Top 8 Most Common Signs of Gluten Intolerance
When you have gluten intolerance, you get ill after eating gluten. You may feel tired, gassy, or bloated. Although it's more common among women, anyone can ... read more...have gluten intolerance. Some people have gluten intolerance from birth, while others get it as they age. Below are some of the Most Common Signs of Gluten Intolerance!
-
Constipation and diarrhea are common, but if they occur frequently, it's possible that something is wrong. Consuming foods that contain gluten might result in digestive problems for those who are sensitive to it. In fact, roughly 25% of gluten-sensitive people get constipation and more than 50% of them consistently experience diarrhea.
After consuming gluten, those with gluten Intolerance have inflammation in the small intestine. This causes nutrition absorption to be poor and destroys the gut lining, which causes substantial digestive discomfort and frequent diarrhea or constipation. Regular diarrhea can lead to serious health problems such as electrolyte loss, dehydration, and fatigue. Due to poor nutrition absorption, people may also have pale and foul-smelling feces.
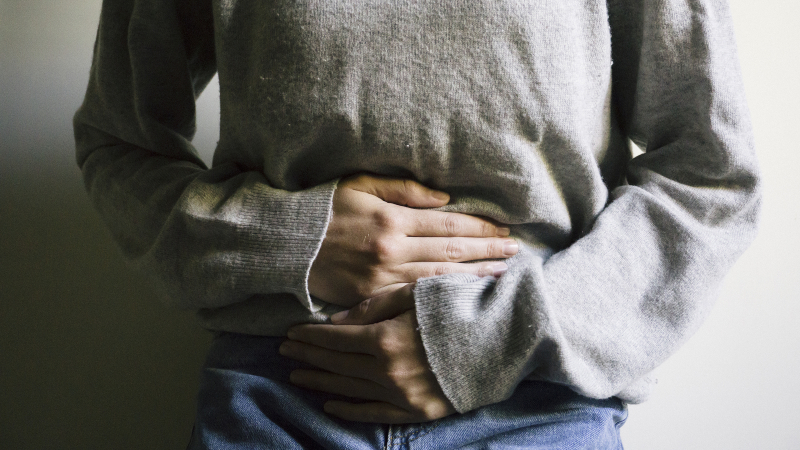

Diarrhea, constipation, and smelly feces 
Diarrhea, constipation, and smelly feces -
Bloating is another typical symptom of gluten intolerance that people report. This describes the feeling of a full stomach that is uncomfortable and lasting. It is common also to feel a buildup of gas.
Bloating can happen for a variety of causes, but it most frequently results from overeating. Bloating may happen often in people with gluten intolerance, and it is not necessarily related to the amount of food they eat. In fact, among those who are sensitive to or intolerant to gluten, feeling bloated is one of the most prevalent problems. One research, for instance, found that 87% of individuals with suspected non-celiac gluten sensitivity reported bloating.
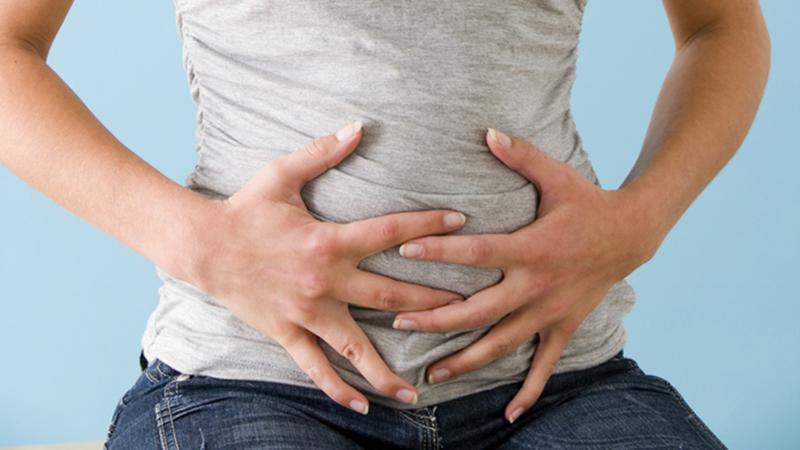

Bloating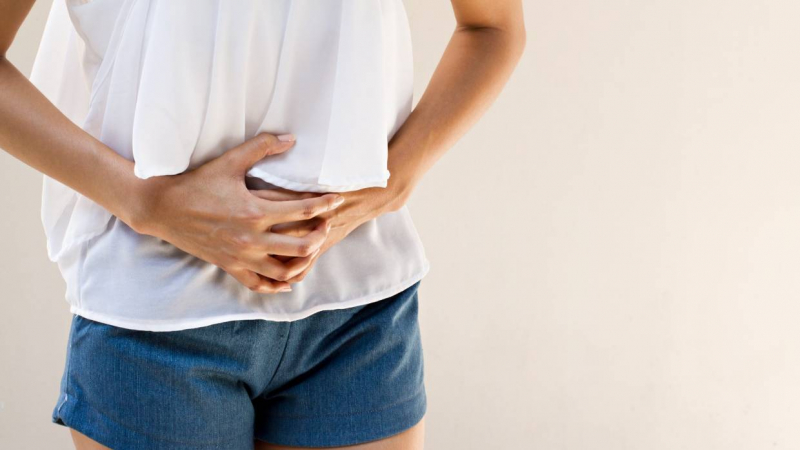 
Bloating -
Gluten sensitivity and celiac disease can have an impact on more than just your digestive system; they can also cause a number of other skin issues. One symptom most common is dermatitis herpetiformis, a skin disorder that causes blisters. It affects 15 to 25% of people with the condition.
However, patients with celiac disease and gluten sensitivity may experience other skin issues as well. These consist of:
- Psoriasis: Scaling and skin reddening are features of this inflammatory condition.
- Alopecia areata: The symptoms of this autoimmune condition include non-scarring hair loss
- Chronic urticaria: This is a skin condition characterized by recurrent itchy pink or red lesions with pale centers.
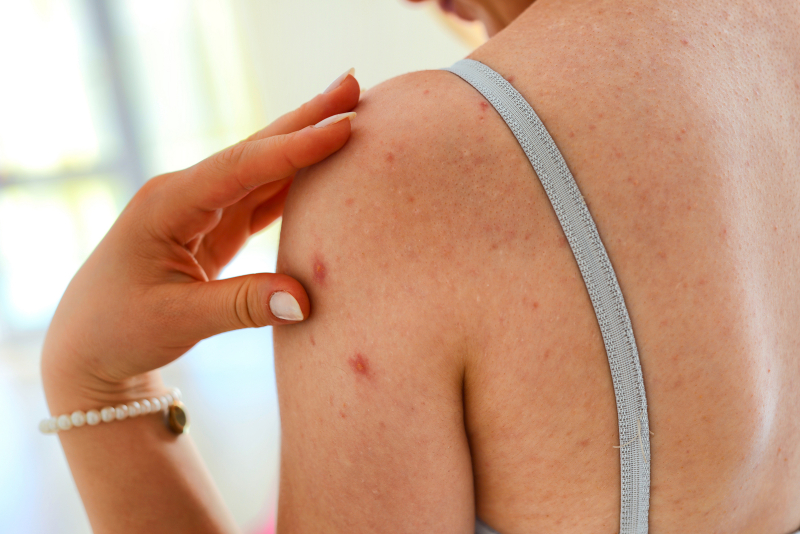
Skin reactions 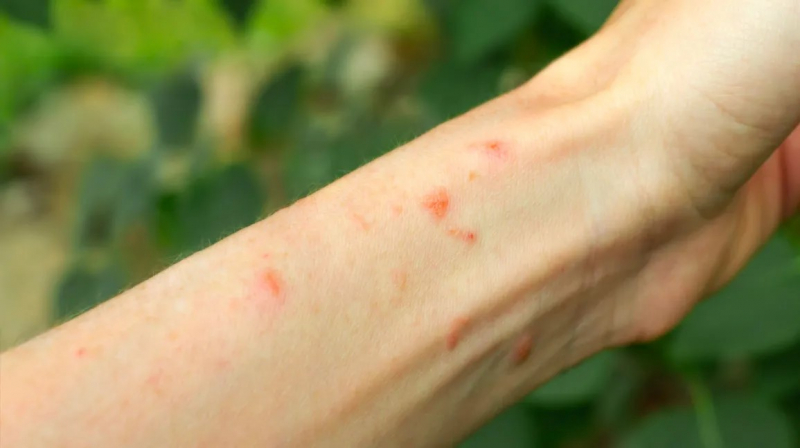
Skin reactions -
Approximately 6% of Americans experience depression each year. The symptoms, which frequently involve hopelessness and sadness, can have a major effect on daily life.
People who have digestive issues appear to be more prone to anxiety and depression than people who don't have any underlying medical illnesses. Several theories explain how depression may be exacerbated by gluten intolerance. These consist of:
- Atypical serotonin levels: high levels of serotonin. A chemical called serotonin allows cells to communicate. It is referred to as one of the "happiness" hormones since decreased levels have been associated with depression.
- Gluten exorphins: These peptides are created when some of the gluten's proteins are digested. They could disrupt the central nervous system, which might make depression more likely
- Changes in the gut microbiota: The central nervous system may be impacted by higher levels of harmful bacteria and lower levels of beneficial bacteria, raising the risk of depression.

Depression and anxiety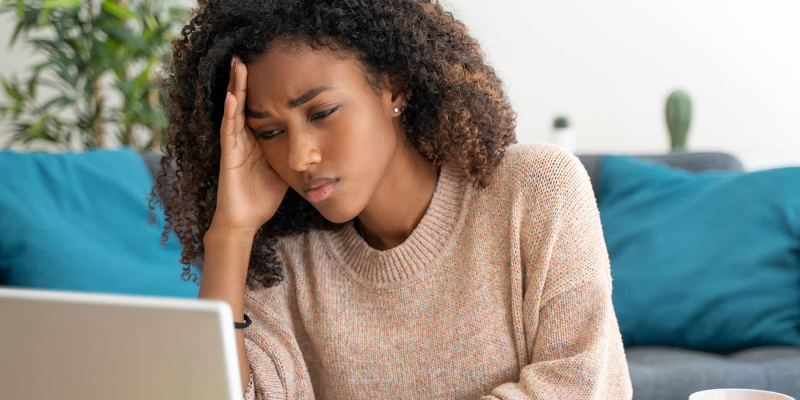 
Depression and anxiety -
It's quite common to feel tired, and it's often not a sign of any disease. However, you should consider the possibility of an underlying problem if you consistently feel extremely fatigued. People who are gluten intolerant are highly prone to feeling fatigued, especially after eating gluten-containing meals.
After eating gluten, a protein found in the grains wheat, rye, barley, and triticale, one may experience fatigue. This symptom might indicate celiac disease or gluten intolerance. The immune response caused by eating gluten may make it difficult for sensitive people to properly absorb nutrients. Your brain, neurological system, and organs are deprived of the nutrition they require as a result. The lack of nutrition is the cause of your fatigue, and you could also have headaches. One study found that 64% of the 486 non-celiac gluten-sensitive subjects experienced fatigue.
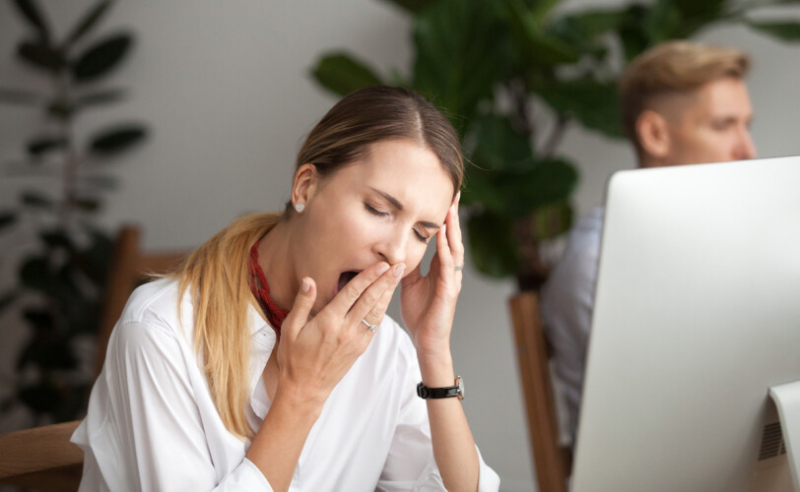

Fatigue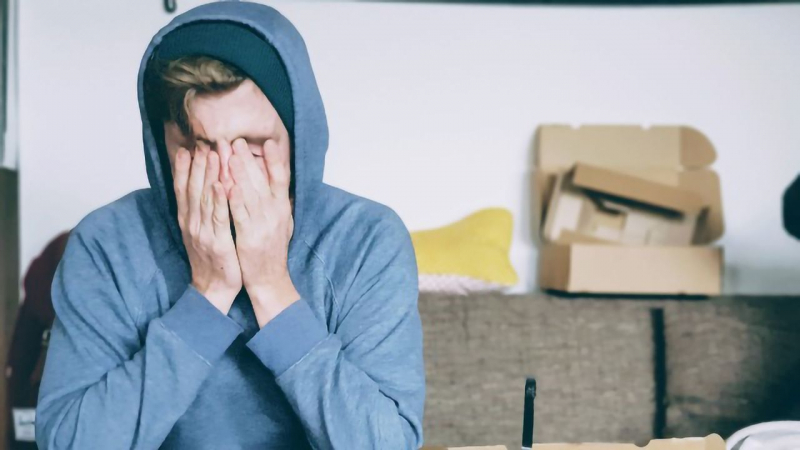 
Fatigue -
Abdominal pain is discomfort anywhere in your belly region — between your ribs and your pelvis. There are several potential reasons for abdominal pain, which is very common. It is, however, also the most typical symptom of gluten intolerance. It has been estimated that up to 83% of patients with gluten intolerance experience abdominal pain and discomfort after consuming gluten.
Numerous symptoms might be associated with abdominal discomfort. As follows:
- Mild or severe
- Burning or achy
- Crampy or colicky
- Constant or intermittent
- Localized (in one spot) or generalized (all over)
- ...
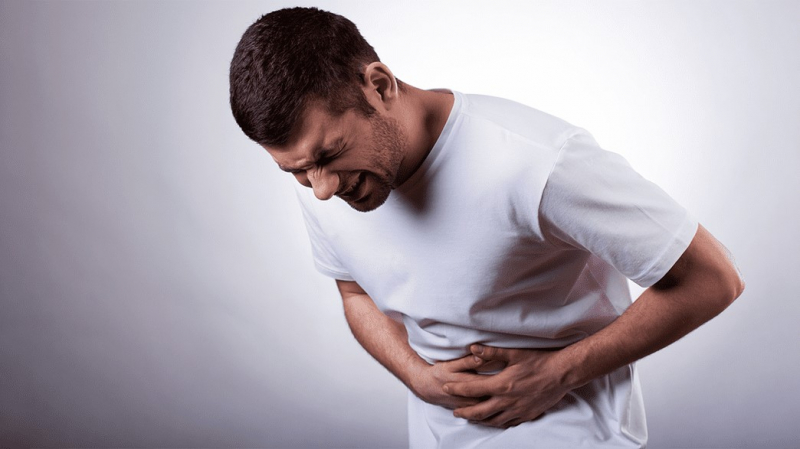

Abdominal pain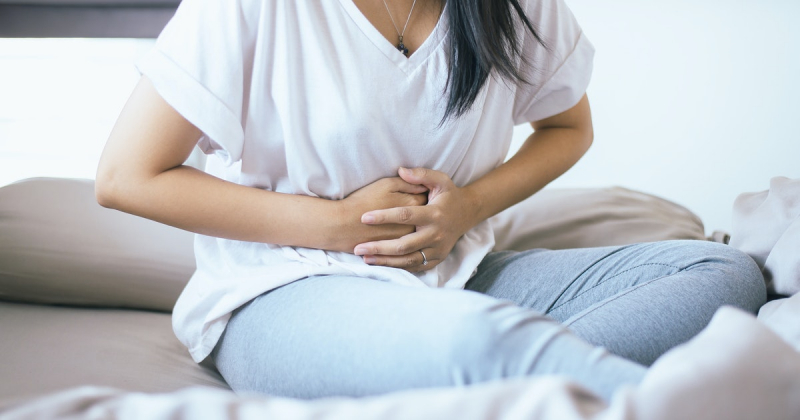 
Abdominal pain -
"Brain fog” isn’t a medical condition. It's a term for a few symptoms that might affect your ability to think. You could feel confused or struggle to concentrate, or have trouble putting your thoughts into words. It has been characterized as:
- Being forgetful
- Having difficulty thinking
- Feeling “cloudy”
- Experiencing mental fatigue
- ...
Nearly 40% of those who are gluten intolerant have a "foggy mind," which is a frequent symptom of gluten intolerance. This symptom could be caused by a reaction to certain antibodies in gluten, but the exact reason is unknown.
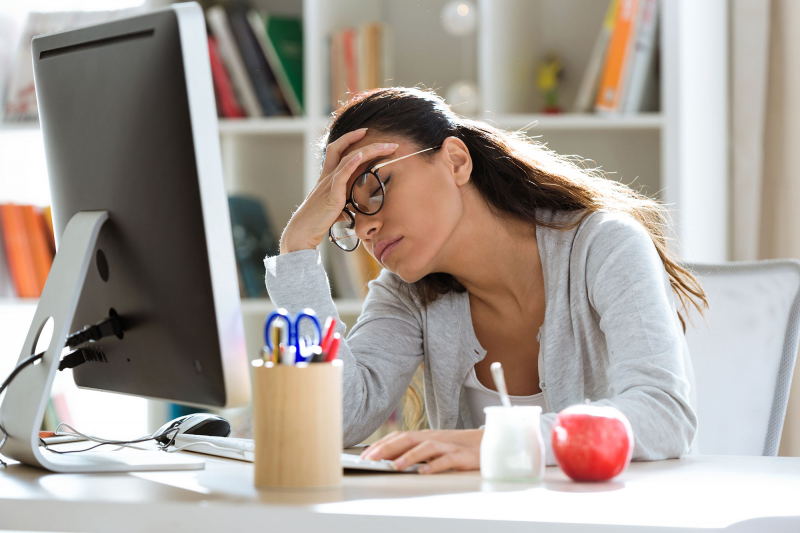

Brain fog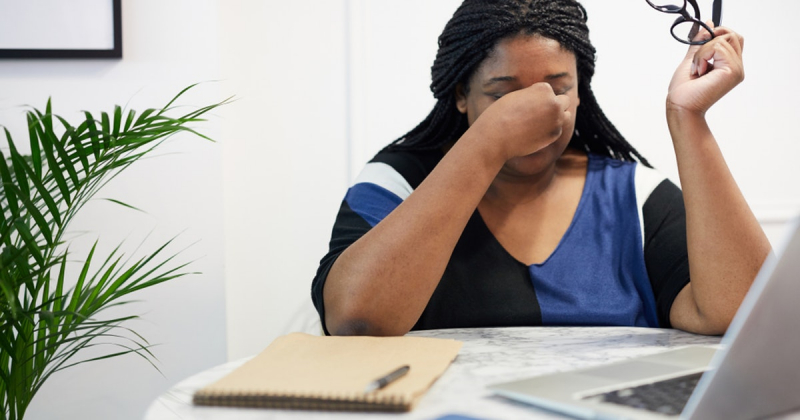 
Brain fog -
Although less severe than celiac disease, gluten intolerance, also known as non-celiac gluten intolerance, shows some of the same symptoms. However, gluten intolerance can still cause significant discomfort, with several of these symptoms may be frequently experienced by people with gluten intolerance. Although they are less frequent, additional symptoms of gluten intolerance are also possible.
These may include:
- Joint and muscle pain
- Leg or arm numbness
- Unexplained weight loss
- Iron-deficiency anemia
- ...
Many of these signs and symptoms appear soon after ingesting gluten. The precise combination of symptoms can change, though. When including gluten-containing foods in regular diets, those who report gluten sensitivity often experience the symptoms listed above.

Other symptoms 
Other symptoms