Top 6 Signs and Symptoms of Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis is a dangerous infectious disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The disease is spread by the tuberculosis bacteria that are ... read more...spread out when a person with pulmonary tuberculosis coughs, talks, sneezes, or spits, which inadvertently a person in close contact can breathe in and cause disease in the lungs. Many people often ignore the signs of tuberculosis until it is discovered that the disease is already in an advanced stage, which takes a long time to treat. Therefore, early recognition of the symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis in the early stages will help control the disease better.
-
Sputum production and coughing can be caused by a variety of factors, the most frequent of which is an infection. Cough is a sign of many respiratory disorders, thus it is frequently missed or misdiagnosed as bronchitis, bronchiectasis, or common pharyngitis-tonsillitis. Sputum expectoration is a sign of increased secretions caused by bronchial airway irritation or injury. If a patient coughs for more than three weeks and medications do not relieve the cough, pulmonary Tuberculosis must be considered.
Coughs that don't go away bother the sufferer more and more at night. Infection is the most common cause of coughing and expectoration. If you have had a cough and green sputum for more than three weeks, you should consider pulmonary Tuberculosis. If you have any of the aforementioned symptoms, get medical treatment right immediately. Never be subjective, and accept it as a normal symptom
Prolonged cough and expectoration of sputum 
Prolonged cough and expectoration of sputum -
Coughing up blood is a pulmonary condition that should not be taken lightly. It functions as a "warning" signal to the body concerning the presence of various respiratory disorders such as Tuberculosis, pneumonia, lung cancer, and so on. According to World Health Organization studies, blood is a symptom in 60% of persons with pulmonary Tuberculosis. This indicates that there is damage or bleeding in your airways.
Although patients with lung abscesses, pneumonia, severe bronchitis, and lung cancer can all cough up blood, it is unquestionably a symptom of pulmonary tuberculosis. Because coughing up blood is an unrecognized early indication of the sickness that occurs as a result of a protracted incubation period. The specific symptom of this cause is that the patient spits up bloody sputum, and the amount of blood secreted may be less or more.

The coughing up of blood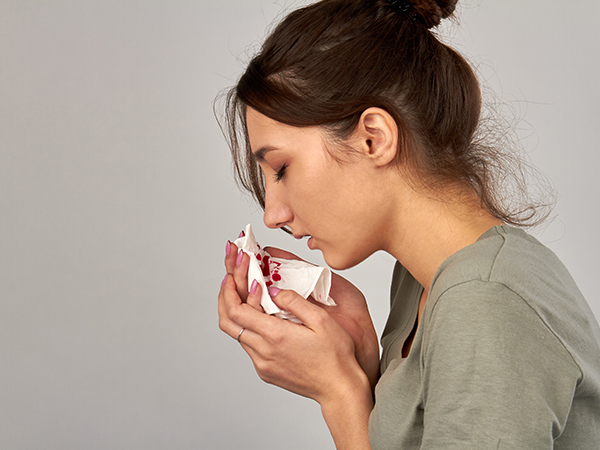 
The coughing up of blood -
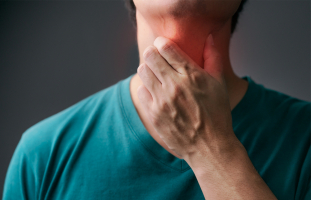
The most evident symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis are chest tightness or shortness of breath. Inhibition, shortness of breath breathing problems, and other symptoms are caused by pressure in the airways and damaged lungs and are frequently accompanied by coughing. Coughing excessively will induce bronchial inhibition, resulting in shortness of breath and chest pain. If the lungs are injured, the capacity to exchange gases will be more difficult. Tuberculosis patients frequently report dull chest pains, particularly when coughing.
When air and fluid overflow excessively, the lungs are compressed to a very tiny capacity. This amount is insufficient to provide adequate gas, leading the patient to suffocate and die. This necessitates close monitoring and direct consultation with the treating physician. The doctor will summarize and assign more tests for evaluation. It is best to seek medical attention early, especially if shortness of breath increases. If you have trouble breathing, you should go to the emergency room.
Short breath and chest pain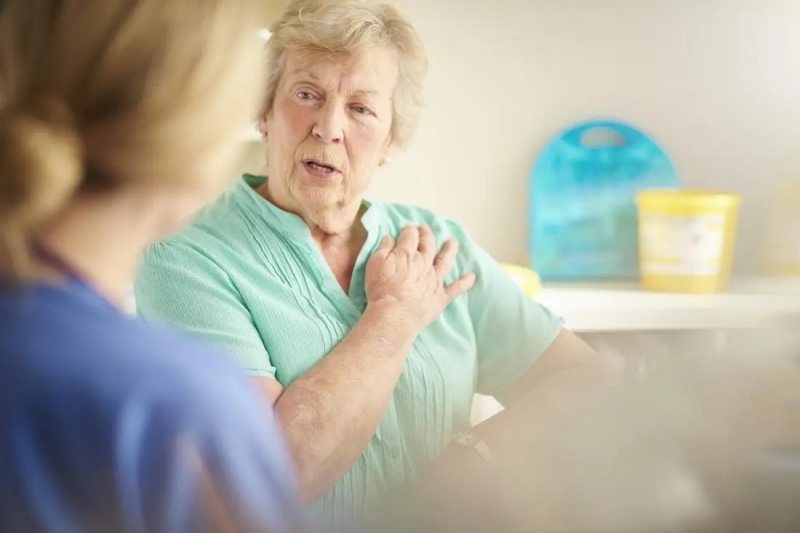 
Short breath and chest pain -
Fever can take numerous forms, including high fever and irregular fever, but the most frequent is moderate fever or afternoon cold spikes. Those who have the above-mentioned fever symptoms together with respiratory symptoms such as cough, sputum, and coughing up blood,... must be considered to have pulmonary tuberculosis. The immune system's response to microorganisms in the body is seen in this measurement. Patients with pulmonary tuberculosis have a slight fever, generally just in the afternoon, rather than a severe or uncommon fever.
Many recent studies have discovered an increase in cortisol levels in patients with acute pulmonary tuberculosis. Cortisol levels fluctuate throughout the day, peaking in the late evening and dropping in the morning, resulting in a rise in temperature from the evening and a fever in the afternoon. It should be noted that cells can alter cortisol activity, therefore not all tuberculosis patients exhibit this evident manifestation. If the fever is accompanied by the symptoms mentioned before pulmonary tuberculosis should be considered.
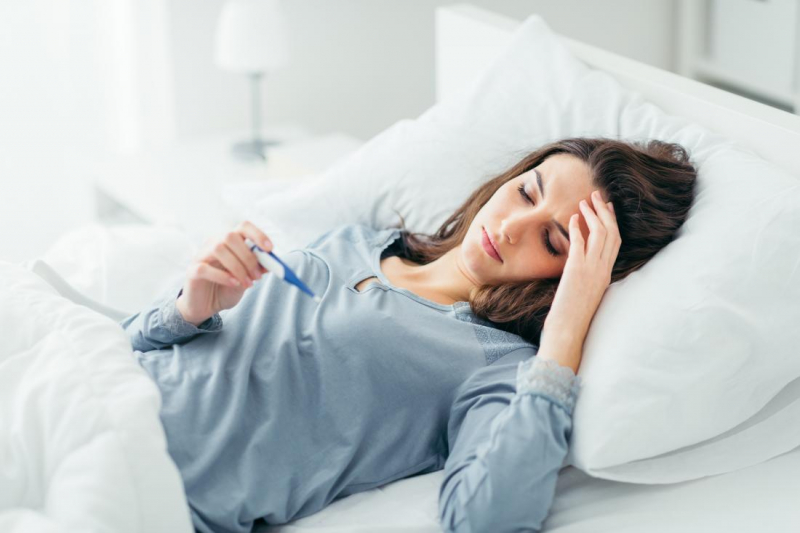

Fever in the afternoon 
Fever in the afternoon -
Weight loss can be caused by a variety of conditions, including diarrhea, HIV, malnutrition, anorexia, and cancer. Weight loss is not an evident symptom of tuberculosis, but it is a sure marker if you are a tuberculosis patient. People with pulmonary tuberculosis frequently experience fatigue, pain, loss of appetite, weight loss, mental decline, and other symptoms, which are exacerbated by coughing and chest pain.
Remember the adage "prevention is better than cure". If you have the aforementioned symptoms and have negative respiratory symptoms, you should immediately think of pulmonary tuberculosis and seek medical attention. If you diagnose the condition early, you have a higher chance of receiving the appropriate therapy. Otherwise, it will bring many difficulties and negatively impact your health and your quality of life.

Anorexia and weight loss 
Anorexia and weight loss -
Tuberculosis sufferers experience a lack of vigor, sluggishness, insufficient energy to work, and a decreased appetite. As a result, many people mistake it for anorexia or work and life which are related to stress. When you are tired, you do not have the energy or concentration to think or operate properly.
In fact, tiredness is a fairly popular symptom, potentially owing to psychological impacts, health issues, stress, tension generating inhibitions that make you fatigued, sleep disturbed, and anorexia. From chronic pain and symptoms that prevent you from being as healthy as you should be. Prolonged weariness accompanied by characteristic symptoms is a red flag for tuberculosis that you should be aware of.

Tired 
Tired