Top 10 Things You Should Know About The Gambia
The Gambia, Africa's Smiling Coast, is known for its friendly, welcoming, and hospitable people. Those who have visited the West African country have also ... read more...raved about its beautiful beaches, which are never crowded, dubbing it a beach lover's dream. Do you want to know more about the country? Here are ten interesting things you should know about the Gambia.
-
The Gambia has a total area of 11,295 km2 and is less than 50 kilometers (31 miles) wide at its widest point (4,361 sq mi). Water covers approximately 1,300 square kilometers (500 square miles) (11.5 percent) of the Gambia's land area. It is the African continent's smallest country. In terms of total area, the Gambia is slightly smaller than the island of Jamaica.
Senegal surrounds the Gambia on three sides, with 80 km (50 mi) of coastline on the Atlantic Ocean marking its western extremity. The Gambia is commonly referred to as the smiling coast of Africa. Despite its small size, the country has a dense population of approximately 2.28 million people. The most people are concentrated around the Gambia's capital, Banjul, and its increasingly urbanized landscape.

africafreak.com 
araioflight.com -
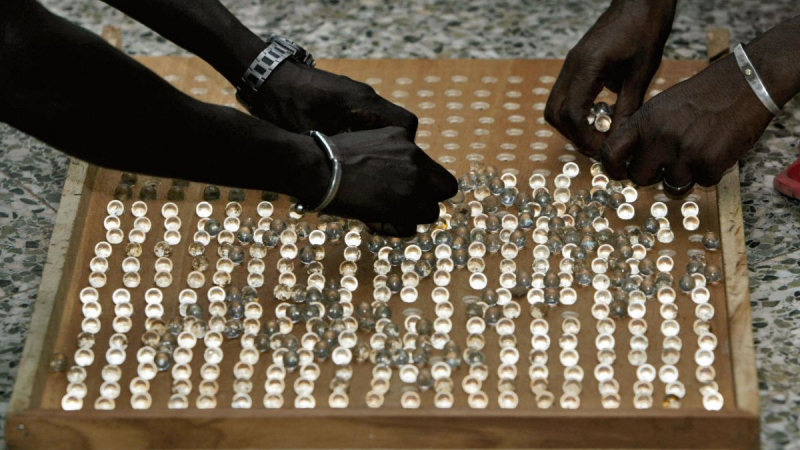
The Gambia holds its elections using a unique voting system that was introduced in the early 1960s to address the country's high levels of illiteracy. This system is based on the use of tokens (clear-glass marbles) that are cast in separate iron-made drums (which serve as ballot boxes) for each individual party/candidate. Each political party and candidate in an election has a drum painted with its own identifying colors, party symbols, and photographs.
On election day, drums are placed behind the polling booths at polling stations. After receiving marbles, voters proceed to the polling booth to vote. When a marble is dropped into the drum of the chosen party/candidate, it strikes a bell, indicating to the audience in the polling station that a vote was cast. Polling officers seal the drum with sand or sawdust to prevent other sounds from being heard. It's also worth noting that, because the sound is similar to a bell, bicycles are prohibited from being in close proximity to polling places on election day. After the voting process has ended, votes are counted by placing the marbles into special trays (with either 200 or 500 holes), a simple system that allows counting officials to quickly ascertain the number of votes cast in each drum. This is unquestionably one of the interesting things you should know about the Gambia.

cnn.com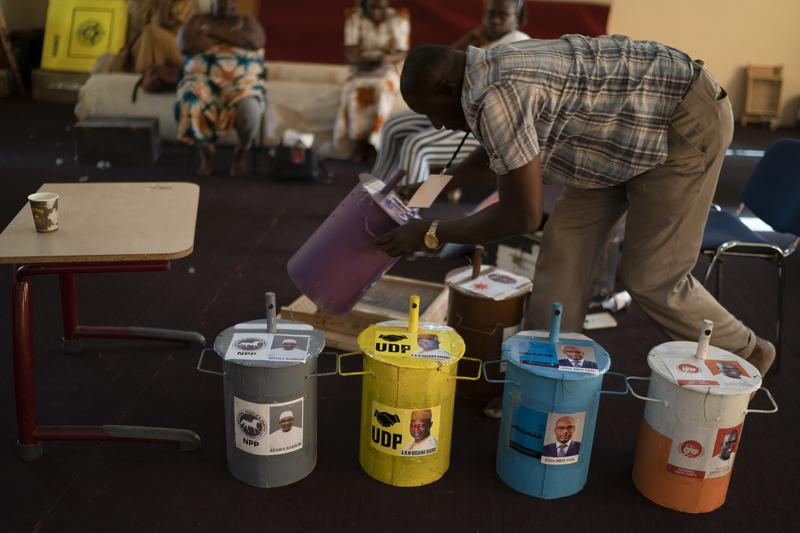 
chinadailyhk.com -
The Mandinka, Fula, and Wolof are The Gambia's most populous tribes. This makes learning any of the local languages more difficult because there are several variations, though English is widely spoken as a former British colony.
The Mandinka, also known as the Mandingo, are a West African ethnic group who are descended from the Mali Empire. The Mandinka arrived in The Gambia during the 14th century, at the height of the Mali Empire. Many people believe that the reasons for emigrating to the west include the need to find a favourable climate for agriculture in the Senegambia region in order to boost crop production. Another reason given was that many Mandinka merchants desired to relocate to areas with less trade competition.
The Fula people are thought to be the world's largest nomadic ethnic group, accounting for nearly one-fifth of The Gambia's population. During the reign of the great Ghana Empire, the Fula people arrived in the Senegambian region. Fula in The Gambia were said to have migrated from Senegal, Guinea, and Mali, but settled there in the 1800s. In Gambia, the Wolof ethnic group (or Jollof, Jolof as they are sometimes known) accounts for 16% of the population and is the third largest ethnic group. They can be found in fairly large numbers in the Gambian areas of Jokadu, Baddibu, Saloum, and Niumi, but the vast majority are found in Senegal.

gambia.co.uk 
mummytravels.com -
Agriculture, one of the things you should know about the Gambia, is the most important sector in the Gambian economy and one of the top development priorities, especially in the new global climate of rising food and oil prices. Agriculture is a major economic driver in The Gambia. It accounts for roughly one-quarter of GDP and employs 75% of the workforce. Peanuts (groundnuts), rice, millet, and sorghum are the main agricultural products grown locally. Mangoes and cashews are the most common fruits grown. These are also the most important cash crops, with rice serving as the staple crop. Only about 38% of the country's total land area, or about 430,000 Ha, is arable.
The Gambia has a lot of potential for irrigated agriculture, thanks to the River Gambia, rainwater that can be harvested, and fossil water that can be drilled. It also has a weather pattern that is suitable for nearly all types of production. The Ministry of Agriculture has a mandate to develop and modernize agriculture, and it states that it will provide all necessary support and incentives to any serious investor who wants to invest and operate in support of the government's efforts to develop the sector.

ifad.org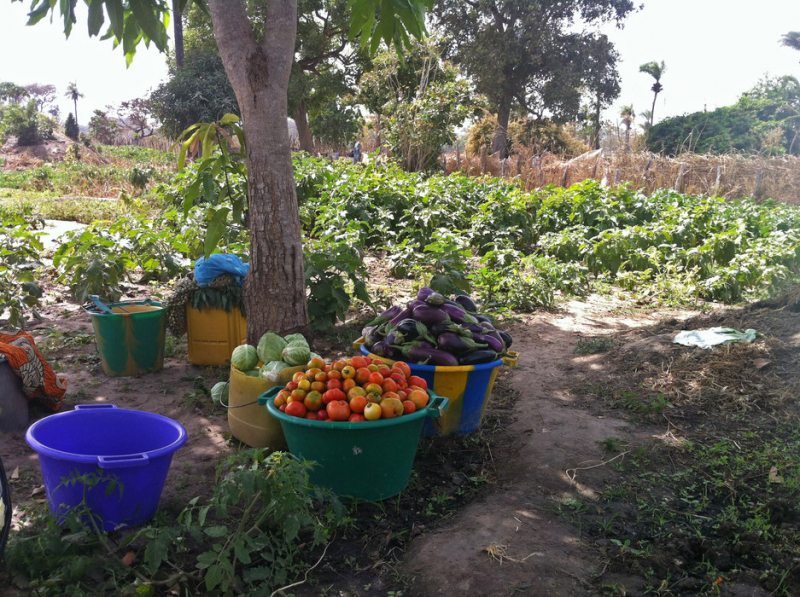 
panafricanvisions.com -
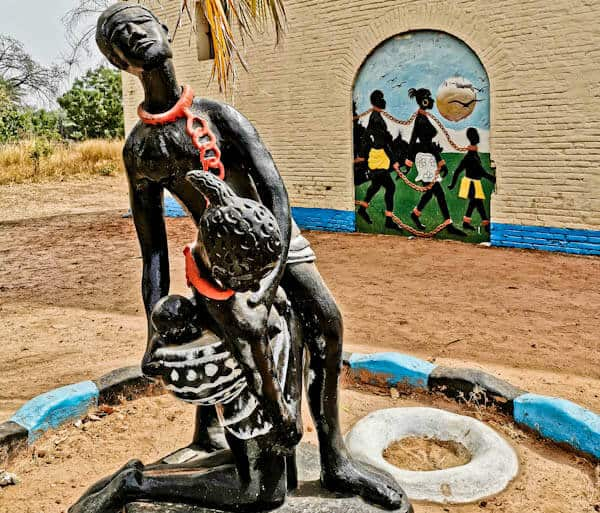
The Gambia was once at the epicenter of the slave trade, and Kunta Kinteh Island, formerly known as James Island, was a major stop on the Transatlantic slave trade. In his best-selling novel Roots: The Saga of an American Family, American author Alex Haley highlighted the slave trade from this region. The book tells the story of Kunta Kinte, a seventeen-year-old kidnapped from The Gambia and sold as a slave, and seven generations of his descendants in the United States. In 1977 and 2016, Roots was adapted for a popular TV miniseries.
Kunta Kinte Island is especially significant because of its connection to the beginning of the slave trade and its abolition. Because of its significance during the transatlantic slave trade, the island was designated a World Heritage Site in 2003. Hundreds of thousands of slaves set sail from this small island for the New World. The island was also a key player in the conflict between European colonial powers present in the region. During this time, Spain, France, Germany, and England were all vying for control due to its strategic trading position.

onlybyland.com 
cnn.com -
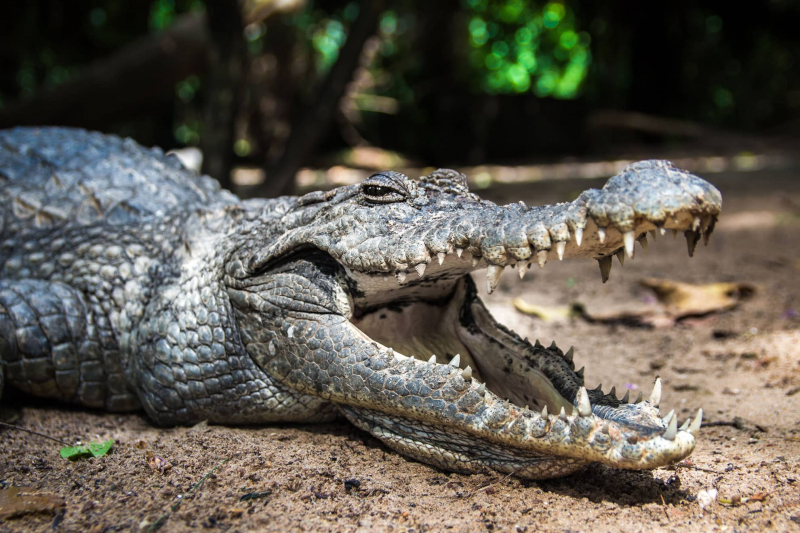
The Kachikally Crocodile Pool (also known as Katchikally or Katchikali) is located on a 9-acre site in the southern section of Bakau Old Town in The Gambia's Kombo St. Mary District, 12 kilometers west of Banjul. A museum of ethnography, a mini-forest nature trail, a souvenir shop, and a refreshment bar are also part of the complex. A parking space is also available just outside the front door.
Local Gambians know the Kachikally Sacred Crocodile Pool for its healing powers and as a place where people come to pray for blessings. It is sometimes regarded as a last resort for infertile women seeking to conceive. Many others with long-term illnesses or misfortune come to the pool to wish them luck and offer kola nuts, cloth, and other offerings in return to the Bojang family and the crocs. Sacred rituals are still held here on occasion, often accompanied by dancing and drumming; however, most of the time, the only visitors are tourists. The place is unquestionably one of the interesting things you should know about the Gambia.

wikipedia.org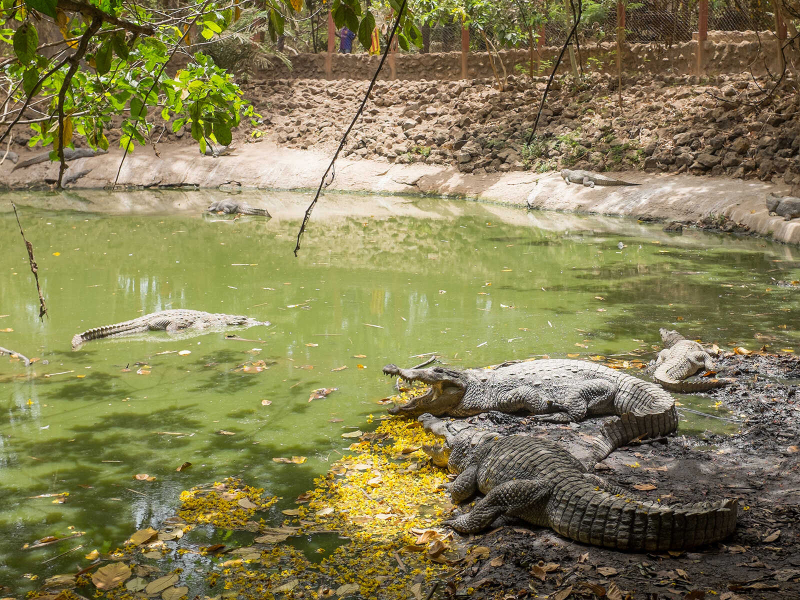 
mustseespots.com -
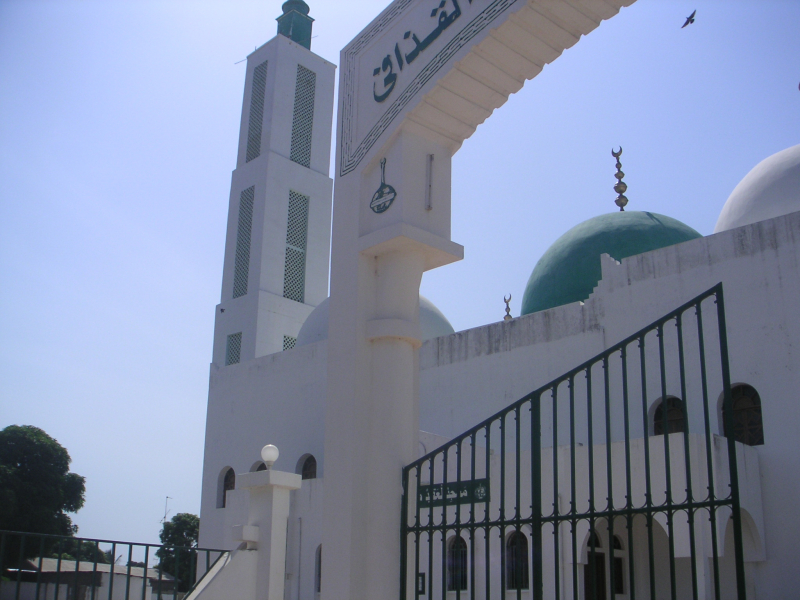
President Yahya Jammeh declared the Gambian is an Islamic republic, saying he wanted to further distance the west African state from its colonial past. The tiny, formerly secular country – named after the river from which British ships are said to have fired cannonballs to secure its borders – has joined the ranks of other officially Islamic republics such as Iran and Afghanistan.
The religion has a visible impact on Gambian life, but it has not completely replaced traditional beliefs in the majority of its adherents. Most Gambians still practice wearing the Juju (Terre), praying at sacred crocodile pools, ancestor worship, animism, and other practices. Some Christians are included in this. The mosque (Juma) or its smaller counterpart, the Jaka, is central to almost every village. It is from these places of worship that the call to prayer is made with Friday being the Muslim Sabbath. The Islamic Courts of the Gambian dispense justice in relation to the areas allowed it by the Government and apply Malikite tenets.

wikipedia.org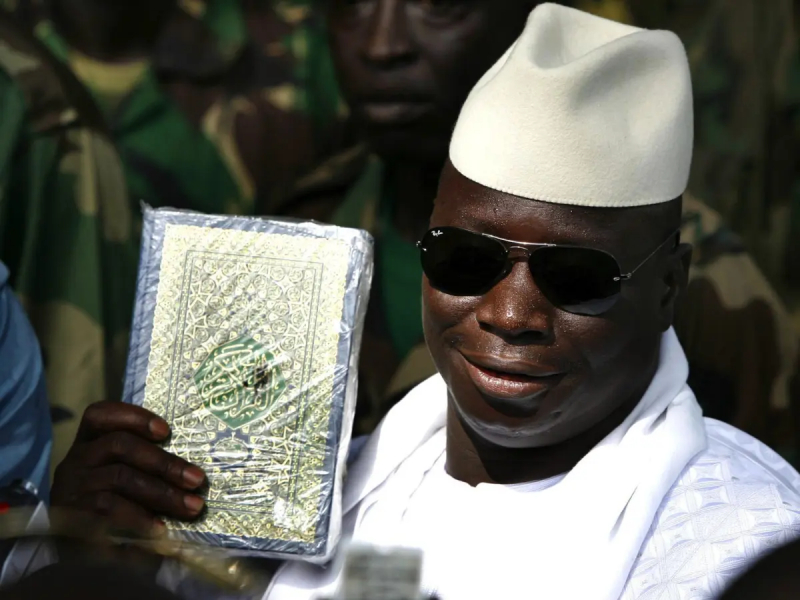 
qz.com -
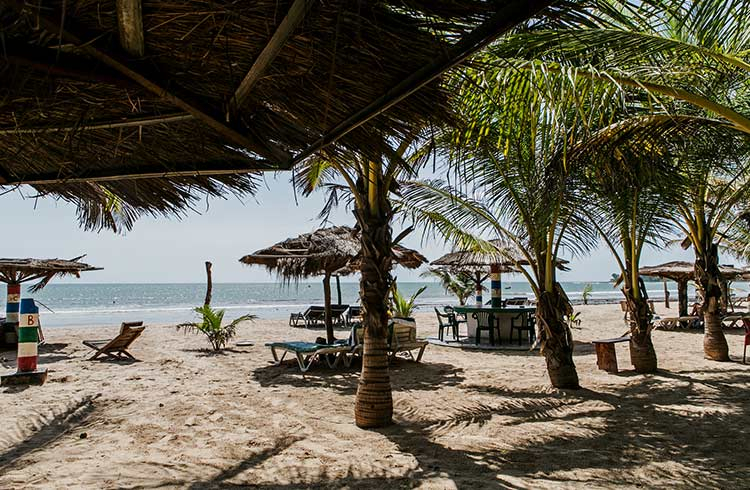
The Gambia is arguably one of the safest and friendliest places for visitors to explore and, upon arrival, it’s easy to understand why it’s garnered such an admirable reputation. "The Smiling Coast", the origins of its nickname, however, were devised in a New York boardroom, and not on its sun-soaked beaches.
The tourism industry is an important part of The Gambia's economy, and it is the industry that provides the most job opportunities for the country's youth. Since the early 1960s, the country has established itself as an important player in the global hospitality industry. The Gambia is known for its spectacular natural landscape, ethnic diversity, religious tolerance, and delectable local cuisine. Its hotels, spas, picturesque riverside villages, and a plethora of one-of-a-kind amazing wonders all serve as tourist magnets. It also has a number of historical buildings, monuments, and archeological sites that have been designated as UNESCO World Heritage sites.

worldnomads.com 
wanderlust.com -
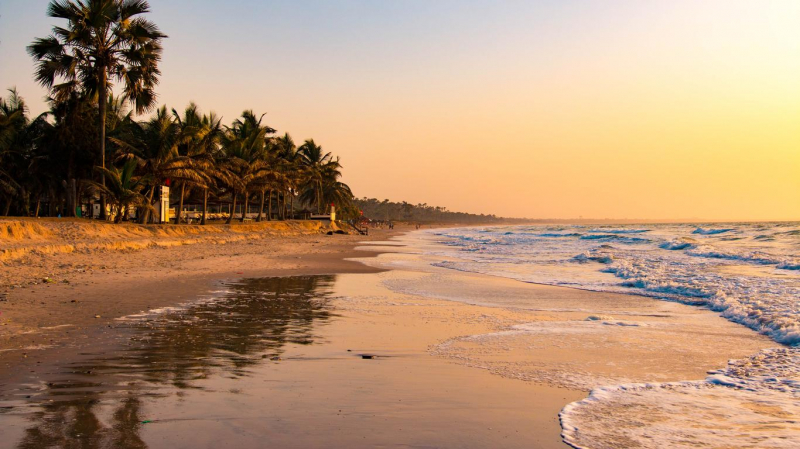
The Gambia is one of several countries where the capital is not the largest city. Serekunda, the country's largest city and commercial hub, is located 13 kilometers (8 miles) southwest of Banjul. Although Banjul is the capital, its location on an island limits its development, which opens up opportunities for Serrekunda. In 2006, the population was 335,733.
The name Serekunda literally means "the Sere family's home." West of Serekunda, there are numerous tourist destinations, particularly seaside resorts such as Bakau, Fajara, and Kotu. Serekunda is also known for its many historic mosques. Serekunda has a well-kept traditional market where you can buy baskets, wood carvings, jewels, fruits and vegetables, and other local specialties. Apart from traditional features, Serekunda has many upgraded restaurants with Italian and Asian menus, such as Gfc, Broadway Fast Food & Restaurant, and Youth Monument Bar & Restaurant, to cater to the tastes of overseas tourists.

kayak.com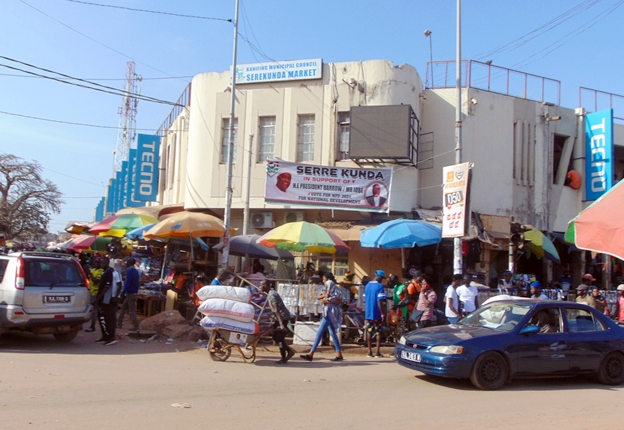 
chronicle.gm -
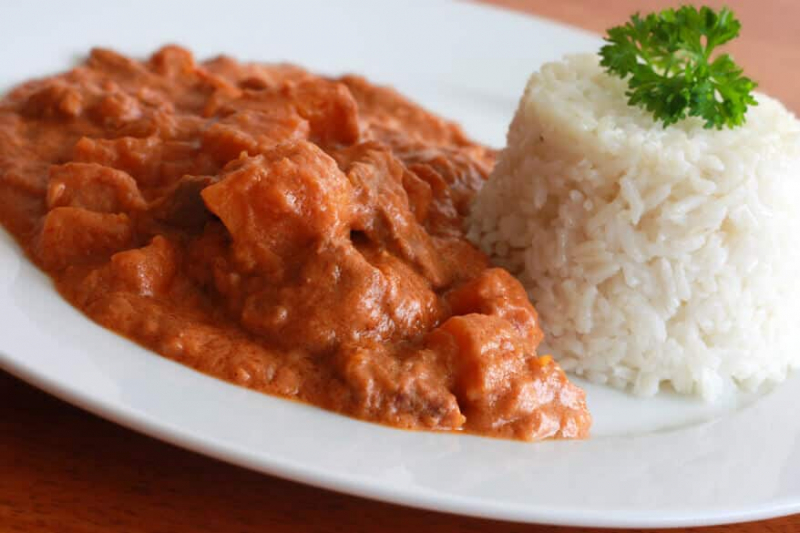
Gambia's national dish, one of the things you should know about the Gambia, is Domoda. It's a delicious "groundnut stew" (peanuts) made with whatever vegetables are in season, usually pumpkin or sweet potatoes, and a saucy base. Whether vegetarian or with meat, the foundation is fairly consistent: A rich and flavorful sauce made with ground peanut paste (or natural, unsweetened peanut butter), fresh tomatoes, and tomato paste. Caramelized onions, chicken and tomato stock, and hot chili peppers are also included. Maggi bouillon cubes are widely available in many parts of Africa and are commonly used in African cooking, including this dish.
Because meat is quite expensive in Gambia, the vegetarian Domoda version is more popular than the meat version. The peanut sauce is rich and flavorful, made from ground peanuts, tomato paste, and fresh tomatoes with onions or chili peppers. This hearty dish is said to taste even better the next day when reheated, thanks to the visually appealing, vibrant colors of the vegetables served over white rice.

daringgourmet.com 
pinterest.com