Top 7 Signs and Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
In fact, magnesium deficiency is thought to affect less than 2% of Americans, it has been shown to affect considerably more hospital and ICU patients, as well ... read more...as people with diabetes and alcohol use disorders. But this condition is an often-overlooked health problem by many people. Below are some of the Signs and Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency!
-
Magnesium deficiency causes twitches, tremors, and muscle cramps. Deficiency might result in seizures in the worst-case scenario.
Scientists believe that a greater flow of calcium into nerve cells causes overexcitation or hyperstimulation of muscular nerves, resulting in these symptoms. While magnesium supplements may help reduce muscular twitches and cramps in certain people who have a deficiency, one study found that they are ineffective in treating muscle cramps in older adults. In other groups, more research is required. Keep in mind that involuntary muscle twitches might be caused by a variety of factors. Stress or too much coffee, for example, might cause involuntary muscle spasms. They might also be a sign of neuromuscular diseases such as muscular dystrophy, multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, or a side effect of some medications. While twitches are common, if your symptoms persist, you should consult a doctor.
Muscle twitches and cramps 
Muscle twitches and cramps -
Another side effect of magnesium deficiency is mental health problems. Apathy, for example, is characterized by mental numbness or a lack of emotion. Deficiency might worsen to the level of delirium and coma.
Low magnesium levels have also been linked to an increased risk of depression in observational studies. Magnesium deficiency has also been considered a cause of anxiety, however, there is no clear evidence supporting this theory. Magnesium supplements may help a subset of people with anxiety problems, according to one review, although the evidence is of poor quality. Before any conclusions can be drawn, higher-quality research is required. In short, it seems that in some people, a deficiency of magnesium might create nerve dysfunction and increase mental health problems.
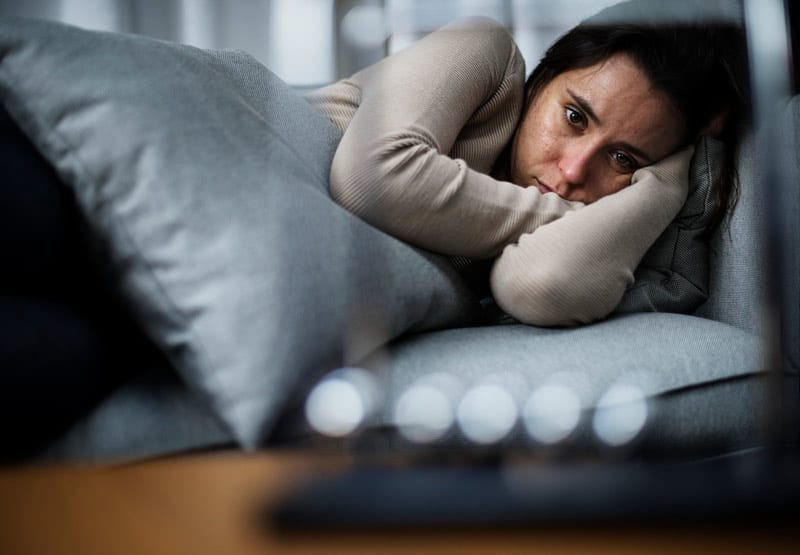

Mental health conditions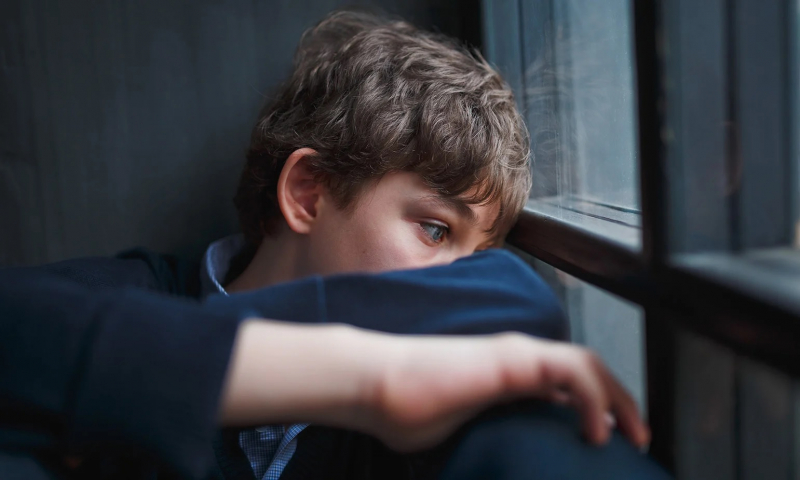 
Mental health conditions -
Osteoporosis is a condition marked by weak bones and a greater risk of fractures. The risk of having osteoporosis is shaped by a number of factors, including aging, lack of exercise or poor dietary intake of vitamins D and K.
Magnesium deficiency is also a risk factor for osteoporosis. Magnesium deficiency causes osteoporosis in two ways: directly by acting on crystal formation and bone cells, and indirectly by affecting parathyroid hormone secretion and activity, as well as increasing low-grade inflammation. Deficiency affects also reduces calcium levels in the blood, which is the main component of bones. Dietary magnesium deficiency causes lower bone mass in rats, according to research. Even though no human studies have been conducted, research has linked low magnesium intake to lower bone mineral density.
Osteoporosis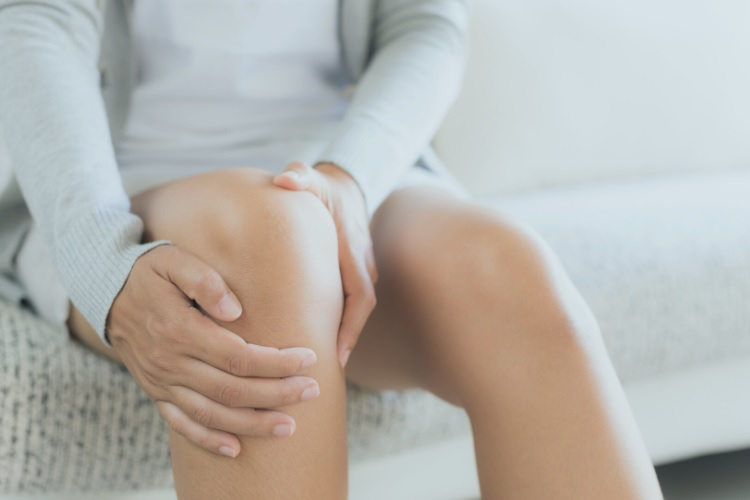 
Osteoporosis -
Another sign of magnesium deficiency is fatigue, which is described as physical or mental exhaustion or weakness. It's important to remember that everyone gets tired from time to time. It usually just means you need to rest.
Severe or persistent fatigue, on the other hand, might indicate a health problem. Because tiredness is a nonspecific symptom, it's impossible to identify its cause unless it's accompanied by other signs and symptoms. Muscle weakness, which can be caused by myasthenia gravis, is one of the specific symptoms of magnesium deficiency. The loss of potassium in muscle cells, which is linked to magnesium deficiency, is thought to be the cause of the weakness, according to scientists. As a result, magnesium shortage can be a cause of fatigue or weakness.

Fatigue and muscle weakness 
Fatigue and muscle weakness -
Magnesium deficiency has been shown in animal studies to increase blood pressure and increase high blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for heart disease.
While there is no direct evidence in people, numerous observational studies suggest that low magnesium levels or a poor diet may raise blood pressure. Controlled studies provide more strong evidence for magnesium's health effects. Magnesium supplements have been found to reduce blood pressure in several studies, particularly in people with high blood pressure. Basically, a lack of magnesium can raise blood pressure, which raises the risk of heart disease. However, further research is required before its role can be fully understood.
High blood pressure 
High blood pressure -
Magnesium deficiency can be seen in people who have severe asthma. Furthermore, magnesium levels are lower in people with asthma than in people who do not have the disease.
Researchers think that a lack of magnesium causes calcium to build up in the muscles lining the airways of the lungs. As a result, the airways constrict and breathing becomes more difficult. People with severe asthma are sometimes given a magnesium sulfate inhaler to help relax and expand their airways. Injections are the preferred method of delivery for patients with life-threatening symptoms. The evidence on the effectiveness of dietary magnesium supplements in people with asthma, on the other hand, is equivocal.

Asthma 
Asthma -
One of the most dangerous side effects of magnesium shortage is a heart arrhythmia or irregular heartbeat. Arrhythmia can happen in a variety of ways, from no symptoms to severe symptoms. It may cause heart palpitations in some people, which are pauses between heartbeats. Arrhythmia can also cause the following symptoms: lightheadedness, shortness of breath, chest pain, fainting, dizziness, and fatigue.
Arrhythmia can raise the risk of stroke or heart failure in the most severe cases. An imbalance of potassium levels within and outside of heart muscle cells, a disease linked to magnesium deficiency, is thought to be to blame, according to scientists. Magnesium levels have been shown to be lower in patients with congestive heart failure and arrhythmia than in people who do not have heart failure. Magnesium injections significantly improved heart function in 68 patients with heart failure in a small study. Magnesium supplements may also benefit some people with arrhythmia symptoms.
Irregular heartbeat 
Irregular heartbeat