Top 5 Signs and Symptoms of Kidney Stones
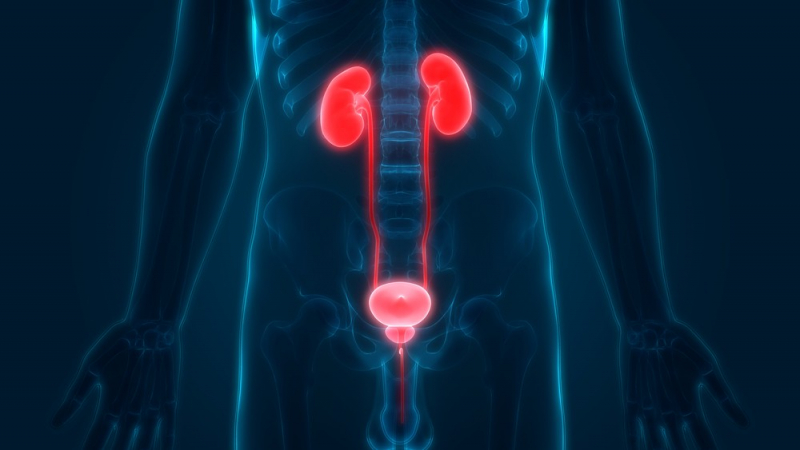
Kidney stones, also known as nephroliths or renal calculi, are the most prevalent urinary system health problem. Stones are hard mineral pieces that can ... read more...develop in the kidneys. They are frequently tiny enough to pass through your body through your urine. However, if they are extremely huge, you may require medical intervention to break them up or remove them. Seek medical assistance right once if you suspect you have a kidney stone. A fever with a kidney stone or a urinary tract infection (UTI) with a kidney stone, in particular, are surgical emergencies. And here are the most common kidney stones signs and symptoms.
-
Kidney stone pain, also known as renal colic, is one of the most intense forms of agony that can be imagined. Some kidney stone sufferers equate the pain to childbirth or being stabbed with a knife. The agony is severe enough that more than 500,000 people visit emergency rooms each year. The discomfort usually begins when a stone slides into the small ureter. This results in a blockage, which increases pressure on the kidney. The pressure stimulates nerve fibers, which provide pain signals to the brain.
Kidney stone pain is frequently severe. The agony shifts in position and severity as the stone travels. The ureter contracts as it tries to force the stone out, causing pain to come and go in waves. Each wave may linger a few minutes before disappearing and reappearing. The discomfort is usually felt along your side and back, just behind your ribcage. As the stone passes down your urinary tract, it may radiate to your belly and groin. Large stones can be more painful than little ones, although the degree of discomfort does not always correlate with stone size. Even a little stone can cause discomfort when it shifts or causes an obstruction.
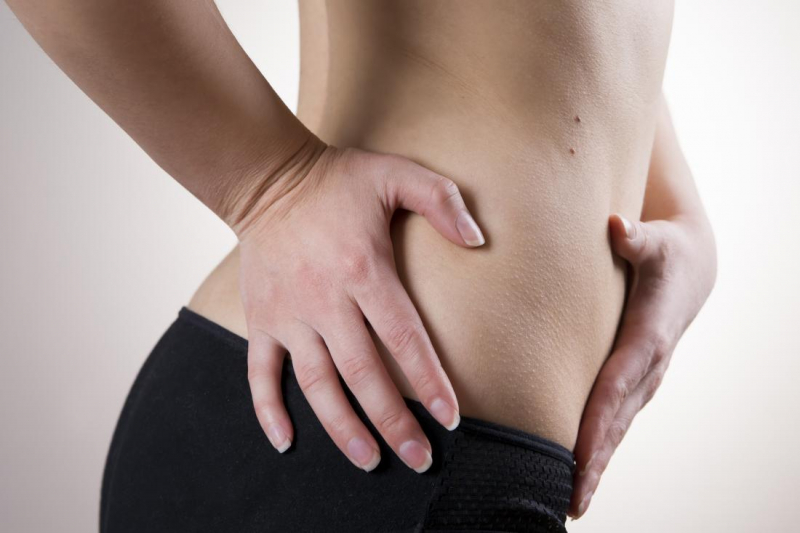
Pain in the back, belly, or side 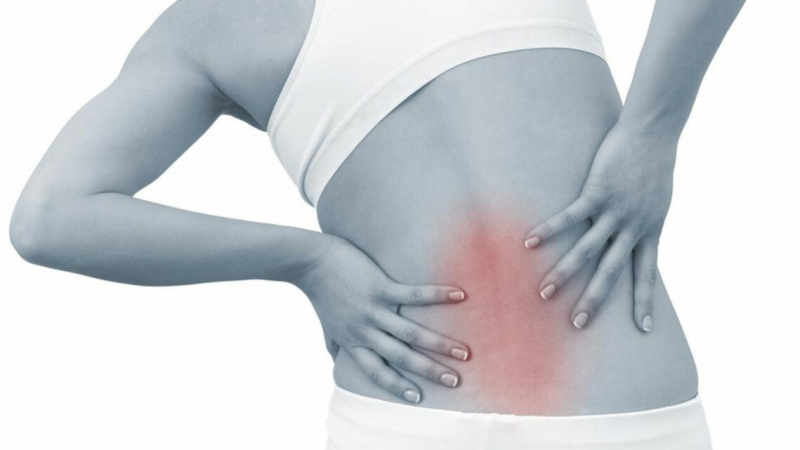
Pain in the back, belly, or side -
When the stone reaches the junction of your ureter and bladder, you will experience pain when urinating. Your doctor may refer to this as dysuria. The discomfort might be acute or scorching. If you don't realize you have a kidney stone, you can mistake it for a urinary tract infection (UTI). It is possible to have an infection in addition to the stone.
Dysuria (painful urination) is a comprehensive word that implies discomfort during urinating. This discomfort might be coming from the bladder, urethra, or perineum. The urethra is the tube that transports pee from your body to the outer world. The perineum is the region between the scrotum and the anus in people who have a penis. The perineum is the region between the anus and the entrance of the vagina in those who have one. Urination that causes pain is fairly prevalent. Pain, burning, or stinging can be symptoms of a variety of medical disorders.
Pain or burning during urination 
Pain or burning during urination -
A typical sign is blood in the urine. People with kidney stones may rely on this reliable source. This condition is also known as hematuria. Blood can be red, pink, or brown in color. Although blood cells are often too minute to view without a microscope (a condition known as microscopic hematuria), your doctor can analyze your urine to check whether it includes blood.
Because of the presence of red blood cells, gross hematuria causes pink, red, or cola-colored urine. It just takes a small amount of blood to create crimson urine, and the bleeding is typically not unpleasant. However, passing blood clots in your urine might be uncomfortable. Certain drugs, such as the laxative Ex-lax, and foods, such as beets, rhubarb, and berries, might cause your urine to become red. Urine color changes induced by medicines, diet, or exercise may resolve within a few days. Bloody urine has a distinct appearance, but you might not be able to tell the difference. It is important to consult your doctor if you notice red-colored urine.

Blood in the urine 
Blood in the urine -
Urine that is healthy is clear and does not have a strong odor. Cloudy or odorous urine may indicate an infection in your kidneys or another portion of your urinary system. According to one 2021 study, around 16% of individuals with acute renal stones had a UTI. Pyuria, or pus in the urine, is indicated by cloudiness. The odor may be caused by the bacteria that cause UTIs. Urine that is more concentrated than usual may also emit an odor. With or without a fever, a UTI with a kidney stone is considered a surgical urgency.
Kidney stones, which are crystallized products of minerals and salts, may generate a foul or hazy smell in urine. If your pee smells strong, you should make an appointment with your doctor.
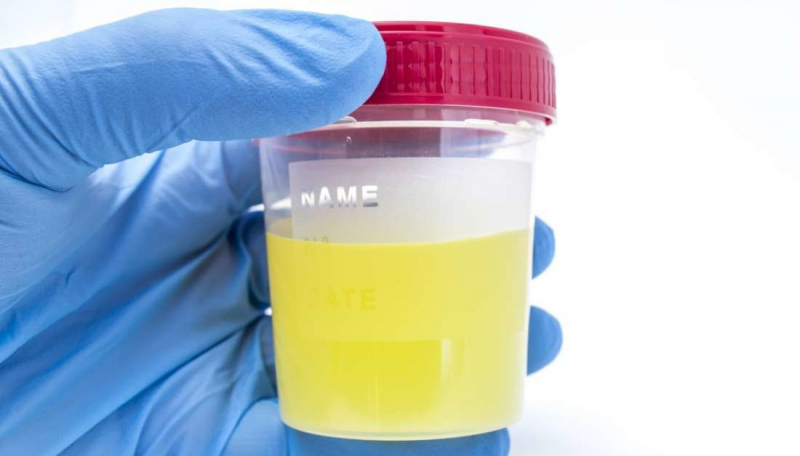
Cloudy or smelly urine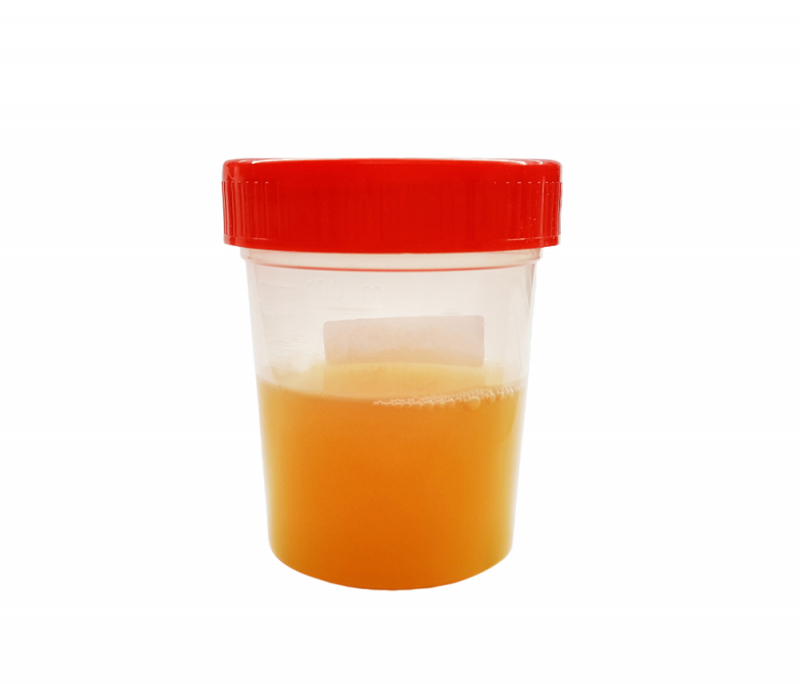 
Cloudy or smelly urine -
Nausea and vomiting are frequent symptoms of kidney stones. These symptoms occur as a result of nerve connections between the kidneys and the GI tract. Kidney stones can stimulate nerves in the GI system, causing an unpleasant stomach. Nausea and vomiting can also be your body's method of coping with excruciating discomfort. Because the nerves of the kidney and gut are related, a full blockage of the ureters may cause nausea.
The vomiting act is divided into two stages. During the retching phase, the abdominal muscles, diaphragm, and respiratory inspiration muscles all engage in a series of synchronized contractions. As a result, this stage may be confused with an incident of intense hiccups. Nothing has been ejected during this retching phase. The following phase, also known as the expulsive phase, is characterized by severe pressure in the stomach caused by massive movements in both the diaphragm and the abdomen. Kidney stones can also impact the gastrointestinal tract, causing you to vomit. If you develop this symptom, see your doctor as soon as possible.

Nausea and vomiting 
Nausea and vomiting