Top 7 Things to Know About Ezetimibe
Ezetimibe is a medicine used to treat high blood cholesterol and certain abnormalities in blood fats. The drug should be used in conjunction with dietary ... read more...changes and physical activity. There are many forms of Ezetimibe on the market with different concentrations, usually white tablets.
-
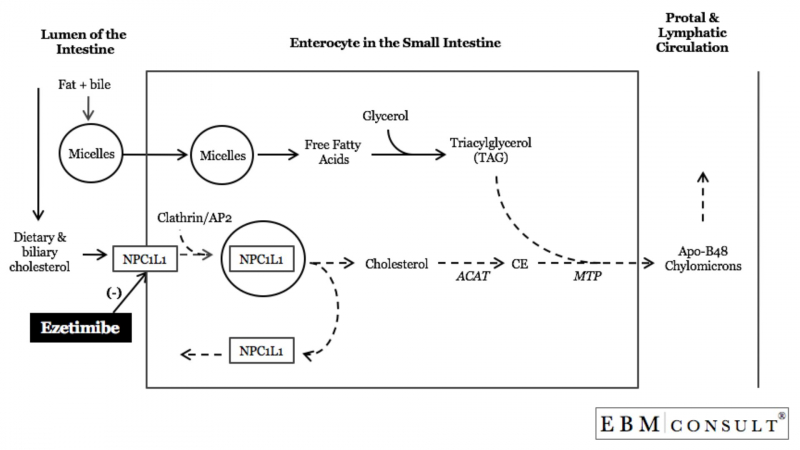
Ezetimibe (Zetia) works by decreasing cholesterol absorption in the small intestine. This means that your liver receives and stores less cholesterol. More cholesterol is then cleared from the blood, which aids in the reduction of cholesterol levels. It belongs to the class of medications known as cholesterol absorption inhibitors.
Ezetimibe inhibits the sterol transporter Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 (NPC1L1), which is involved in the uptake of cholesterol and phytosterols in the intestine.
Ezetimibe is a prescription medication that lowers your blood total and LDL (bad) cholesterol levels. LDL and HDL cholesterol make up your total cholesterol.
Ezetimibe is used to treat high cholesterol in people who are unable to control their levels through diet and exercise alone. While taking this medication, you should also follow a cholesterol-lowering diet and an exercise regimen.
To maximize the effect of ezetimibe, your doctor may prescribe additional cholesterol-lowering medications.
EBM Consult Drug Chug -
Ezetimibe can be taken with or without other cholesterol-lowering medications such as statins, fenofibrate, or bile-acid sequestrants. These medications work in a different manner and complement ezetimibe.
In the United States, ezetimibe is available as a generic product in a 10 mg tablet and is very affordable. It is also available under the brand name Zetia, which is manufactured by Organon.
Ezetimibe is taken once a day as an oral tablet that is swallowed with or without food. The typical daily dose is 10 mg.
There are no recommended dosage adjustments for people with kidney disease, mild liver disease, or advanced age; however, ezetimibe is not recommended for people with moderate to severe liver disease.When ezetimibe is used alone (without a statin), no increase in liver enzymes has been observed in studies. Some older people may be more sensitive than others. Ezetimibe has not been shown to cause changes in blood pressure.
Ezetimibe is also available in combination products, which may be more convenient. Brand-name products that contain both ezetimibe and a statin include Vytorin (ezetimibe and simvastatin) and Roszet (ezetimibe and rosuvastatin). These brands are also available as generics at a lower cost.
Ezetimibe can also be taken in combination with bempedoic acid (brand name: Nexlizet), a non-statin cholesterol-lowering medication. Bempedoic acid reduces the amount of cholesterol produced in the liver.

Drugs.com 
Drugs.com -
You are more likely to have the following side effects if you are between the ages of 18 and 60, do not take any other medications, or have any other medical conditions:
- When ezetimibe is used alone, it can cause diarrhea, upper respiratory tract infection, joint pain, sinusitis, and fatigue. When ezetimibe is combined with a statin, common cold symptoms, muscle aches, upper respiratory tract infection, joint pain, and diarrhea may occur.
- Although ezetimibe has been shown to lower cholesterol, it will not aid in weight loss. Maintain your doctor-recommended diet and exercise routine.
- There is no evidence that ezetimibe can prevent heart disease or heart attacks.
- Severe muscle pain may occur in rare cases when ezetimibe is used alone or in combination with a statin. This could include myopathy and rhabdomyolysis. If you have severe muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness, see your doctor right away because it could lead to muscle breakdown and kidney damage.
- You may not be able to use ezetimibe alone if you have active liver disease. Your liver function will be monitored by your doctor.
- In rare cases, statins have been linked to memory loss, forgetfulness, and confusion. This can also happen when statins are combined with ezetimibe. When your doctor discontinues the statin, these symptoms usually go away.
- Some people may experience severe allergic reactions. A rash or hives; swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and/or throat that may cause difficulty breathing or swallowing; joint pain and muscle aches; changes in laboratory tests; liver problems; stomach pain; pancreas inflammation; nausea; dizziness; tingling sensation; depression; headache; gallstones; gallbladder inflammation.
- You cannot take ezetimibe with a statin if you have active liver disease, are pregnant or plan to become pregnant, or are breastfeeding. Consult your doctor to see if ezetimibe is right for you.
- It is unknown whether Zetia works for Fredrickson Type I, III, IV, and V dyslipidemia.
- Children under the age of ten have not been studied for Zetia.
In general, those who are older or younger, have specific medical conditions (including liver or kidney issues, heart disease, diabetes, or seizure disorders), use other medications, or are seniors or young children are more likely to experience a greater range of adverse effects.
Mount Sinai 
Dr Jeffrey Chacko -
When taken on a regular basis, ezetimibe is effective at lowering cholesterol levels and can be combined with a statin or fenofibrate in some patients to further reduce lipids. Although ezetimibe is generally well tolerated, its use may be limited by side effects such as muscle pain or liver toxicity, especially when combined with a statin. There is no evidence that ezetimibe reduces the risk of heart disease or a heart attack.
Froedtert Hospital 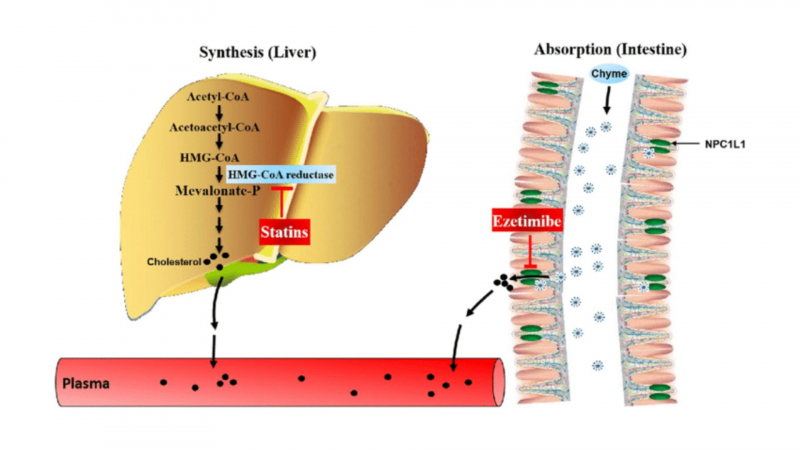
ResearchGate -
Take one capsule once daily, with or without food. Can be taken at any time of day (morning or night); however, it is best to stick to a consistent schedule.
Take your medication exactly as your doctor has prescribed. If your doctor advises you to change your dose or discontinue treatment, do so.
If you are taking another cholesterol-lowering medication, check with your doctor to see if you can take it alongside ezetimibe.
While taking this medication, you must adhere to a cholesterol-lowering diet and exercise regimen. If you require diet advice, consult your doctor. If you smoke, speak with your doctor about quitting.
If you notice any yellowing of your skin or eyes, shortness of breath, unexplained cough, severe muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness, call your doctor right away. Inquire with your doctor about how to spot liver problems.
If you are a woman of childbearing age, you should use an effective method of birth control to avoid pregnancy while taking ezetimibe in combination with a statin.
It is critical to inform your doctor and pharmacist about any other medications you are taking, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter (OTC) medications, vitamins, herbs, and dietary supplements. Do not discontinue any medications without first consulting your doctor.

Verywell Health 
Harvard Health -
In studies, ezetimibe (Zetia) was shown to lower total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C or "bad" cholesterol), apolipoprotein B (Apo B) levels, non-HDL-C, triglycerides (TG), and increase high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C or "good") levels when compared to a placebo (an inactive product).
The maximum effect is usually achieved within two weeks and is maintained throughout the course of treatment. In two studies, ezetimibe reduced LDL cholesterol levels by 18% when used alone and compared to a placebo.
In a clinical study, ezetimibe was combined with atorvastatin (a statin) at the start of treatment and reduced LDL cholesterol levels by 54%.
In a 12-week study, ezetimibe was combined with fenofibrate in patients with mixed hyperlipidemia, and LDL-C was reduced by 20%, compared to a 6% reduction with fenofibrate alone, a 13% reduction with ezetimibe alone, and 0% with a placebo.
Ezetimibe has also been shown to lower LDL-C levels significantly in patients with Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (HoFH) who are also taking a statin.
Ezetimibe significantly reduced plasma sitosterol and campesterol by 21% and 24% from baseline in patients with Homozygous Sitosterolemia (Phytosterolemia) who were continuing their current therapeutic regimen (which may include diet, bile-acid-binding resins, statins, ileal bypass surgery, and/or LDL apheresis). Patients who received a placebo, on the other hand, experienced 4% and 3% increases in sitosterol and campesterol, respectively.
ResearchGate 
Medical Laboratories -
Medicines that interact with ezetimibe may reduce its effectiveness, increase its side effects, or alter how other medications work. An interaction between two medications does not always necessitate the discontinuation of one of them; however, it can. Consult your doctor or pharmacist about how to handle drug interactions.
- Bile acid sequestrants: Ezetimibe should be taken 2 hours before or 4 hours after taking a bile acid sequestrant (such as cholestyramine). Taking these medications at the same time may reduce ezetimibe absorption and effectiveness.
- Cyclosporine: Combining ezetimibe and cyclosporine may increase blood levels of both drugs and worsen side effects for one or both. Consult your doctor before combining these two medications. Cyclosporine levels in your blood may need to be checked. Fenofibrate: Combined use may result in increased ezetimibe blood levels. Both medications can be harmful to the gallbladder, and their effects are amplified when taken together. Fibrates can cause cholesterol gallstones by increasing cholesterol excretion into the bile.
- Fibrates may increase cholesterol excretion into the bile, resulting in cholesterol gallstones. Gallbladder side effects include severe stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, unusual weakness, or fever. If you experience any of these side effects, please contact your doctor. A special gallbladder study and/or a medication change may be required.
- Fibrates: Coadministration of ezetimibe with fibrates other than fenofibrate is not recommended until additional research is completed.
- Statins: If ezetimibe is combined with another medication, such as a statin, serious interactions such as liver disease and severe muscle problems (rhabdomyolysis) may occur.
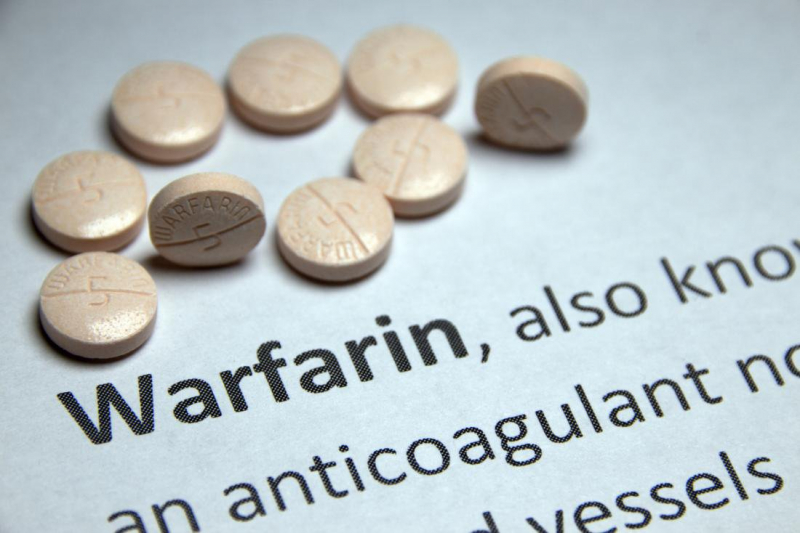
- Warfarin: If you take warfarin and ezetimibe, your doctor will closely monitor your INR.
It should be noted that this list is not exhaustive and only includes common medications that may interact with ezetimibe. For a complete list of interactions with ezetimibe, consult the prescribing information.
Vinmec 
CreakyJoints