Top 5 Signs and Symptoms of Thrombocytopenia
Platelets are blood cells that play an important role in blood clotting. Thrombocytopenia occurs when the number of platelets in the blood is too low. This ... read more...condition is the result of a health problem or the effects of certain medications. Mild thrombocytopenia will cause few signs or symptoms. In rare cases, the platelet count can be too low to cause dangerous internal bleeding. Thrombocytopenia can affect all ages both children and adults. In the case of thrombocytopenia, if the patient is not treated in time, it can lead to cerebral hemorrhage, which can be fatal. Here are some signs and symptoms that Toplist wants to bring out to warn people more.
-
Bruises on the skin are caused by the rupture of blood vessels that carry blood between the heart, tissues, and organs of the body. Broken blood vessels due to injury or weakness cause red blood cells to escape from the vessel wall and degenerate, causing bruises. In some diseases, even a light touch can cause a large area of bruising. Unexplained bruises can be a sign of blood cancer or other blood clotting disorders.
If there are frequent bruises on the body that are not caused by an impact, it can be a warning sign of thrombocytopenia. Bruising occurs due to high blood sugar, which weakens blood vessels, skin, and nerves, causing internal capillary bleeding. Bruising in addition to the cause of thrombocytopenia has other causes, so you need to go to a medical facility and do tests to know if there is a decrease in platelets.
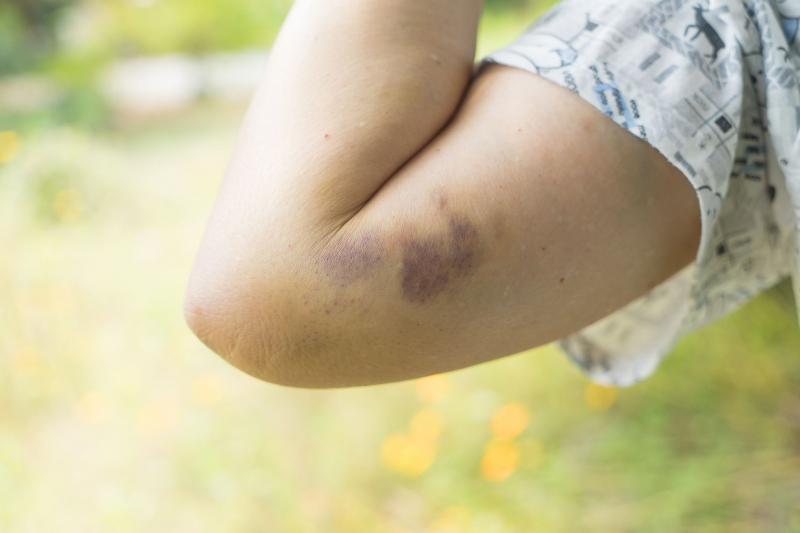
Bruise 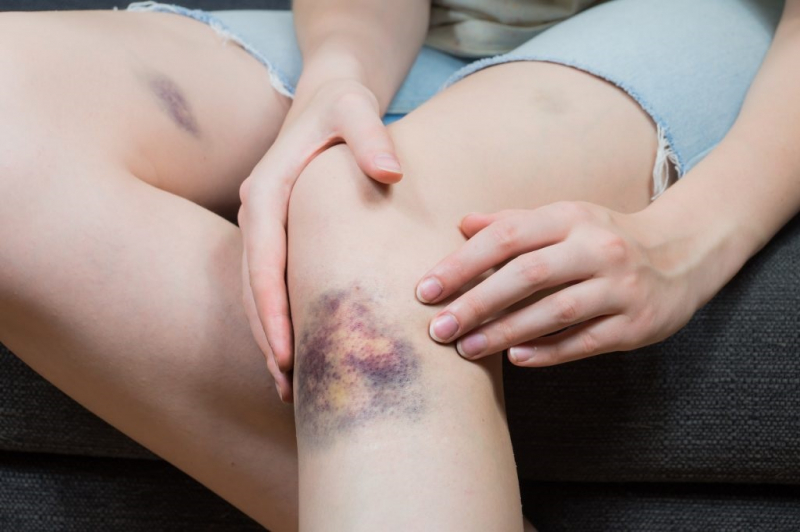
Bruise -
Nosebleeds are bleeding from one or both sides of the nose. About 60% of adults have at least one nosebleed, but only about 6% require medical intervention. Doctors warn that if nose bleeding is frequent, difficult, and takes a long time to stop bleeding on its own, especially after nosebleeds, you should not be subjective because this may be a sign of a dangerous disease.
Platelets are produced in the bone marrow and play an important role in blood clotting. When blood vessels have lesions, platelets are concentrated there, sticking together to form a platelet block that seals the wound, thereby preventing bleeding. When the number of platelets in the blood is lower than normal, platelet function continues to be maintained as normal in mild cases. However, if the blood platelet level is too low, will slow down the clotting process, and can even cause spontaneous internal bleeding, typically nosebleeds.

Nosebleeds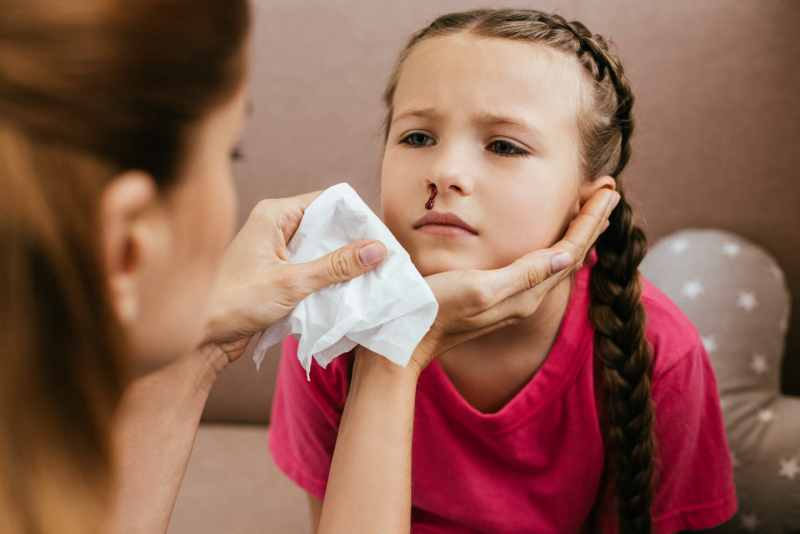 
Nosebleeds -
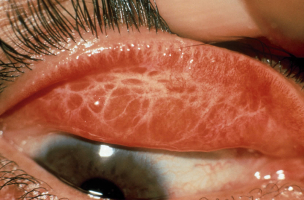
When platelets decrease, the main symptom and sign are bleeding. Bleeding is very diverse, it can be subcutaneous hemorrhage, bleeding in the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose, or mouth, or more seriously, the patient has blood in urine, blood in the stool, or vomiting blood. People with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura often have many red spots on the body called subcutaneous hemorrhage. Subcutaneous hemorrhage can be patches or dots that look like rashes.
Hemorrhage from the skin due to idiopathic thrombocytopenia can occur in both children and adults. It is a symptom of the development of the disease and it differs between men and women of different ages. In young people, the disease is more common in women. At an older age, the disease appears to be more common in men. Children can get it after an episode of some common viruses. Viruses such as chickenpox, mumps, and measles have also been found to be associated with thrombocytopenic purpura.
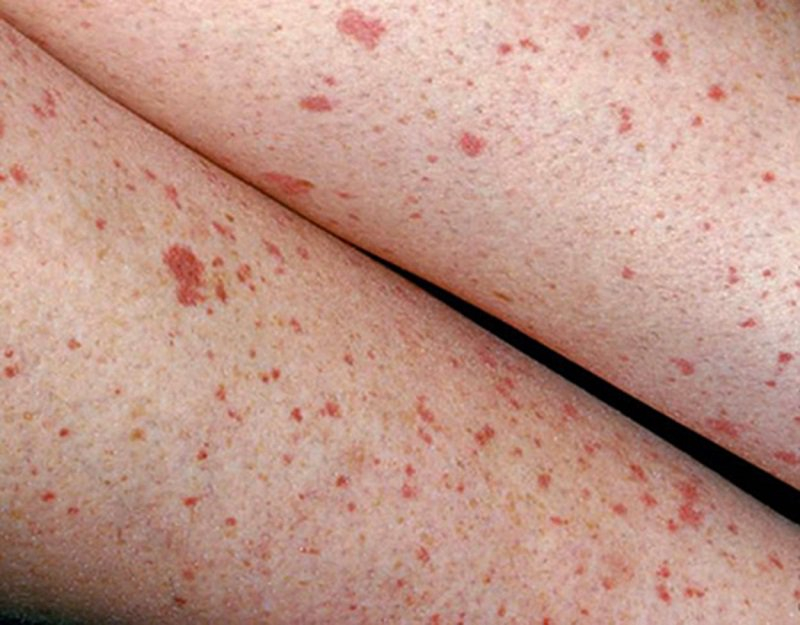
Subcutaneous hemorrhage 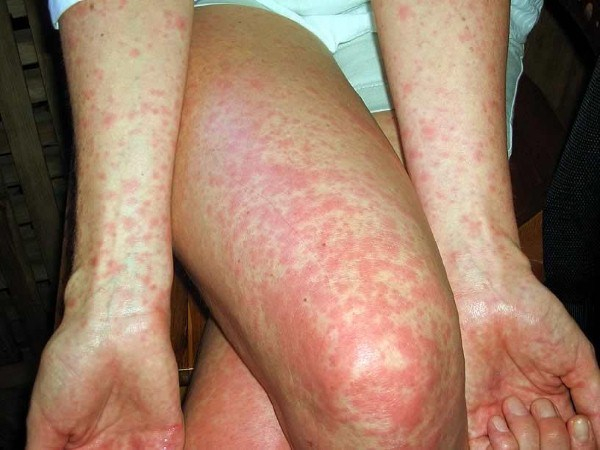
Subcutaneous hemorrhage -
When the red blood cell count is too low, you will often feel tired, especially when you have thrombocytopenia - a chronic autoimmune disease. Excessive fatigue can make it difficult to maintain your daily routine and also increases your risk of injury. Therefore, people need to maintain the number of platelets in the body at an acceptable level for the organs of the body to function properly.
Thrombocytopenia is a rather dangerous disease but not an incurable disease. However, the course of immune thrombocytopenic purpura is difficult to predict. Focusing on the signs to find out the cause and measures to reduce the risk of complications from thrombocytopenia is the best way to control the condition. Talk to your doctor to learn more about proper diagnosis, detection, and effective treatment options and lifestyle changes.

Tired 
Tired -
Normally, platelets are involved in blood clotting. When you are unfortunate enough to be injured, the platelets work to their fullest capacity so that too much blood is not lost. However, when you have immune thrombocytopenic purpura, there are not enough platelets to participate in the formation of blood clots. As a result, your wound will not stop bleeding even with a temporary bandage. In that case, you must seek emergency medical help if the bleeding cannot be stopped.
Excessive bleeding can increase the risk of anemia. Although there are many causes of anemia, in immune thrombocytopenic purpura, uncontrolled bleeding is the main cause of anemia. Blood enters the skin and deeper tissues causing hemorrhagic nodules, bruises on the surface of the skin, or hematomas… Blood loss can occur with both internal and external bleeding. In women, anemia is also associated with heavy blood loss through the menstrual cycle.
Anemia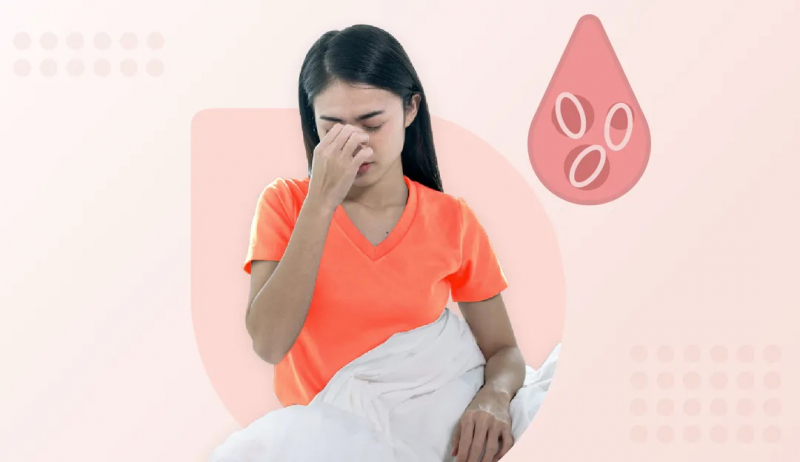 
Anemia