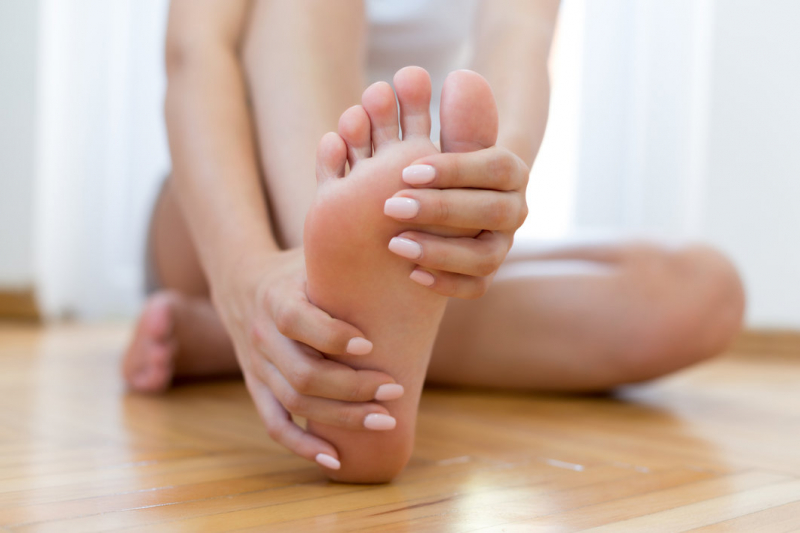

Paresthesia in hands and feet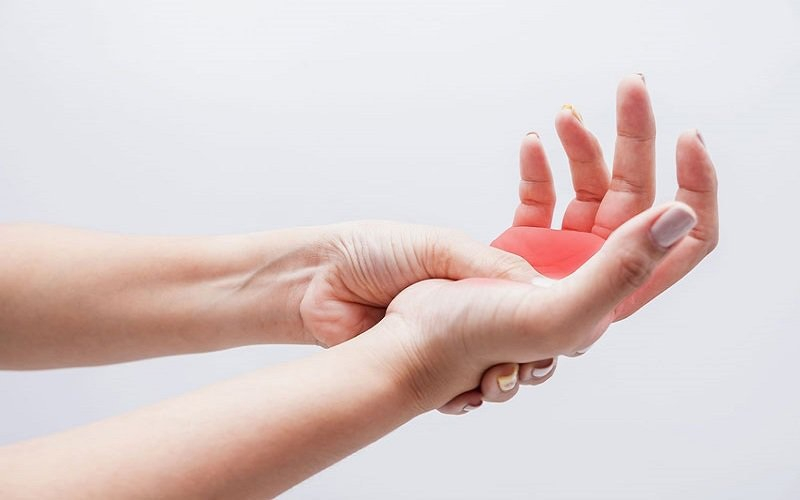 
Paresthesia in hands and feet -
B12 insufficiency can cause the following symptoms in addition to the ones listed above:
- Muscle aches and pains, as well as muscle weakness: B12 deficiency can cause muscle cramps and weakness by impairing motor and sensory neuron function.
- Coordination problems: B12 deficiency can cause ataxia, or decreased balance and coordination, which is a neurological symptom. As a result, a B12 deficiency can make walking and balance difficult.
- Erectile dysfunction: This is a condition that affects men. As a result of elevated homocysteine levels in the body, men with B12 deficiency may have erectile dysfunction.
- Vision problems: B12 deficiency can cause vision problems, possibly due to optic nerve damage.

Other signs and symptoms of B12 deficiency 
Other signs and symptoms of B12 deficiency