Top 10 Tricks You Can Try on Your Own Brain
With the exception of times when you are chemically changed, really sleepy, or overly smitten with a handsome person you're trying to impress, your brain is ... read more...nearly always there when you need it. And even if your brain is a biological marvel that is capable of amazing things, it is only human. It's doubly astounding because it's the one assisting you in playing the tricks in the first place, but you can perform some tricks on it if you work hard enough. Let's look at ten of the best ones now.
-
Pain has a significant psychological component, but how significant may surprise you. Things like alien hand syndrome and phantom limb syndrome demonstrate how your brain's view of how your body actually is can differ greatly from reality while still persuading you that it is true. Even with chronic diseases, a skewed body image can actually alter how your mind experiences pain, and it can be tricked in some surprising ways.
In one study, those with persistent arm pain were instructed to look at the painful arm, make a few motions, and then rate the pain they experienced thereafter. The other three involved binoculars, while the first was simply normal. Under various circumstances, they repeated this four times. The other three involved binoculars, while the first was simply normal. They examined the arm in three different ways: without magnification, with increased magnification, and last with inverted binoculars, making their arms appear small. Nothing else had changed.
Participants claimed that when their arm was amplified, the pain was worse. However, they experienced less discomfort when they peered through the reversed binoculars at a little arm. The fact that this wasn't simply in their imaginations was more intriguing. After the experiment, researchers assessed inflammation and found that there was less swelling after seeing the arm made to appear little. Therefore, it had a real, physical impact on pain; it wasn't just a perception.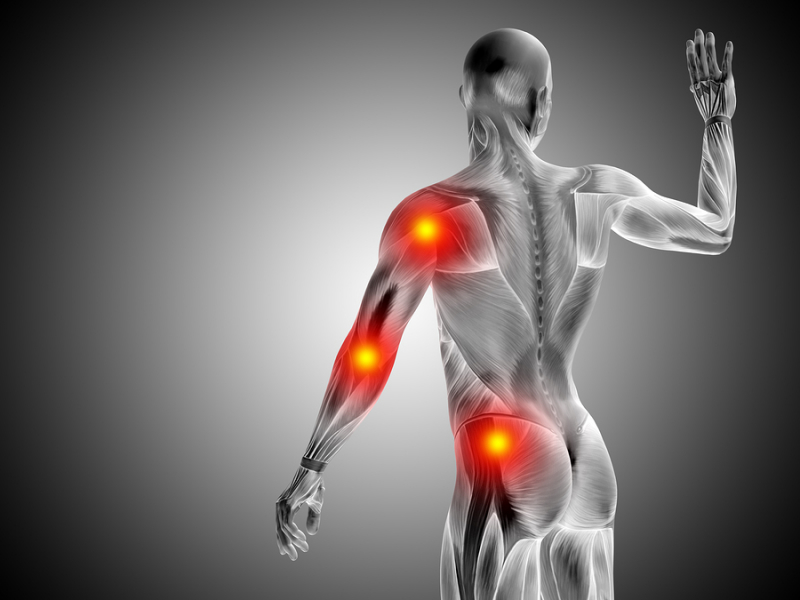
https://integratedtherapies.ca/ 
https://healthblogs.org/ -
You can be deceived into believing that you are outside of your body by using virtual reality. Similar to the rubber hand illusion, but with total body absorption. All it takes to make you feel uncomfortable in a virtual reality setting is for someone to poke you with a stick.
Your sense of self and body are built using a variety of sensory data, according to one neuroscientist. While sight plays a significant role, other factors include what you can physically feel and how you perceive your body to be situated. The brain freaks out a little bit when you fool it by presenting it with new information that doesn't line up. In tests, researchers were able to make individuals feel their own bodies when they looked at virtual ones that were being touched and whose sensations matched their own. The participants experienced terror responses, such as increased sweating and heart rate, as though they were actually experiencing the assault at one point when the virtual body was shattered with a hammer.
In a different experiment, subjects were asked to enter a virtual body and virtually wear it. Then, instead of being within the corpse, they found themselves staring at it. Afterward, everyone who had visited the body and gazed at it saw that their dread of dying had significantly decreased. In this instance, researchers hypothesized that leaving the body helped individuals detach their bodies from their mind and let go of some of their traditional fears associated with passing away.
https://www.engadget.com/ 
https://www.youtube.com -
Finding color where there is none is a common gimmick that caught on TikTok. In particular, if you concentrate on a central place and the image is changed to a high contrast negative color image, you can trick your brain into perceiving a black and white image as full color. This method can transform a black and white image into full color, illuminating how the human eye perceives color. hit the jump button, then adhere to the directions in the movie.
The color receptors in your eyes start to get tired as you fixate on the place. Your three cones, which are sensitive to wavelengths of blue, red, and green, detect color. Your eyes will be able to distinguish the colors that were missing from the contrasted version once the reverse color image has been switched back to black and white. The illusion lasts only a little second, but during that time you should see the black-and-white image in its authentic, full color.

https://crescentarts.org/ 
http://favim.com -
The cutaneous rabbit illusion, sometimes referred to as cutaneous saltation and cutaneous saltation effect, or CRE, is a tactile illusion elicited by rapidly tapping two or more different parts of the skin. On areas of the body surface with relatively weak spatial acuity, such the forearm, the illusion is most easily induced. Although no physical stimulus was provided between the two actual stimulus locations, a quick series of taps delivered first near the wrist and then near the elbow causes the illusion of sequential taps hopping up the arm from the wrist towards the elbow.
The illusion was first identified by Frank Geldard and Carl Sherrick of Princeton University in the early 1970s. Geldard (1982) and numerous other research have since further defined the phenomenon. The phenomenon's name comes from Geldard and Sherrick, who compared the sensation to a rabbit hopping along the skin. Similar sensory saltation illusions have been noted in vision and audition, even though the rabbit illusion has been investigated the most in the tactile realm. The term "saltation" describes the percept's leaping or jumping quality.
https://ebrary.net/ 
https://www.mygroovyday.com/ -
Ever feel as though the day is not long enough? You're in luck though, as there is a method for stopping time. Or at least make your mind believe you did for a brief period of time. Saccadic suppression, which causes rapid eye movements to produce visual distortions, is what keeps you from detecting your own eyes moving when you stare in a mirror. Additionally, they create a delusion known as chronostasis at the same time. When you swiftly dart your eyes to an analog clock on a wall, it appears as though the second hand has stopped moving.
This is known as the stopped clock illusion. Rapid eye movements that generate a void in visual input are the cause of it. For example, if you glance rapidly from your computer to a clock, you won't actually pay attention to everything in between. Your brain sort of holds that moment, only for a moment, and makes it appear like the world has stopped, even if only for a split second, to ensure a smooth transition.

https://www.pinterest.com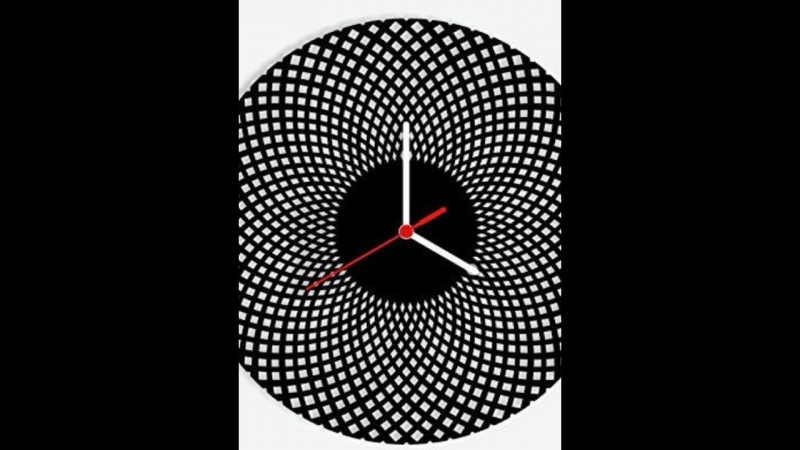 
https://www.youtube.com/ -
Toplist's already listed about placebos, so let's move on to the nocebo effect. By fooling your brain, this can actually cause you to feel ill and in agony for absolutely no reason at all. Essentially, it's believing that something negative will occur, and then it occurs solely as a result of your negative thoughts.
The placebo effect serves as a good illustration of how this may operate, and in fact, it accounted for half of what occurred in the placebo sleep case. Placing a useless medication in your mouth after a doctor assures you it will make you feel fantastic, and it does is called a placebo. However, the nocebo effect occurs when you start to feel ill after the doctor warns you of its terrible adverse effects. Your brain creates symptoms based on information provided to it, even if that information is false.

https://dynamicdiscdesigns.com 
https://placebo.com.au -
Moreover, you would think that your brain would at least be able to recognize where your body parts are and how they feel. Unfortunately, there is a method called the Rubber Hand Illusion that you can use to make it stop trying to do that.
This trick may be performed at home if you'd like and is as easy as it is difficult. You'll need a fake hand of some sort, and all it takes is a rubber glove that has been blown up to work. Your hand is hidden from view in a box or behind cardboard, resting on a table with your right forearm. Line up the hand with your shoulder and extend it in front of you. To further complete the illusion, you might cover it with a cloth below the wrist. Your second hand can be resting beneath the desk.
Have someone sit across from you and simultaneously stroke the rubber hand and your hidden hand with two paintbrushes. Keep your eyes on the pretend hand. When the stimulation is timed and synchronized correctly, most people start to mistake the phony hand for their own. Your brain will truly react as though your real hand is about to be stabbed when the rubber hand is threatened, such as with a knife or needle.
https://www.youtube.com/ 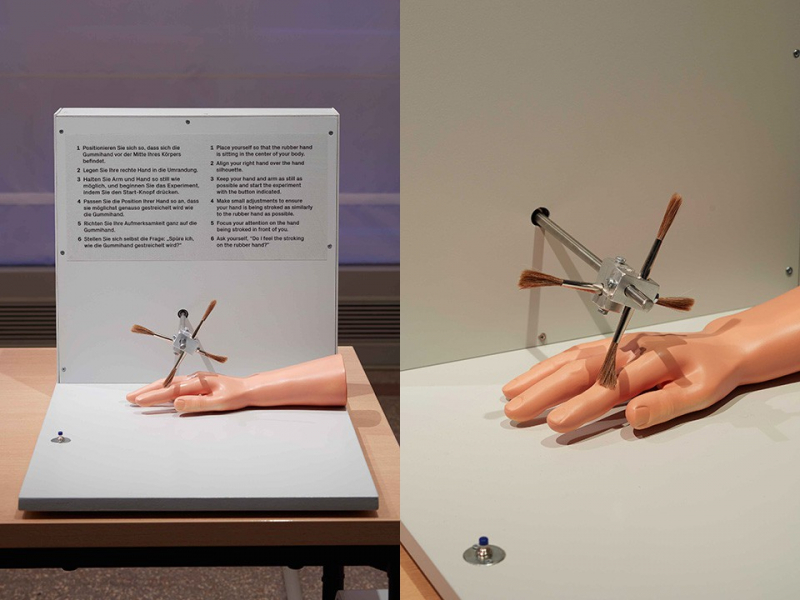
http://mirror-images.de/ -
One in three adults, according to the CDC, don't get enough sleep. Finding a way to obtain more sleep sounds like a good idea just for that reason. What if you could simply fool your brain into believing you slept when you actually didn't? It appears that's a viable alternative, and it functions. Like other placebos, placebo sleep works when your mind creates the illusion that something has happened even when it hasn't. You can convince yourself that you are rested even when you are not with the correct stimulus.
The significance of REM sleep was discussed to two groups of participants before a sleep study was conducted. They were informed that 20% to 25% of total sleep should be REM sleep. One group's sleep study revealed that they spent 28.7% of the night in REM sleep. One group was informed that their REM content was only 16.2%. Those stats weren't accurate.
Cognitive tests performed better for those who were told they slept better after the fact. When compared to control groups, those who were informed they slept worse performed worse. It made absolutely no difference how any of them truly felt.
http://www.worldclass.sg/ 
http://www.mariefranceasia.com -
Do you think people who wear sunglasses appear happier than others? They might be, and not just because they have a really cool appearance. Your brain is fooled into feeling better by sunglasses. Sunglasses' effectiveness is linked to how emotions operate in people. Perhaps you yourself aren't the best at keeping your emotions hidden, and you've probably heard some people described as wearing their hearts on their sleeves.
The way we act and look can affect how we feel, and even something as basic as frowning can make you feel depressed or even angry and hostile. To be clear, you don't necessarily need to be grinning to be sad or furious. The act of squinting and frowning in response to bright sunlight is sufficient to elicit the unfavorable feelings that are associated with frowning.
In a study, participants who used sunglasses said they were generally less furious and violent than those who did not. This seems to be consistent with earlier research that indicates even the act of smiling might produce hormones that reduce stress. Put on some shades to fool your brain into believing you're joyful if you're feeling a little tense on a sunny day.
https://eyewear.en.made-in-china.com 
https://www.versace.com -
Memes, viral videos, and internet phenomena all come and go. The Ice Bucket Challenge from yesterday is now Yanny/Laurel from tomorrow. The Hanger Challenge was also the coolest activity in May 2022 for nearly two weeks. The idea was as absurd as it was straightforward. If you tie a wire hanger around your head, whether you want it to or not, your head will turn.
Everyone had to try it for themselves and then publish their own films of the results because nobody believed it to be true. As a result of the explosion in video production and widespread skepticism that the bizarre effect could possibly be real, a viral trend was established. Though it was! Your head will actually turn unintentionally if a hanger is stretched appropriately around it.
The phenomena was recognized considerably earlier and even discussed in scientific articles back in 2015, while only becoming popular in 2022. As early as 1995, it was even discussed on Japanese television. It's safe to suppose that it has existed for as long as hangers and heads have. Just never this much media attention before. The movement is involuntary when the unilateral fronto-temporal region of your skull is compressed, but it's not quite apparent why this occurs. However, in a research, over 95% of participants reported experiencing feeling, while only 4.2% appeared immune.
https://kitairu.net/ 
https://boards.weddingbee.com/






























