Top 5 Signs and Symptoms of Tetanus
Tetanus is a dangerous neurological disease caused by the toxin of the tetanus bacterium Clostridium tetani. Pathogens are mainly found in the soil and ... read more...intestinal tract of animals and humans. The main route of transmission is through infected wounds. Infected wounds can be large or small. However, in recent years, the number of cases of tetanus from small wounds has been increasing, possibly due to subjective psychology, so these small wounds have not been properly disinfected and treated. According to the statistics, the rate of patients dying from tetanus is relatively high. To treat the disease in time, you should actively learn the common tetanus symptoms and monitor your health regularly. The following article will be useful for you!
-
The time from injury to the appearance of the first symptom of tetanus, usually a stiff jaw. The incubation period can range from 2 days to 2 months, with most cases occurring within 8 days. The shorter the incubation period (< 7 days), the more severe the disease. From the moment of jaw stiffness to the first convulsion or the first laryngopharyngeal spasm, it is usually 1-7 days. The shorter the onset time (<48 hours), the more severe the disease. From the onset of the first generalized convulsion or pharynx/laryngospasm to the onset of remission, which usually lasts 1 to 3 weeks.
The first clinical symptom of the disease is usually a stiff jaw, difficulty opening the mouth without trauma, no swelling, redness, or high fever, but simply the patient feels difficulty opening the mouth, swallowing, or speaking. When the tongue is pressed down, the jaw is bitten harder (trismus sign). This sign was found in all patients. On examination, masticatory muscle tone is increased. In the early stages, the patient did not appear to have convulsions or increased muscle tone in the whole body, so the patient was easily confused with dental diseases with the diagnosis of arthritis, and dislocation,...

Stiff jaw 
Stiff jaw -
Generalized convulsions on the background of muscle spasms appear spontaneously, increasing upon stimulation with the following manifestations: Continuous generalized muscle spasms, increasing when stimulated, the patient is very painful, and typical spasticity makes the patient bends. During a seizure, the patient remains awake and is characterized by clenched fists, flexing the back and arms in a flexed or flexed position, with the legs extended, often stopping breathing when in these positions. The seizure lasts a few seconds to a few minutes or more. When seizures occur, patients are very susceptible to laryngospasms, and respiratory muscle spasms leading to hypoventilation, hypoxia, cyanosis, apnea, and possibly death.
This is a severe stage of the disease with many obvious symptoms, usually, this stage lasts 1-3 weeks with manifestations such as generalized spasticity, shortness of breath, cyanosis, sphincteric muscle contraction causing urinary retention, urinary retention, and urinary retention defecation. Severe cases also have autonomic dysfunction. So, when you have a wound, scratch, or animal bite, it is necessary to treat the wound immediately by releasing all the foreign objects in the wound and immediately going to a medical facility.

Convulsions 
Convulsions -
Symptoms of tetanus are manifested as muscle spasms accompanied by pain, first of the chewing muscles, the muscles of the face, the muscles of the back of the neck, and then the muscles of the trunk such as the chest, abdomen, and buttocks. Contraction of the lumbar muscles creates the characteristic back flexion. Spasms of the respiratory muscles affect breathing. Strong, sudden, prolonged muscle contractions cause muscle pain, which can both tear muscles and breaks bones. Other symptoms include fever, headache, restlessness, irritability, urinary retention, burning when urinating, and incontinence.
The incubation period is usually 3 to 10 days but can also be up to 3 weeks. The shorter the incubation period, the higher the risk of death. If not treated in time, tetanus will lead to dangerous complications. Common fractures will cause muscle spasms or convulsions, severe cases can be broken due to contractions. To avoid getting tetanus, after being injured, you should go to medical facilities for timely tetanus vaccination. Procedures and surgeries must be carried out in sterile facilities.
Fracture 
Fracture -
Sweating is the body's self-cooling mechanism. Your nervous system automatically activates sweat glands when body temperature rises. Most people sweat during exercise or exertion, in hot environments, or when nervous or stressed. However, the amount of sweat produced due to increased sweating is far more than normal. The spasticity makes the patient feel pain, and difficulty moving, leading to high fever, sweating, and fast heart rate,... In severe cases with manifestations: of pale skin, sweating, increased secretion of phlegm, and a high fever of 39-40 degrees Celsius or more, an increase or decrease in blood pressure, blood pressure fluctuations, and arrhythmia may stop the heart.
Tetanus is a dangerous disease, which can be life-threatening at any time, and is very contagious, so prevention is extremely necessary to protect your health and life. Currently, vaccination is considered the best way to prevent tetanus. There are many vaccines for each object, both young children and pregnant women, so everyone can and should be vaccinated to prevent this dangerous disease.

Sweat 
Sweat -
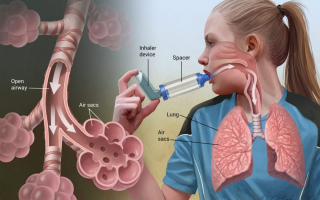
Severe muscle spasms caused by tetanus can interfere with or stop your breathing. Respiratory failure is the most common cause of death. The lack of oxygen will cause cardiac arrest and death. They have chest pain, and sharp pain when inhaling. The patient cannot take a deep breath, the deeper the breath, the more painful it is. The body is tired, has no energy, and is often shocked. It is caused by a large blood clot that interferes with the pumping and circulation of the heart, leading to a drop in blood pressure. A thrombus that has ruptured and is free-floating in a blood vessel can travel to another area of the body and block a blood vessel there.
If there is a thrombus in the venous system, the thrombus will travel from the veins to the right heart and then from the right heart into the main pulmonary artery and may become trapped there or continue to travel into either lung. When a thrombus lodges in the pulmonary artery, it blocks blood flow to the lungs to receive oxygen. If there is not enough blood to receive oxygen and move it to the left heart, the oxygen levels in the body drop dangerously and can cause damage to all organs in the body, including the brain and kidneys, or heart.

Shortness of breath and pulmonary embolism 
Shortness of breath and pulmonary embolism