Response and effectiveness

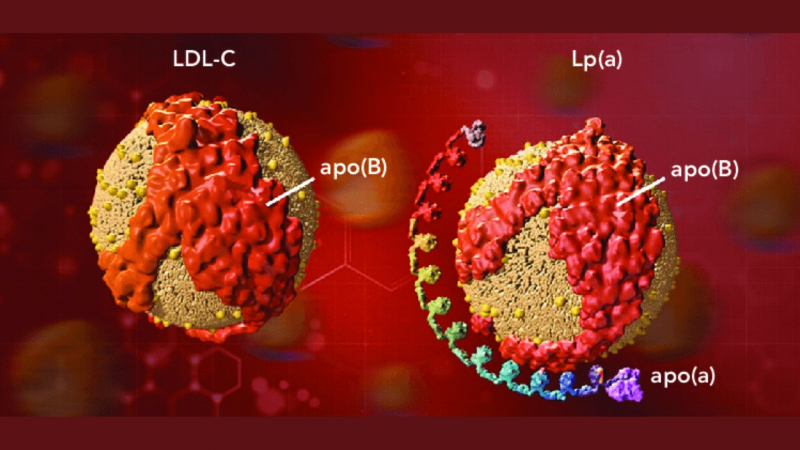
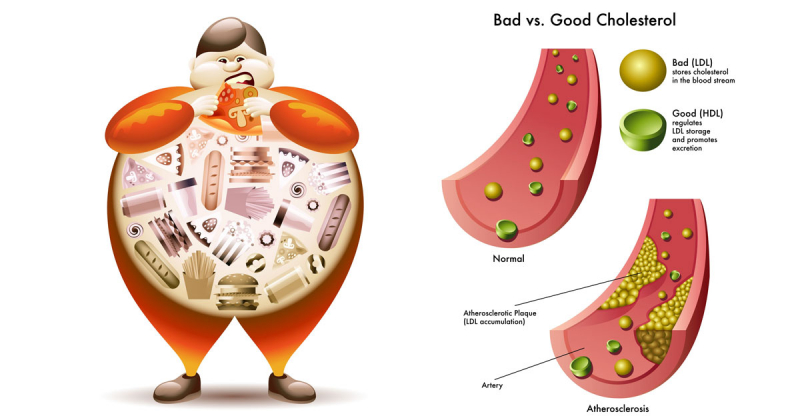
In studies, ezetimibe (Zetia) was shown to lower total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C or "bad" cholesterol), apolipoprotein B (Apo B) levels, non-HDL-C, triglycerides (TG), and increase high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C or "good") levels when compared to a placebo (an inactive product).
The maximum effect is usually achieved within two weeks and is maintained throughout the course of treatment. In two studies, ezetimibe reduced LDL cholesterol levels by 18% when used alone and compared to a placebo.
In a clinical study, ezetimibe was combined with atorvastatin (a statin) at the start of treatment and reduced LDL cholesterol levels by 54%.
In a 12-week study, ezetimibe was combined with fenofibrate in patients with mixed hyperlipidemia, and LDL-C was reduced by 20%, compared to a 6% reduction with fenofibrate alone, a 13% reduction with ezetimibe alone, and 0% with a placebo.
Ezetimibe has also been shown to lower LDL-C levels significantly in patients with Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (HoFH) who are also taking a statin.
Ezetimibe significantly reduced plasma sitosterol and campesterol by 21% and 24% from baseline in patients with Homozygous Sitosterolemia (Phytosterolemia) who were continuing their current therapeutic regimen (which may include diet, bile-acid-binding resins, statins, ileal bypass surgery, and/or LDL apheresis). Patients who received a placebo, on the other hand, experienced 4% and 3% increases in sitosterol and campesterol, respectively.