Top 6 Signs and Symptoms of Zinc Overdose
Zinc is a mineral that is required for over 100 chemical processes in your body. It is required for growth, DNA synthesis, and flavor perception. It also aids ... read more...in wound healing, immune system function, and reproductive health. Zinc-rich foods include red meat, chicken, shellfish, whole grains, and fortified cereals. Zinc poisoning can, however, arise through dietary supplements, such as multivitamins, or from unintentional intake of zinc-containing household goods. The most prevalent indications and symptoms of zinc overdose are listed here.
-
The most prevalent adverse symptoms of zinc overdose are nausea and vomiting. A 2012 assessment of 17 trials on the usefulness of zinc supplements for treating the common cold discovered that zinc may shorten the duration of a cold, but it was not without side effects. In fact, the trial participants who received zinc had a 64% greater incidence of nausea than the control groups, according to the evaluation.
Although vomiting may aid in the removal of hazardous levels of zinc from the body, it may not be sufficient to avoid subsequent difficulties. Seek medical attention right once if you have ingested dangerous levels of zinc.

Nausea and Vomiting 
Nausea and Vomiting -
Typically, stomach discomfort and diarrhea coexist with nausea and vomiting. Approximately 40% of participants in a 2021 review on zinc supplementation for the common cold complained of gastrointestinal pain and diarrhea. Although less common, gastrointestinal discomfort and bleeding might occur.
An individual developed intestinal hemorrhage after using 220 mg of zinc sulfate twice a day to treat acne in one case study. Although zinc chloride is not included in supplements, accidental intake of household goods can result in poisoning. Zinc chloride is found in adhesives, sealants, soldering fluxes, cleaning solvents, and wood finishing products.
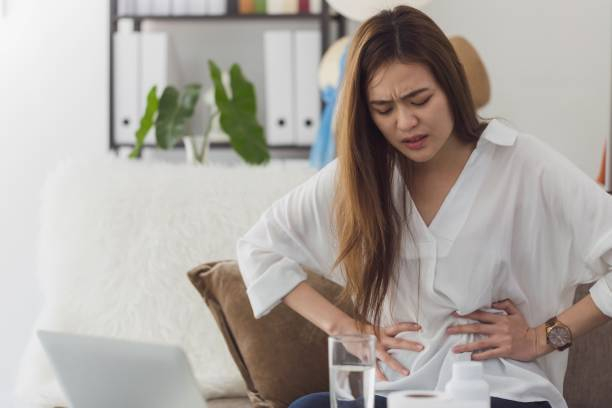

Stomach Pain and Diarrhea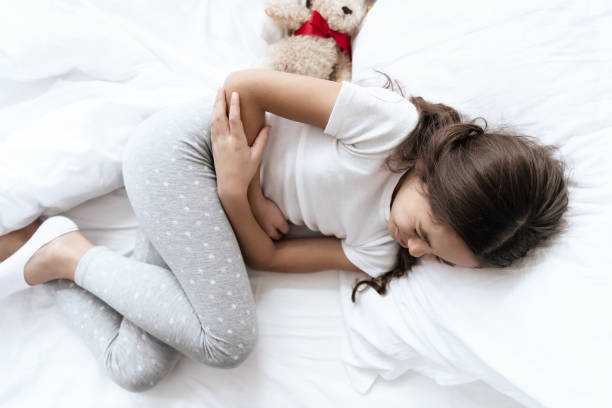 
Stomach Pain and Diarrhea -
"Good" high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol reduces your risk of heart disease by removing cholesterol from your cells and avoiding the formation of artery-clogging plaque. Adults should have HDL levels higher than 40 mg/dL, according to health experts. Lower levels increase the risk of heart disease.
A 2015 meta-analysis discovered that taking roughly 40 mg of zinc per day can reduce low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol by 11.25 mg/dl in non-healthy people. According to the researchers, zinc supplementation in non-healthy persons can induce a considerable increase in HDL cholesterol. While many factors influence cholesterol levels, these findings are worth considering if you use zinc supplements on a daily basis.

Low “Good” HDL Cholesterol 
Low “Good” HDL Cholesterol -
Zinc is essential for your taste buds. In fact, zinc deficiency can cause hypogeusia, a malfunction in your sense of taste. Surprisingly, zinc in excess of the allowed amounts can induce taste changes, such as a foul or metallic taste on your tongue. This symptom is typically observed in trials looking at zinc lozenges (cough drops) or liquid supplements for treating the common cold. While some trials show positive outcomes, the dosages used are frequently much over the UL of 40 mg/day, and side effects are widespread.
Some people, for example, may take zinc dosages of up to 100 to 150 mg/day for months with few side effects. As a result, a zinc intake of 80 mg/day for 1-2 weeks beginning with the first symptoms of the common cold is unlikely to produce long-term harm. If you use zinc lozenges or liquid supplements, keep in mind that these symptoms may persist even after therapy.
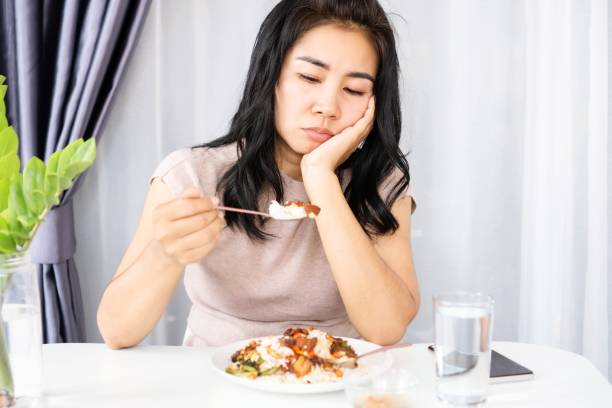

Changes in Your Taste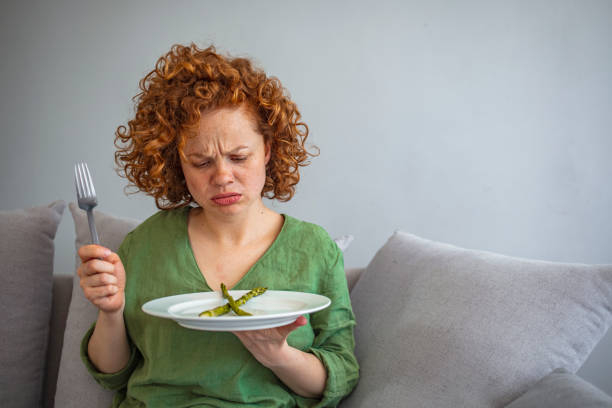 
Changes in Your Taste -
In your small intestine, zinc and copper fight for absorption. Zinc doses over the approved UL might impair your body's capacity to absorb copper. This can lead to a copper shortage over time. Copper is a necessary mineral. It is required for red blood cell synthesis because it assists in iron absorption and metabolism. It is also involved in the production of white blood cells. Red blood cells carry oxygen throughout your body, whereas white blood cells play an important role in your immune system.
The copper shortage caused by zinc is linked to a number of blood disorders:
- Iron deficiency anemia: A shortage of healthy red blood cells caused by a lack of iron in your body.
- Sideroblastic anemia: A deficiency of healthy red blood cells caused by an inability to correctly digest iron.
- Neutropenia is the absence of healthy white blood cells as a result of a disturbance in their development.
Copper Deficiency 
Copper Deficiency -
Zinc is essential for immune system function, and a zinc deficit can impair it. Too much zinc, on the other hand, might inhibit your immune response. Zinc toxicity is uncommon, and immune function deficiencies are typically caused by concomitant anemias and neutropenia, although they can also occur independently of zinc-induced blood problems. Excess zinc inhibited the function of T cells, a kind of white blood cell, in test-tube tests. T cells play an important part in your immune response by adhering to and killing infections.
Taking more zinc than the recommended daily allowance may result in flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills, cough, headache, and exhaustion. These symptoms can arise in a variety of situations, including mineral toxicity. As a result, identifying zinc poisoning can be challenging. For suspected mineral poisoning, your doctor may want a full medical and nutritional history, as well as blood testing. If you're taking supplements, make sure to tell your doctor about them.

Frequent Infections 
Frequent Infections