Top 7 Things to Know About Clindamycin
Clindamycin is a type of antibiotic. Clindamycin is sometimes prescribed by doctors to treat bacterial infections. The medication is available in a variety of ... read more...forms, including oral capsules, topical creams, lotions, gels, intravaginal suppositories, injections, and intravenous drips. Clindamycin can either kill or stop the growth of bacteria, depending on the type of infection and the dosage. Clindamycin topical is a popular treatment for vaginal acne and bacterial infections. Clindamycin is also used to treat infections in people who are allergic to penicillin. Clindamycin, on the other hand, is not for everyone and can have a number of serious side effects. Clindamycin uses, dosages, and symptoms are discussed in this article. It also looks at different types and alternatives.
-
Clindamycin is used by doctors to treat a wide range of bacterial infections. When penicillin is ineffective and the type of bacteria involved in the infection has been determined, it is prescribed.
This is because the type of clindamycin prescribed by the doctor is determined by the type of infection the patient has.
Clindamycin may be prescribed by a doctor in the form of oral capsules or dissolvable granules for the following conditions:
- respiratory infections with streptococci, pneumococci, and staphylococci bacteria
- empyema, anaerobic pneumonitis, or an abscess in the lung
- blood poisoning
- infections from anaerobic bacteria in the gut, resulting in peritonitis or an abscess in the abdomen
- endometriosis, pelvic cellulitis, an abscess in the reproductive system, or a vaginal cuff infection
Clindamycin intravenous or injectable may be prescribed by a doctor for severe infections such as:
- respiratory infections
- lung infections
- blood poisoning
- infections in the reproductive system
- abdominal infections
- bone and joint infections, and they may sometimes prescribe it alongside other medications during surgery for chronic bone and joint infections
- serious skin infections
Clindamycin as an oral solution may be prescribed by a doctor for children to treat:
- serious respiratory infections
- serious infections of the skin or soft tissue
- blood poisoning
- infections in the abdomen
- infections in the female reproductive tract
Clindamycin may be prescribed by a doctor as a transvaginal suppository to treat bacterial vaginal infections. For vaginal infections, they may instead prescribe clindamycin lotion. The lotion is safe to use during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
Clindamycin can also be used for purposes that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not formally approved. Clindamycin is sometimes used to treat anthrax and malaria, for example.
Clindamycin is also used as a preventive treatment by dentists.
Endocarditis is an infection of the lining of the heart that can occur after a dental procedure in people who are at risk.
Practo 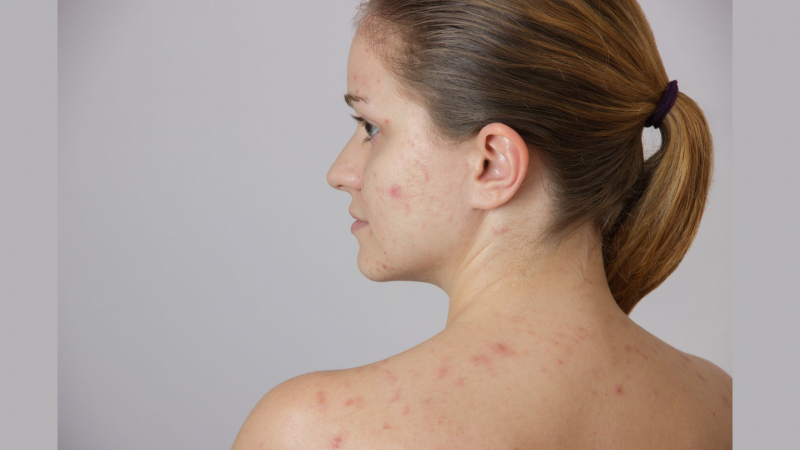
Drugs - SelfDecode -
Clindamycin comes in four different forms: injectable, intravaginal, oral, and topical.
Injectable
- clindamycin phosphate injection 6 mg/ml
- clindamycin phosphate injection 12 mg/ml
- clindamycin phosphate injection 12 mg/ml
- clindamycin phosphate injection 12 mg/ml
Intravaginal
- Cleocin cream 2%
- Cleocin suppository100 mg
Oral
- clindamycin capsule 75 mg
- clindamycin capsule 150 mg
- clindamycin capsule 300 mg
- clindamycin palmitate hydrochloride granules 75 mg/5 ml
Topical
- Evoclin foam 1%
- Clindagel 1%
- Cleocin T lotion10 mg/ml
- clindamycin phosphate solution 1%
Dosage for capsules
The dosages for clindamycin capsules for adults are:
- for serious infections, 150–300 mg every 6 hours
- for more severe infections, 300–450 mg every 6 hours
The dosages for children who can swallow capsules are:
- for serious infections, 8–16 mg per kilogram (mg/kg) per day, divided into three or four equal doses
- for more severe infections, 16–20 mg/kg per day, divided into three or four equal doses
Dosage for suppositories
One suppository pill contains 100 mg of clindamycin. People can use this form once daily at bedtime for 3 consecutive nights.
Dosage for topical gels and lotions
Doctors prescribe Clindagel 1% to be applied once daily to the affected area.
Dosage for injectable clindamycinInfants (younger than 1 month old):
- 15–20 mg/kg per day in 3 or 4 equal doses
Children and adolescents (ages 1 month to 16 years):
- 20–40 mg/kg per day in 3 or 4 equal doses
People older than 16 years:
- 600–1,200 mg per day in 2, 3, or 4 equal doses
- for more severe infections:1,200–2,700 mg per day in 2, 3, or 4 equal doses
- for life-threatening infections: up to 4,800 mg per day

DailyMed 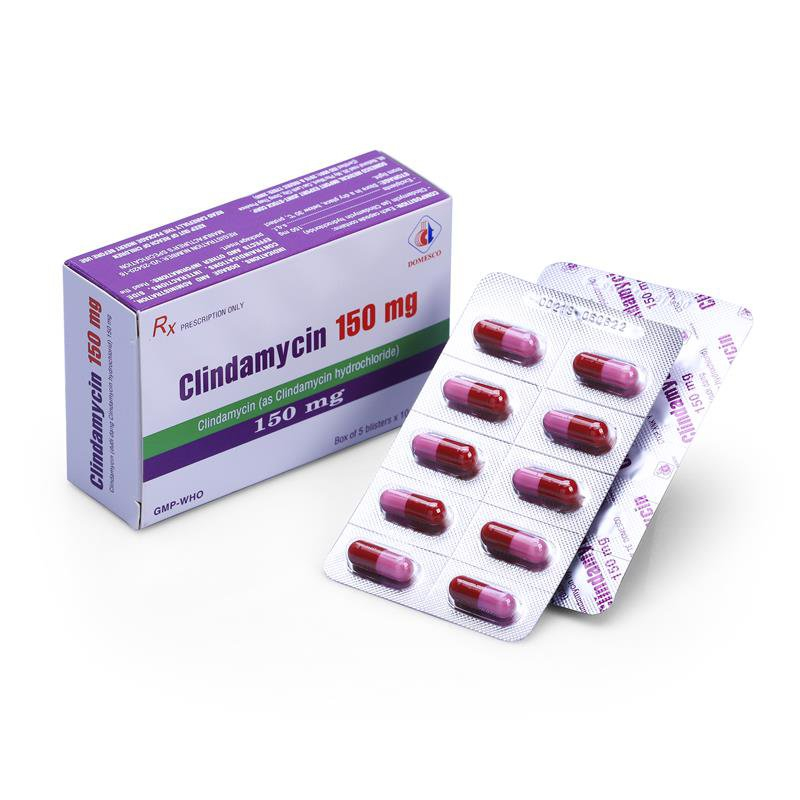
Vinmec -
The form and dosage of clindamycin prescribed by a doctor will vary depending on the infection.
How to take oral capsules and granules
Clindamycin should be prescribed only to people who are allergic to penicillin or if a different antibiotic would be inappropriate for that person. This is done to reduce the risk of colitis, which is inflammation of the inner lining of the colon.
If at all possible, the doctor should collect samples from the infection site in order to determine which bacteria are causing the infection.
Clindamycin capsules may irritate the esophagus, which connects the mouth to the stomach. Clindamycin capsules should be taken with a full glass of water to avoid irritation.
Clindamycin is available in granules that dissolve in water for people who have difficulty swallowing.
How to use vaginal creams and suppositories
Topical clindamycin can be used to treat vaginal bacterial infections.
The cream is packaged with an applicator. One applicator containing approximately 100 mg of clindamycin can be inserted into the vagina once daily at bedtime for 3 or 7 consecutive nights.
Cleocin vaginal cream is safe to use during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. A pregnant woman needs 7 days of treatment.
Clindamycin vaginal suppositories should not be used by pregnant women. The safety of suppositories during pregnancy has yet to be confirmed by researchers.
To use a suppository, insert one suppository pill containing 100 mg of clindamycin into the vagina once daily at bedtime for three consecutive nights.
Clindamycin creams and suppositories should not be used by people who have a history of colitis.
How to use lotions, gels, and solutions
Clindamycin lotions, gels, and solutions are prescribed by doctors to treat acne.
A person suffering from acne can treat it by applying a thin layer of Cleocin T 1% lotion or clindamycin 1% solution to the affected area of the skin twice daily.
When acne appears, apply Clindagel 1% to the affected area once daily.
Clindamycin applied topically can cause diarrhea. This treatment should be avoided by anyone who has had colitis.
How to take injectable clindamycin
If a patient has a severe infection and is unable to take other antibiotics, they may be given injectable clindamycin at the hospital.
Watsons 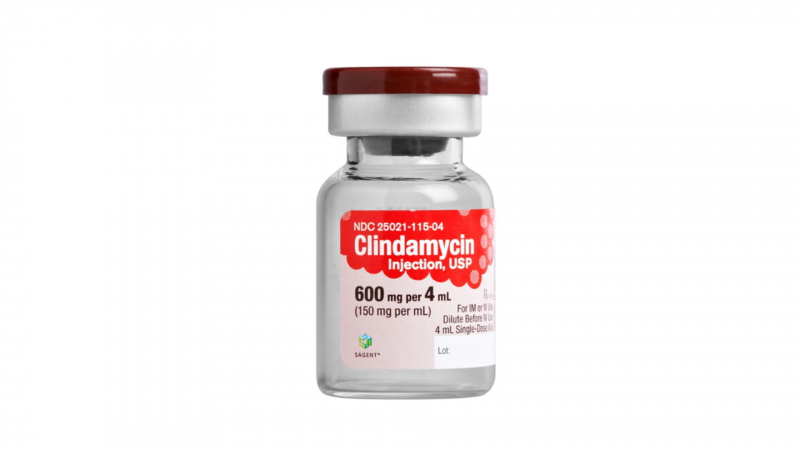
DVMed.com -
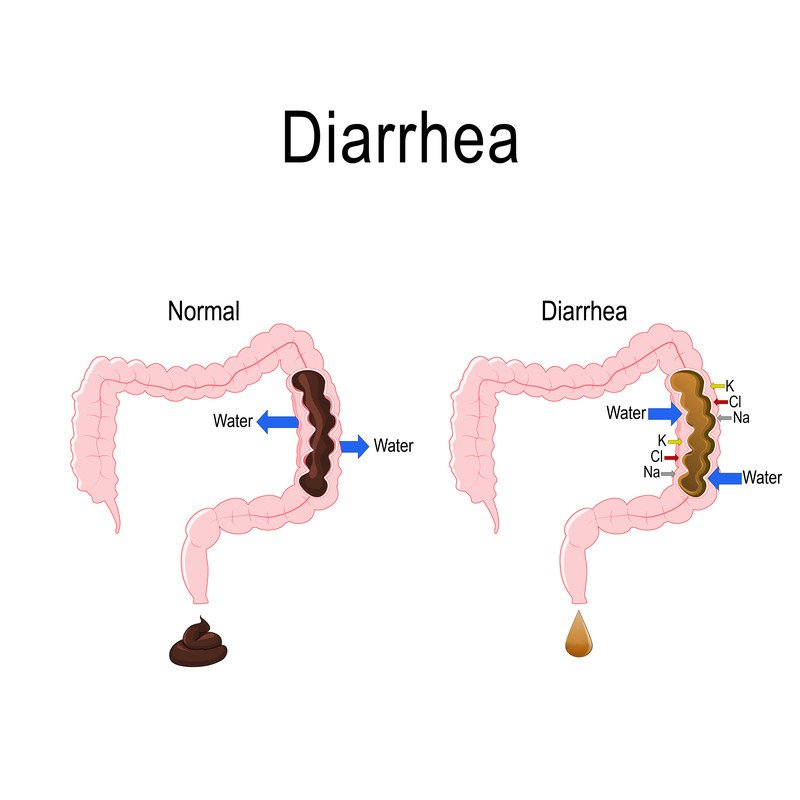
Diarrhea is one of the most common side effects of many antibiotics. When taking clindamycin, some people experience severe diarrhea.
Clindamycin can alter the bacterial composition of the colon and cause Clostridium difficile bacterium overgrowth. Toxins produced by this bacterium can cause C. difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD).
CDAD is a severe and potentially fatal infection. If a person develops CDAD while taking clindamycin, their doctor will immediately discontinue their antibiotic treatment.
Other potential side effects of either oral or injectable clindamycin include:
- abdominal pain
- irritation of the esophagus
- nausea and vomiting
- allergic skin reactions
- severe allergic reactions
- inflammation of the vagina
- fluid buildup under the skin
- impeded liver function
- impeded kidney function
- blood disorders
- disrupted function of the immune system
- arthritis
People using a clindamycin solution or lotion for acne may report skin-related side effects, including:
- dryness
- flushing or discoloration
- a burning or stinging sensation
- peeling
- itchiness
- oiliness
For example, the most common side effects of Clindagel for acne are itchiness and skin peeling.
Clindamycin topically is rarely associated with diarrhea or colitis. However, some people do report abdominal pain.
Clindamycin suppositories and vaginal creams may have the same side effects as the injectable or oral forms.
A person may develop colitis if they use a vaginal clindamycin product.
Other adverse reactions to clindamycin suppositories or vaginal creams include:- vaginal fungal infections
- inflammation of the vagina and vulva
- disorders of the vagina or vulva
- vaginal pain
Drugs.com 
www.self.com -
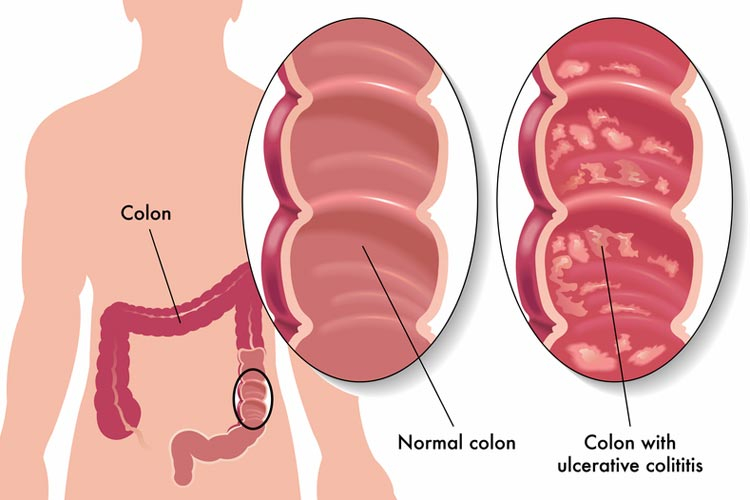
Clindamycin should not be used if you have a history of pseudomembranous or ulcerative colitis. Both of these conditions cause severe inflammation of the intestine lining. Clindamycin side effects can aggravate these two conditions.
Clindamycin should only be given to people who have bacterial infections, according to doctors. This helps to reduce clindamycin resistance in bacteria.
MyDr.com.au 
Verywell Health -
When using any form of clindamycin, drug interactions may occur. Anesthesiologists have previously expressed concern that clindamycin could delay the effectiveness of neuromuscular blocking agents during surgery.
However, researchers have recently discovered that the drug may enhance the effect of a blocking agent.
Clindamycin is broken down in the body by the liver enzyme CYP3A4 when it is taken orally. Clindamycin levels can be reduced by stimulating the function of this enzyme. Clindamycin levels in the blood may rise if something inhibits CYP3A4.
Certain drugs can impair CYP3A4 function. Doctors must monitor patients who are taking CYP3A4 stimulants in conjunction with clindamycin to ensure that the antibiotic is effective.
If a person takes clindamycin with a CYP3A4 inhibitor, the increased levels of the antibiotic may cause side effects. Doctors should keep an eye out for any increase in adverse effects.
HIVinfo - NIH 
Burt's Pharmacy -
The only members of the lincosamide family are clindamycin and lincomycin.
Lincomycin is only available as an injectable solution, and it is only used to treat serious infections.
A doctor may choose another class of antibiotics instead, depending on the infection and the person's history of antibiotic allergies and side effects.
Zyfas Pharma 
Kepro