Top 9 Signs and Symptoms of Iodine Deficiency
Iodine is a mineral that is abundant in shellfish. It is used by your thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones, which help control growth, repair damaged ... read more...cells, and maintain a healthy metabolism. Unfortunately, up to one-third of the world's population is in danger of iodine deficiency. Iodine shortage can create unpleasant and even dangerous symptoms. They include neck swelling, pregnancy-related problems, weight gain, and learning difficulties. The most prevalent indications and symptoms of iodine insufficiency are listed here.
-
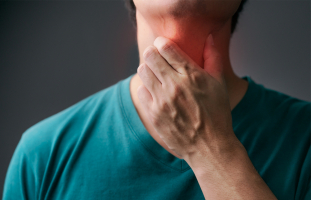
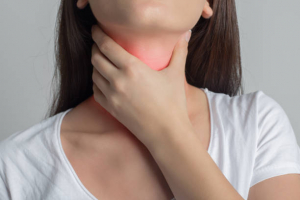
The most frequent sign of iodine deficiency is swelling in the front of the neck. A goiter develops when the thyroid gland becomes very large. The thyroid gland is a tiny butterfly-shaped gland located at the front of the neck. When it receives a signal from thyroid-stimulating hormone, it produces thyroid hormones (TSH).
When TSH levels in the blood rise, the thyroid gland utilizes iodine to produce thyroid hormones. However, if your body is deficient in iodine, it cannot produce enough of them. To compensate, the thyroid gland works harder to produce more thyroid hormone. This causes the cells to replicate and develop, eventually resulting in a goiter. Most instances, fortunately, can be cured by increasing your iodine intake. However, if a goiter goes untreated for a long time, it can cause chronic thyroid damage.
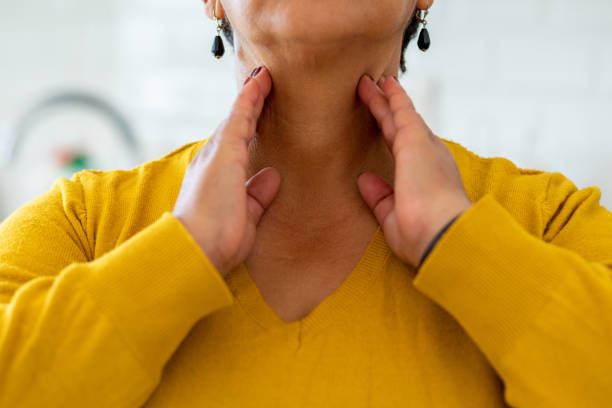
Swelling in the neck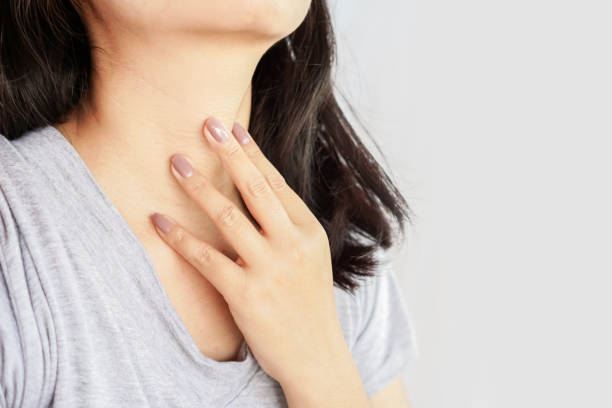 
Swelling in the neck -
Another indicator of iodine shortage is unexpected weight gain. It might happen if the body does not have enough iodine to produce thyroid hormones. This is due to the fact that thyroid hormones assist regulate the rate at which your body transforms food into energy and heat.
When you have low thyroid hormone levels, your body burns fewer calories at rest. Unfortunately, this implies that more calories from your diet are deposited as fat. Increasing your iodine intake may help counteract the consequences of a sluggish metabolism by allowing your body to produce more thyroid hormones.
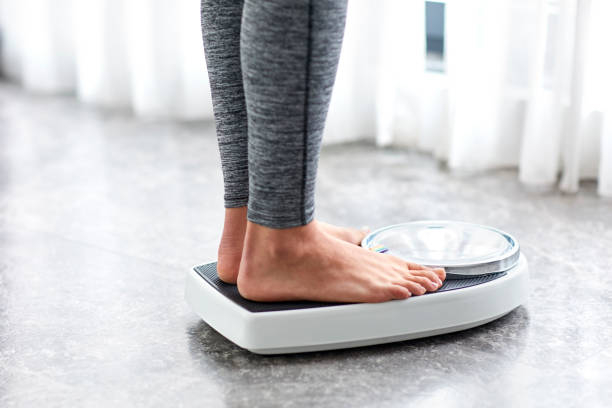

Unexpected weight gain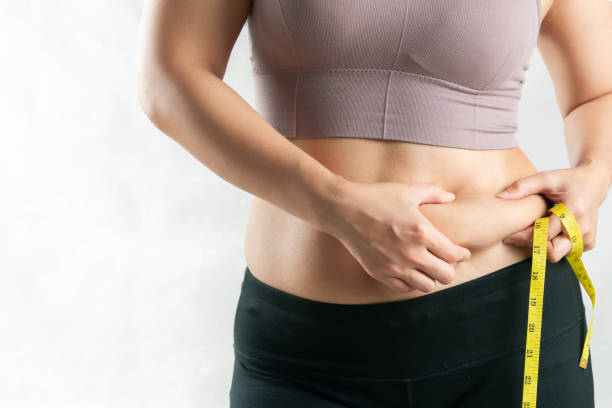 
Unexpected weight gain -
Iodine shortage is often associated with fatigue and weakness. According to some research, approximately 80% of persons who have low thyroid hormone levels due to iodine deficiency feel fatigued, sluggish, and weak. These symptoms develop because thyroid hormones assist the body in producing energy.
When thyroid hormone levels are low, the body is unable to produce as much energy as normal. This may cause your energy levels to drop and leave you feeling exhausted. In fact, according to research of 2,456 participants, weariness and weakness were the most prevalent symptoms among those with low or somewhat low thyroid hormone levels.
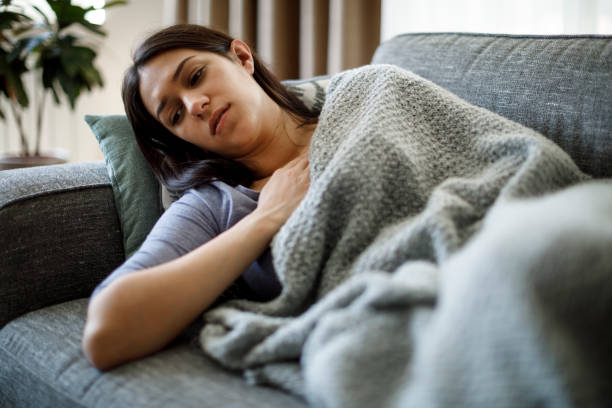

Fatigue and weakness 
Fatigue and weakness -
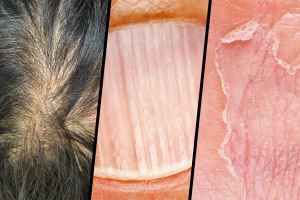
Thyroid hormones aid in the regulation of hair follicle development. Hair follicles may cease renewing if your thyroid hormone levels are insufficient. This can lead to hair loss over time. As a result, persons who are deficient in iodine may have hair loss.
According to one research of 700 adults, 30% of those with low thyroid hormone levels reported hair loss. Other studies, however, have indicated that low thyroid hormone levels only appear to promote hair loss in people who have a familial history of hair loss. If you have hair loss due to a lack of iodine, increasing your intake of this mineral may help restore your thyroid hormone levels and halt hair loss.
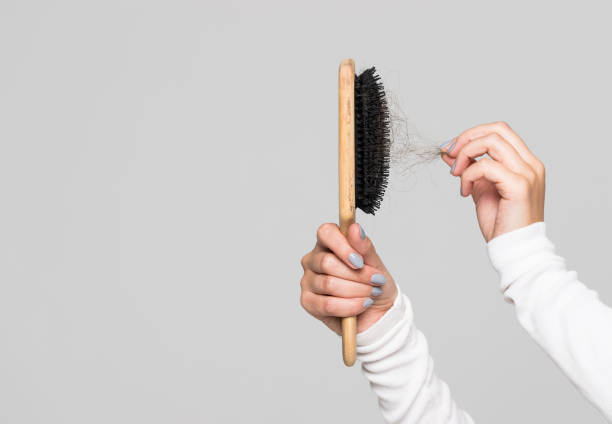

Hair loss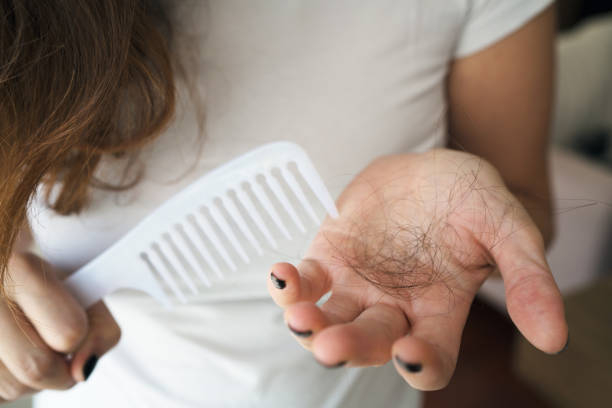 
Hair loss -
Many people who are deficient in iodine experience dry, flaking skin. According to some research, up to 77% of patients with low thyroid hormone levels may develop dry, flaky skin. Thyroid hormones, which include iodine, aid in the regeneration of skin cells. When thyroid hormone levels are low, this regeneration is less frequent, which may result in dry, flaky skin.
Thyroid hormones also assist the body in sweat regulation. People with low thyroid hormone levels, such as those suffering from iodine shortage, sweat less than those with normal thyroid hormone levels. Because perspiration keeps your skin wet and moisturized, a lack of sweat might be another reason why dry, flaky skin is a typical sign of iodine deficiency.
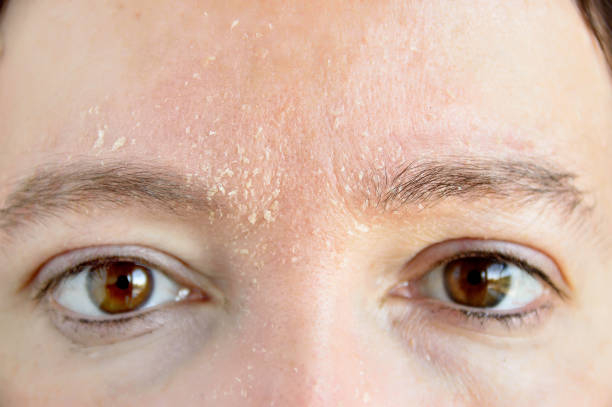
Dry, flaky skin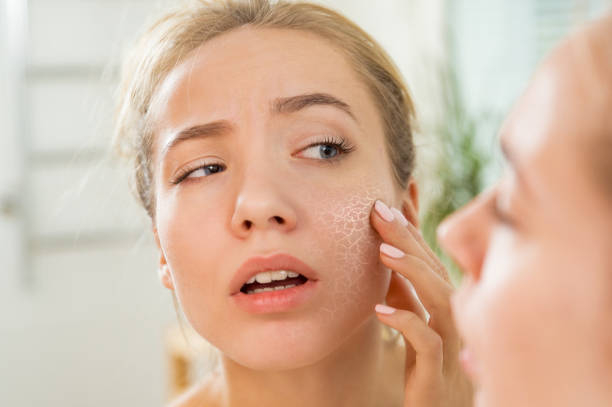 
Dry, flaky skin -
Coldness is a typical sign of iodine insufficiency. According to some research, over 80% of persons with low thyroid hormone levels may be more susceptible to cold temperatures than typical. Because iodine is required for the production of thyroid hormones, a lack of iodine might result in a drop in thyroid hormone levels.
Because thyroid hormones regulate the rate of your metabolism, low thyroid hormone levels can cause it to slow down. A slower metabolism produces less heat, making you feel cooler than normal. Thyroid hormones also assist to increase the activity of brown fat, a kind of fat that specializes in producing heat. This suggests that low thyroid hormone levels, which may be caused by iodine shortage, may inhibit brown fat from performing its function.
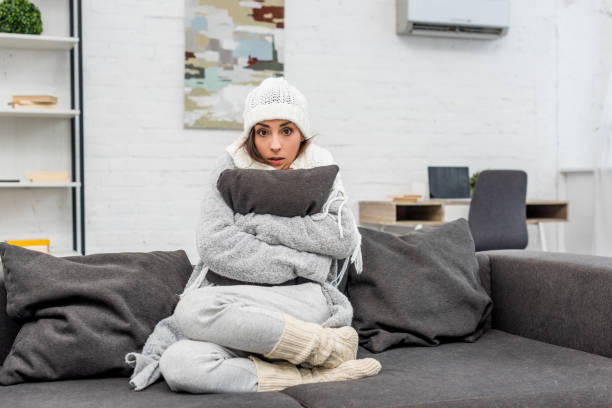

Feeling colder than usual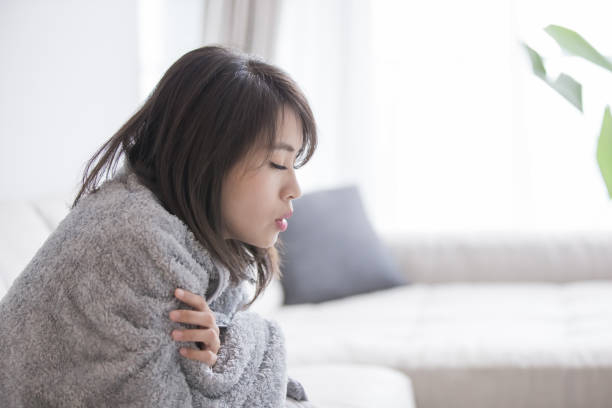 
Feeling colder than usual -
Your heart rate is the number of times your heart beats each minute. It might be influenced by your iodine levels. A lack of this mineral may cause your heart to beat slower than normal, while a surplus may cause your heart to beat faster than usual. An abnormally slow heart rate might result from an acute iodine shortage. This might make you feel weak, tired, dizzy, and perhaps faint.
A lack of iodine may impair your capacity to learn and recall. A study of over 1,000 people indicated that those with greater thyroid hormone levels outperformed those with lower thyroid hormone levels on learning and memory tasks. Thyroid hormones aid in the growth and development of your brain. That is why a lack of iodine, which is essential for the production of thyroid hormones, might impair brain development. In fact, studies have discovered that those with low thyroid hormone levels have a smaller hippocampus, the portion of the brain that governs long-term memory.

Trouble learning and remembering 
Change in heart rate -
Pregnant women are more vulnerable to iodine deficiency. This is due to the fact that they must consume enough to fulfill both their own daily demands and the needs of their growing kid. The increased requirement for iodine lasts throughout breastfeeding since newborns get iodine from breast milk.
Not getting enough iodine during pregnancy and nursing can have negative consequences on both the mother and the infant. A goiter, weakness, exhaustion, and feeling chilly are among indications of underactive thyroid in mothers. Meanwhile, a lack of iodine in babies may impair physical growth and mental development. A severe iodine deficit may also raise the chance of stillbirth.

Problems during pregnancy 
Problems during pregnancy -
An iodine deficit can cause heavy and irregular menstrual bleeding. Because iodine is required for the production of thyroid hormones, this, like other symptoms of iodine shortage, is linked to low levels of thyroid hormones.
According to one research, 68% of women with low thyroid hormone levels had irregular menstrual periods, whereas just 12% of healthy women did. According to research, women with low thyroid hormone levels had more frequent menstrual periods with severe bleeding. This is due to low thyroid hormone levels interfering with the signals of hormones involved in the menstrual cycle.

Heavy or irregular periods 
Heavy or irregular periods