Top 10 Symptoms of Hepatitis E
Symptoms of Hepatitis E can range from being extremely serious to fatal. A person may experience a severe loss of appetite before their illness manifests any ... read more...symptoms. Along with general malaise, nausea, vomiting, and frequently fever, the patient may also have these symptoms.
-
Physical discomfort is frequently connected to fever, and most people feel better after getting treatment for their fever. However, you could or might not need medical attention for the fever alone, depending on your age, physical health, and the underlying reason for your fever. Numerous scientists think that fever is the body's natural defense mechanism against illness. Fever can also have a variety of non-infectious causes.
The reason for the fever determines the appropriate treatment. For a bacterial infection like strep throat, for instance, antibiotics would be prescribed. Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen and naproxen are the most frequently used therapies for fever. Aspirin shouldn't be given to kids or teenagers because Reye's syndrome has been linked to it.
There are times when you may experience a "fever of unknown origin," in which case the underlying condition may be unusual or obscure, such as a persistent infection, a connective tissue disorder, cancer, or another issue.
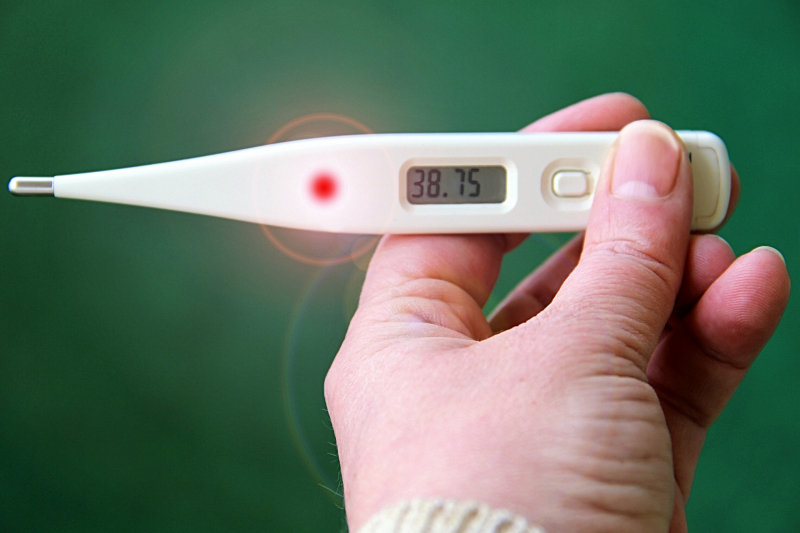
Photo by Gundula Vogel via Pixabay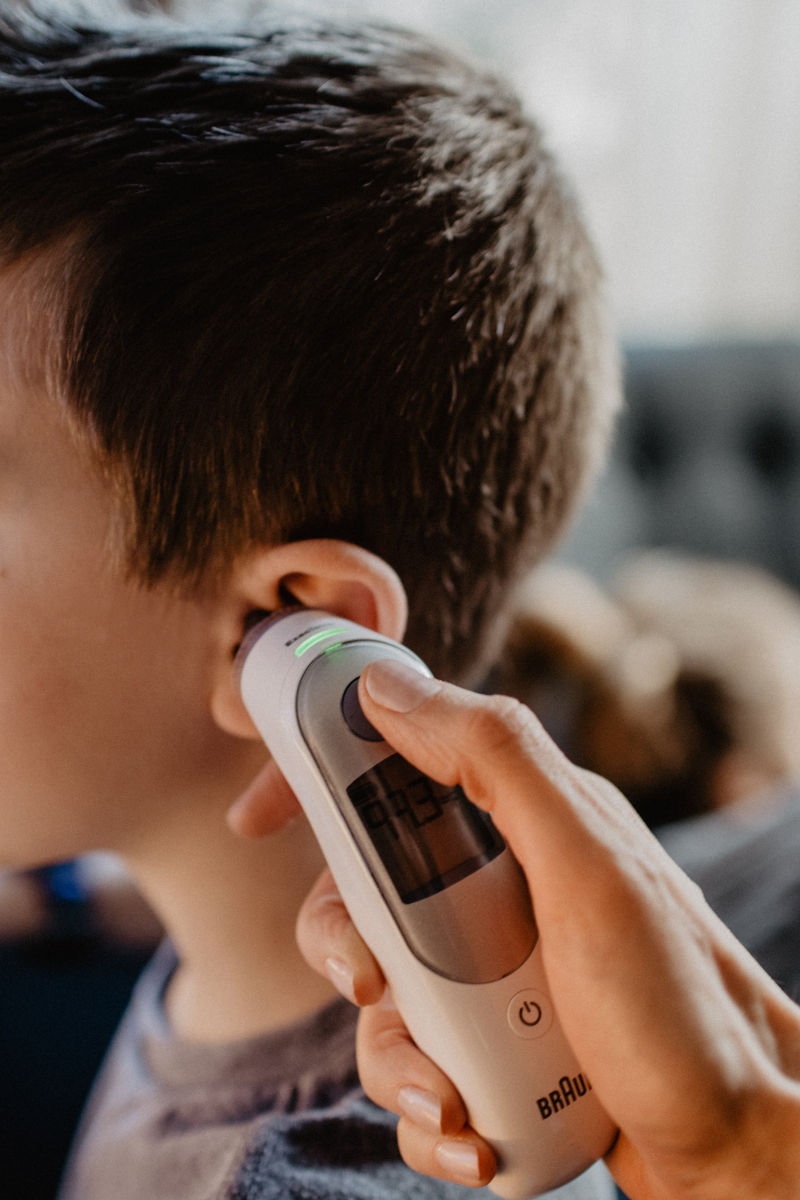 
Photo by Kelly Sikkema via Unplash -
Vomiting, also known as emesis and throwing up, is the forceful ejection of the stomach’s contents. Vomiting is a frequent sign of a wide range of minor to major illnesses, disorders, and ailments. It might or might not make you feel sick. Depending on the underlying disease, problem, or condition, vomiting may come along with other symptoms. Other body systems may be affected by symptoms that frequently affect the digestive system.
In some cases, vomiting may occur with other symptoms that might indicate a serious or life-threatening condition that should be immediately evaluated in an emergency setting. Treatment for vomiting is not usually required. The cause, the intensity, and your comfort will all influence whether you need therapy. Medications are also available to treat vomiting.
There are several temporary home remedies to help manage vomiting and prevent it when nausea occurs. Avoiding alcoholic beverages, coffee, and spicy, fatty, or fried foods; avoid strong scents, such as those from cooking; and sip on clear, cool, sweet liquids often, such as ginger ale and non-citrus juices

Photo by hhach via Pixabay 
Photo by Clker-Free-Vector-Images images via Pixabay -
Normal stools can come in different tones of brown, largely depending on your diet. Stools that are pale are abnormal. Your liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and other components of your biliary system may not be draining properly if your feces are pale or clay-colored. However, the pale stool is abnormal and one of the signs of hepatitis E. If you experience this kind of odd shift, you should see a doctor right away for an evaluation. The Hepatitis E virus is what causes the pale or clay-like feces, which can be a sign of a dangerous upcoming underlying problem.
Pale stool can occasionally be a symptom of liver illnesses such as cirrhosis and hepatitis. The stool can also become white due to the usage of aluminum hydroxide in some drugs, such as antacids, and the white material barium, which is used for X-rays of the digestive system.

Photo by Hafidz Alifuddin via Pexels 
Photo by Alexa via Pixabay -
A broad loss of appetite or interest in food characterizes anorexia. Some people immediately conjure up the eating disorder anorexia nervosa when they hear the word "anorexia." However, there are distinctions between the two. Loss of appetite is not a symptom of anorexia nervosa. Anorexics consciously forgo eating to avoid gaining weight. Anorexics (those who lack appetite) accidentally lose interest in food. An underlying medical problem is frequently the cause of appetite loss. If you observe a dramatic decline in your appetite, consult your doctor because anorexia is frequently a sign of a medical issue. In theory, any medical condition could cause loss of appetite. Appetite loss is one of the signs and symptoms of Hepatitis E.
Symptoms of hepatitis E can include fatigue, poor appetite, stomach pain, nausea, and jaundice. But many hepatitis E patients, particularly young children, show no signs of the disease. The majority of patients experience complete recovery without any consequences from the illness, with the uncommon exception of chronic hepatitis E in those with weakened immune systems. In the United States, there is currently no hepatitis E vaccination.

Photo by SHVETS production via Pexels 
Photo by cottonbro studio via Pexels -
The abdomen is that portion of the body that is between the chest and the pelvis. Between your chest and your groin area, your body may experience abdominal pains. You could experience stomach cramps, localized pain, or generalized pain. Abdominal discomfort might be strong, achy, dull, or sharp. Localized discomfort only exists in one area of the abdomen. Such discomfort is typically brought on by issues with a particular organ. With no need for hospital treatment, this discomfort varies and could go away on its own.
Significant abdominal discomfort is caused by bacterial, viral, or parasitic illnesses that harm the intestines and stomach, including the hepatitis A virus in this instance. You should seek emergency medical assistance if the pain is so severe that it prevents you from sitting still or requires you to curl up into a ball to feel comfortable. Despite the fact that this virus is not persistent, it has been reported to be contagious, therefore you should focus on getting protection against it. This list of hepatitis symptoms is provided to you with the intention of raising community awareness.

Photo by Andrea Piacquadio via Pexels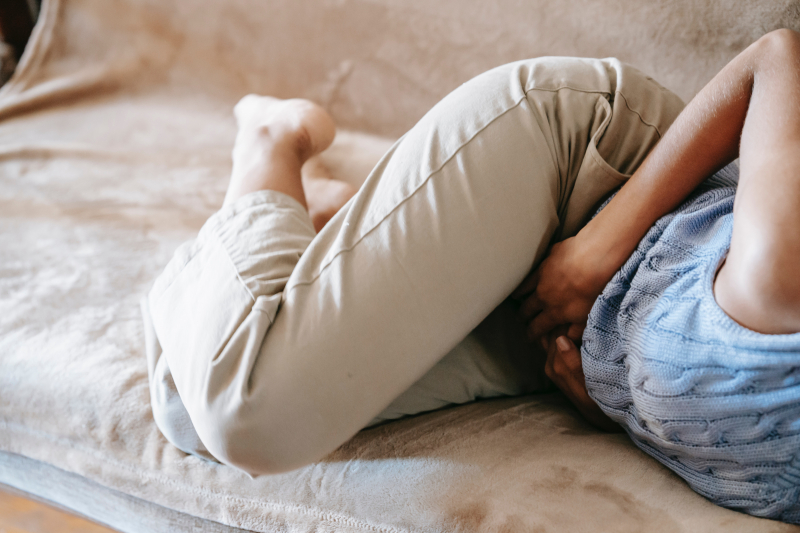 
Photo by Sora Shimazaki via Pexels -
Hepatitis E virus infections frequently go unnoticed at first, but if they persist for a long time, they may develop consequences. Inflammation and soreness in the joints is one of them. Joint pain can occasionally be the initial sign of the hepatitis E virus, and it can occasionally be an indication of arthritis. Hepatitis E virus is linked to other illnesses including fibromyalgia that can lead to joint pain.
The immune system plays a role in how the hepatitis E virus might cause joint pain. The immune system becomes active as the body works to eliminate and discharge the virus, which might result in joint inflammation. This symptom often goes away after the immune system eliminates the acute hepatitis E virus.

Photo by Tree of Life Seeds via Pexels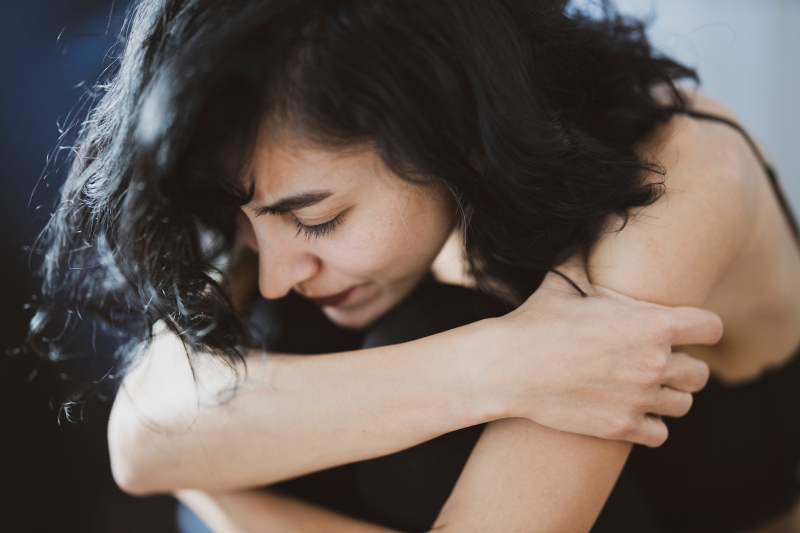 
Photo by Engin Akyurt via Pexels -
Dark urine is usually the first specific sign of acute hepatitis E, followed a day or two later by jaundice (yellow skin and eyes) and pale-colored bowel motions. Normal urine is light to dark yellow due to the urochrome. Various pigments and compounds found in foods and certain medications can change the color of urine. However, dark urine indicates liver problems. If there is an infection, tumor, etc, the urine changes color from light yellow to dark. It is recommended that patients who see regular yellow urine accompanied by jaundice, fatigue, abdominal discomfort, and pain, need to promptly do liver-related tests.

Photo by Markus Spiske via Pexels 
Photo by CDC via Unplash -
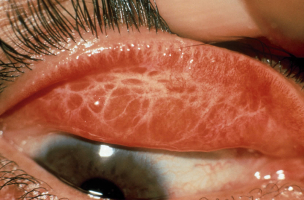
One of the many typical signs of Hepatitis E is "jaundice," which is the medical term for a yellowing of the skin and eyes. Jaundice is not a disease in and of itself, but it can be a symptom of a variety of illnesses. Jaundice appears when your body has an excessive amount of bilirubin. The liver produces bilirubin, a yellow pigment, as a result of the breakdown of dead red blood cells. The liver normally gets rid of bilirubin and old red blood cells.
Additionally, jaundice may be an indication of a serious problem with your pancreas, liver, gallbladder, or red blood cells. An infection, an autoimmune condition, significant blood loss, substances such as drugs or alcohol, or prescription medications can all cause this liver inflammation. Hepatitis E viral infection causes this particular form of liver inflammation. The hepatitis E virus can be warded off with regular vaccination. Therefore make sure you're immunized against hepatitis E.
Owner: Dr. Eric Berg DC via Youtube Owner: Daniel González M.D. via Youtube -
Usually, hepatitis E lasts only a few days to a few weeks with mild symptoms, rarely leaving long-term consequences like other hepatitis. After being exposed to the virus that causes the disease, they will incubate in the body for about 15 - 60 days. At first, the patient is often tired, the body temperature gets high, and the whole body aches. These symptoms are quite similar to the common cold, so it is easy to confuse and ignore.
Weakness or fatigue is one of many common symptoms of hepatitis E. Fatigue, which can range from mild to severe, can have an impact on every facet of life. While some people only feel sleepy occasionally, others are always fatigued. It takes patience to deal with exhaustion because there are no simple fixes. But you can do the following things to help control it: regular exercise, well-balanced diets, healthier sleeping habits, afternoon naps, etc.

Photo by Zohre Nemati via Unplash 
Photo by Christian Erfurt via Unplash -
if you experience nausea when eating. This is associated with the liver's production and excretion of bile but may also be a symptom of another sickness. Lipids (fats) are emulsions and broken down by bile so they may be digested. The feeling of nausea and loss of appetite is one of the warning signs that the liver is having problems.
A healthy diet, regular exercise, and enough sleep are three components of a healthy life. Avoid consuming liver-damaging foods including alcohol, beer, cigarettes, caffeine, and refined carbohydrates in excess. A daily glass of lemon water can aid in toxin removal and reduce the workload of the liver. Consume a lot of fresh, dark-green veggies, like spinach and green cabbage. Consuming a lot of water and eating fruits like walnuts, avocados, and berries are also highly healthy.

Photo by 愚木混株 Cdd20 via Pixabay 
Photo by Christian Dorn via Pixabay