Top 15 Best Foods to Lower Your Blood Sugar
Diet is an important part of maintaining healthy blood sugar levels for those with prediabetes, diabetes, or other conditions that impact blood sugar. Although ... read more...other factors such as body weight, activity, stress, and genetics have a part in blood sugar regulation, sticking to a balanced diet is essential. Here are some foods that may help with blood sugar control you can refer to!
-
Sulforaphane is an isothiocyanate that helps lower blood sugar levels. A reaction between a glucosinolate compound called glucoraphanin and the enzyme myrosinase, both of which are abundant in broccoli, produces this plant chemical when broccoli is chopped or chewed. Sulforaphane-rich broccoli extract has substantial antidiabetic benefits, according to test-tube, animal, and human research, helping to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar and oxidative stress markers.
Broccoli sprouts are high in glucosinolates like glucoraphanin, and when taken as a powder or extract, they've been demonstrated to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Consumption of cruciferous vegetables has also been associated with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes. Keep in mind that the best way to increase sulforaphane availability is to eat broccoli and broccoli sprouts raw or barely steamed, or to cook broccoli with active myrosinase sources like mustard seed powder.
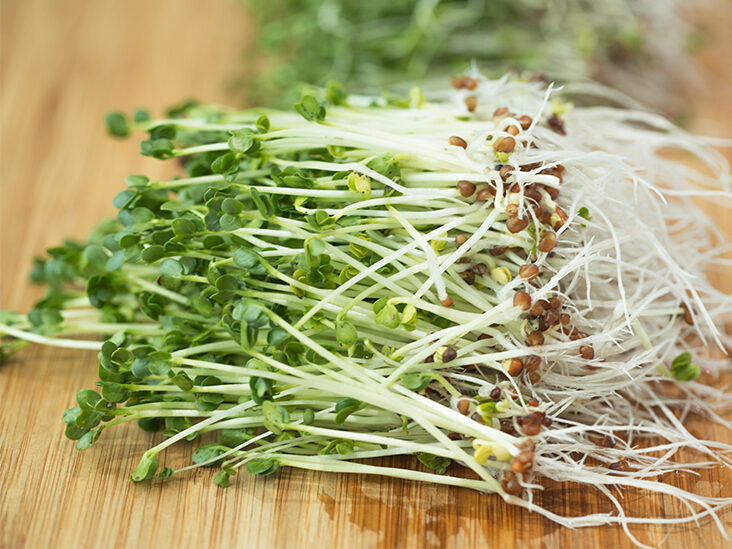

Broccoli and broccoli sprouts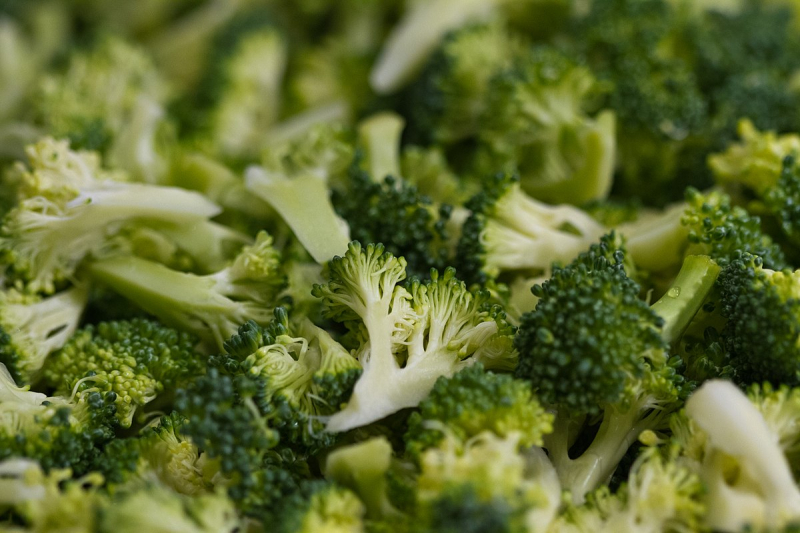 
Broccoli and broccoli sprouts -
Seafood, such as fish and shellfish, is an excellent source of protein, good fats, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, all of which may help in blood sugar control. Protein is necessary for blood sugar regulation. It helps digestion and prevents blood sugar spikes after meals, as well as increasing feelings of fullness. It may also aid in the prevention of overeating and the reduction of extra body fat, both of which are necessary for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
Fatty fish, such as salmon and sardines, have been demonstrated to help control blood sugar levels. A study of 68 overweight or obese people found that those who ate 26 ounces (750 grams) of fatty fish per week had significantly lower post-meal blood sugar levels than those who ate lean fish.

Seafood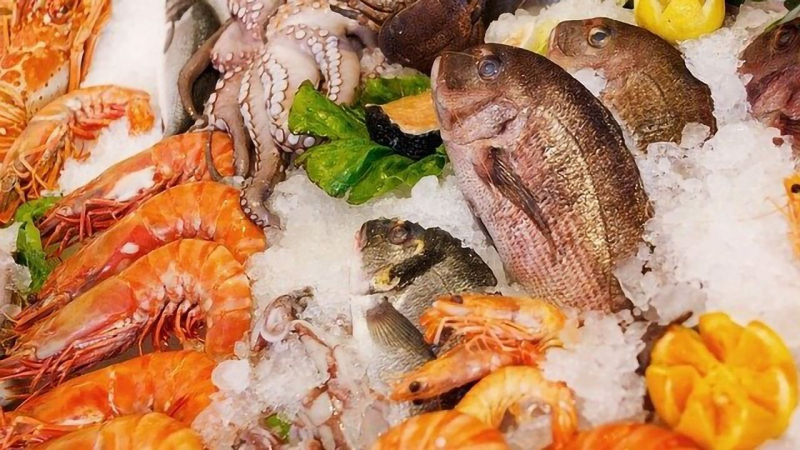 
Seafood -
Pumpkin is a great choice for blood sugar management since it is brightly colored and high in fiber and antioxidants. In fact, many countries, including Mexico and Iran, use pumpkin as a traditional diabetic remedy.
Pumpkin is abundant in polysaccharides, which have been studied for their ability to regulate blood sugar levels. In both human and animal studies, treatments with pumpkin extracts and powders were proven to significantly lower blood sugar levels. However, more study is needed to see how the whole pumpkins might help with blood sugar. Pumpkin seeds are high in healthful fats and proteins, making them a good choice for blood sugar management. In a 2018 study of 40 people, researchers discovered that eating 2 ounces (65 grams) of pumpkin seeds decreased post-meal blood sugar by up to 35% compared to a control group.
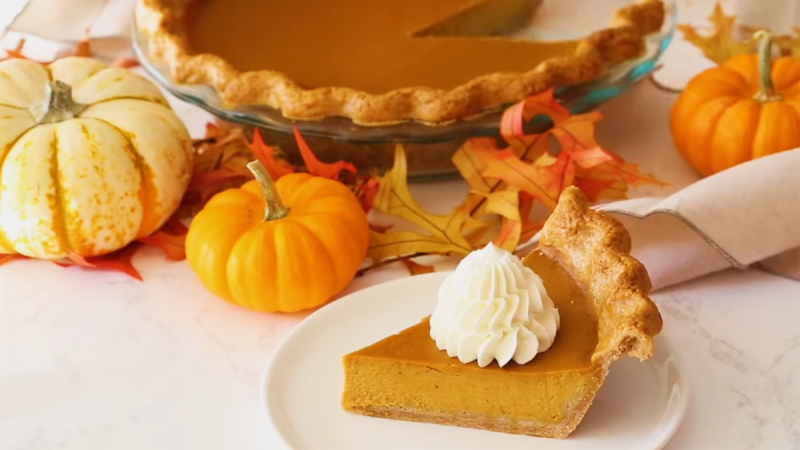

Pumpkin and pumpkin seeds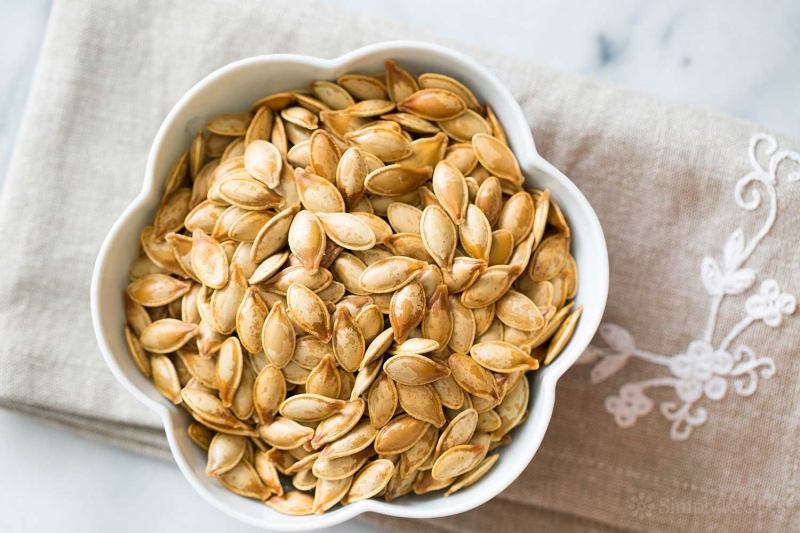 
Pumpkin and pumpkin seeds -
Nuts have been demonstrated to be an excellent way to help manage blood sugar levels in studies. When eaten alongside high-carbohydrate or high-GL foods, peanuts and peanut butter have been found to help reduce blood sugar spikes. Peanuts and peanut butters are low GI and GL foods because they include healthful oils, protein, and fiber that help regulate blood sugar levels.
A study of 25 people with type 2 diabetes found that eating peanuts and almonds throughout the day as part of a low-carb diet decreased blood sugar levels both fasting and post-meal. Furthermore, a review found that in people with type 2 diabetes, diets emphasizing tree nuts at an average daily consumption of 2 ounces (56 grams) significantly lowered fasting blood sugar and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), a marker of long-term blood sugar management.

Nuts and nut butter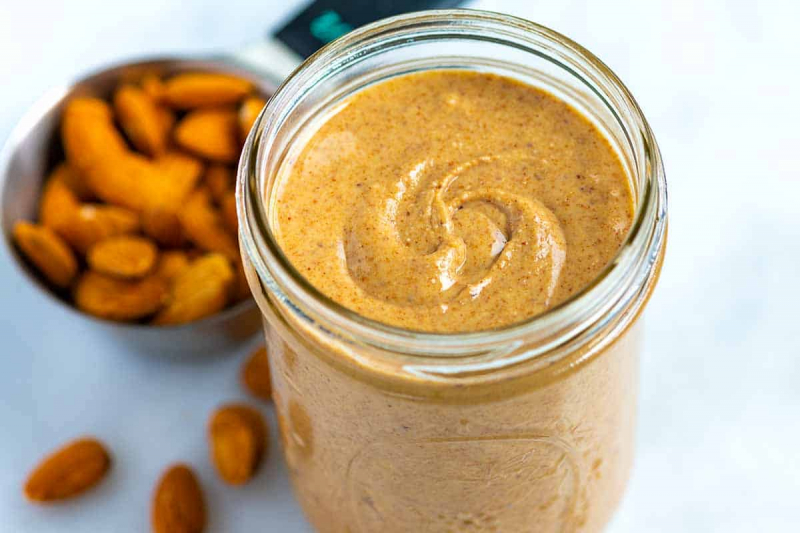 
Nuts and nut butter -
Okra is a fruit that is frequently used as a vegetable. Polysaccharides and flavonoid antioxidants, which lower blood sugar, are abundant in okra. The fiber in the green, seedy part of the okra, lowers blood sugar by reducing sugar absorption from the intestines.
Okra seeds have long been used in Turkey as a natural diabetic treatment due to their blood sugar-lowering properties. The major polysaccharide in okra, rhamnogalacturonan, has been found as a potent anti-diabetic compound. Okra also includes the flavonoids isoquercitrin and quercetin 3-O-gentiobioside, which inhibit certain enzymes and so help lower blood sugar. Although animal studies show that okra has potent anti-diabetic benefits, further human research is required.
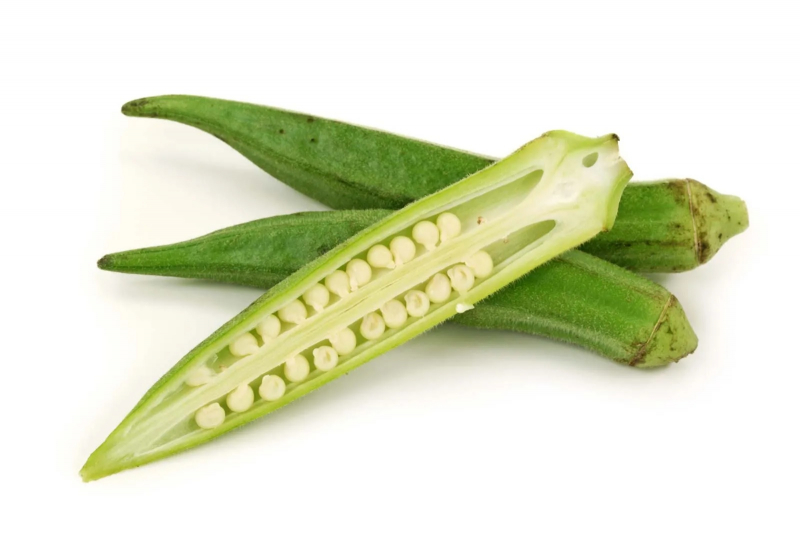

Okra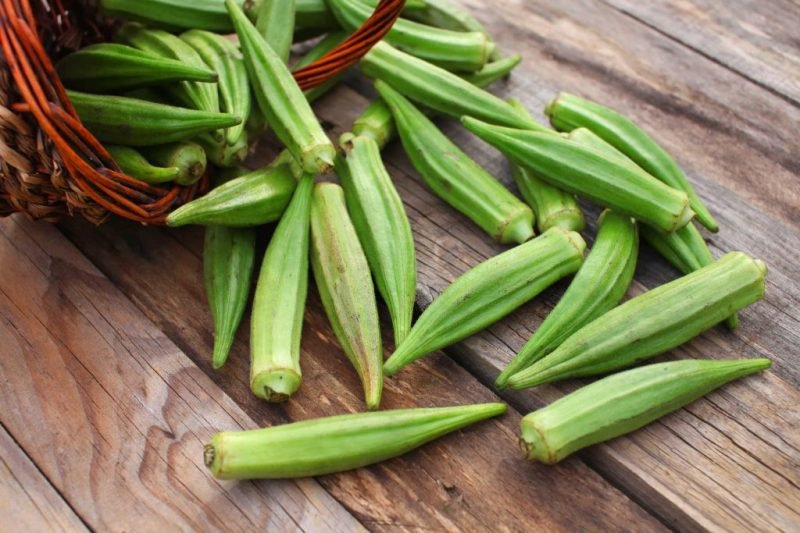 
Okra -
Flax seeds and flaxseed oil provide a number of health benefits that might help diabetics control their disease. They may enhance blood sugar management, and insulin sensitivity, and minimize risk factors for heart disease since they're high in fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and unique plant compounds.
Flax seeds are high in fiber and healthy fats, and their health benefits are widely known. Flax seeds, in particular, may help lower blood sugar levels. In a study of 57 patients with type 2 diabetes over the course of eight weeks, those who took 7 ounces (200 grams) of 2.5 % fat yogurt with 1 ounce (30 grams) of flax seeds per day had significantly lower HbA1c levels than those who had plain yogurt. Furthermore, a review of 25 controlled studies found that eating whole flax seeds improved blood sugar management significantly.
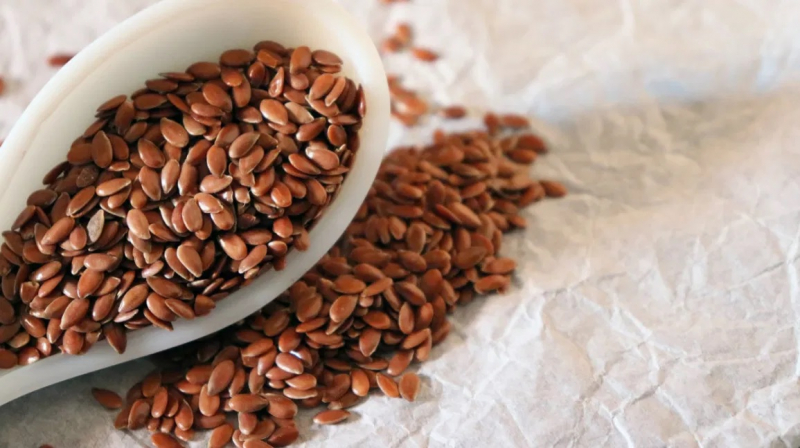

Flax seeds 
Flax seeds -
Beans are an excellent diabetic food. People with diabetes should have dried beans or low-sodium canned beans in several meals each week, according to the American Diabetes Association. They have a low glycemic index, making them better for controlling blood sugar levels than many other starchy foods.
Beans and lentils are high in magnesium, fiber, and protein, all of which can help reduce blood sugar levels. They're high in soluble fiber and resistant starch, both of which aid digestion and may enhance blood sugar response after meals. A study of 12 women found that adding black beans or chickpeas to a rice meal decreased post-meal blood sugar levels much more than eating rice alone. Many additional studies have found that eating beans and lentils can help not only regulate blood sugar but also prevent the development of diabetes.
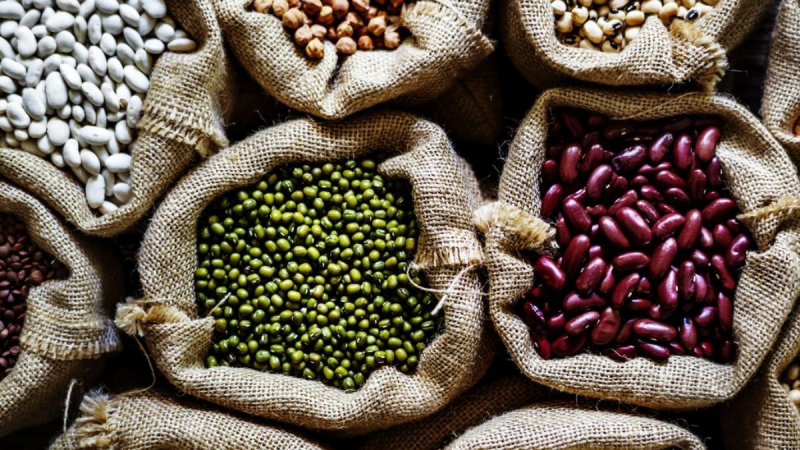

Beans and lentils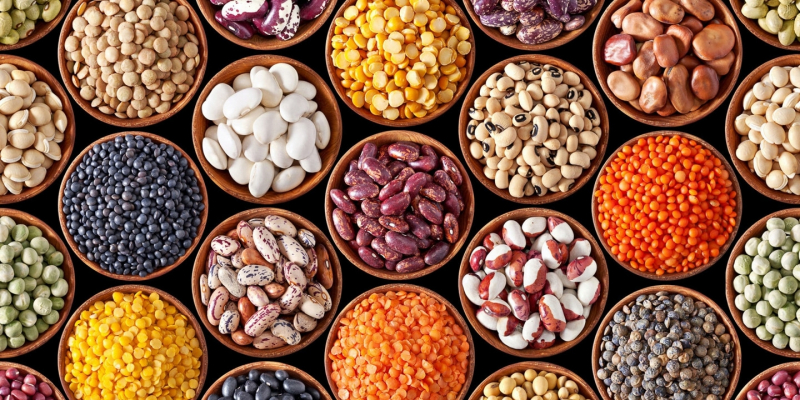 
Beans and lentils -
Fermented foods, such as kimchi and sauerkraut, are high in health-promoting compounds such as probiotics, minerals, and antioxidants, and have been associated with increased blood sugar and insulin sensitivity.
In a study of 21 people with prediabetes, eating fermented kimchi for eight weeks increased glucose tolerance in 33% of participants, whereas just 9.5% of those who ate fresh kimchi improved glucose tolerance. Another research on 41 diabetes found that following a traditional Korean diet rich in fermented foods like kimchi for 12 weeks resulted in lower HbA1c levels than following a control diet. Meanwhile, one weeklong research involving 100 people found that eating 0.5–7.5 ounces (15–210 grams) of kimchi daily reduced blood sugar, total cholesterol, and LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, all of which are risk factors for heart disease.
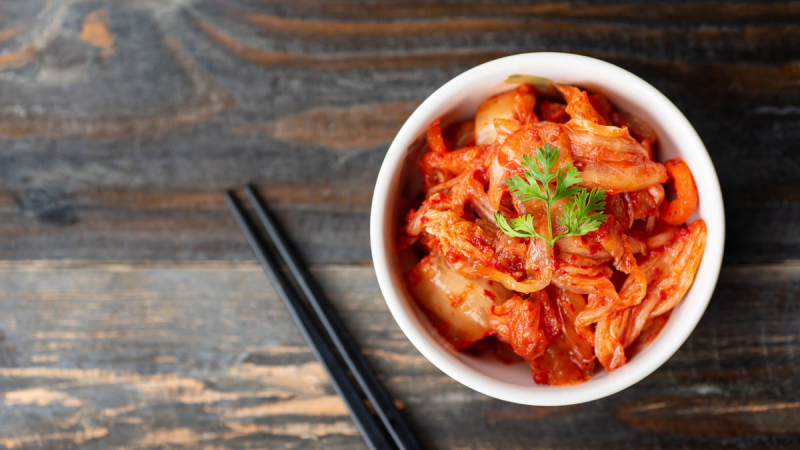

Kimchi and sauerkraut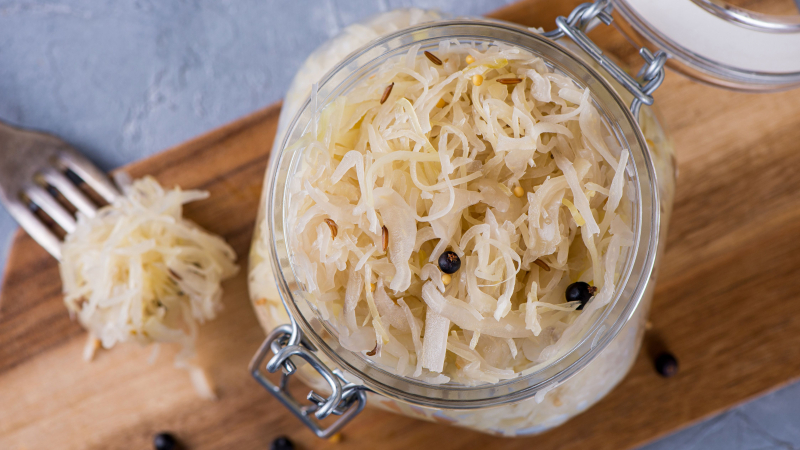 
Kimchi and sauerkraut -
Chia seeds may help regulate blood sugar levels. Chia seed consumption has been associated with lower blood sugar levels and improved insulin sensitivity in studies.
Chia seeds may help improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar management, as well as potentially lower disease risk, including diabetes risk, according to a review of 17 animal studies published in 2020. In addition, a study of 15 healthy people found that consuming 1 ounce (25 grams) of ground chia seeds with 2 ounces (50 grams) of sugar solution reduced blood sugar levels by 39% compared to those who consumed the sugar solution alone. Chia seeds also have a high fiber content. Fiber may help reduce insulin resistance and improve blood sugar levels, lowering your risk of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes, according to research.
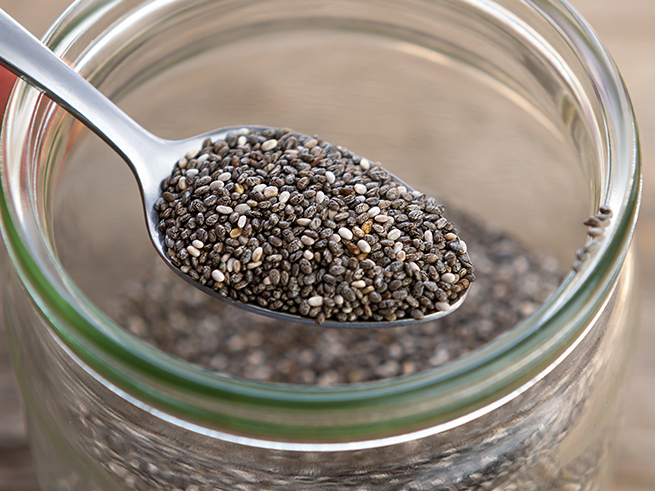

Chia seeds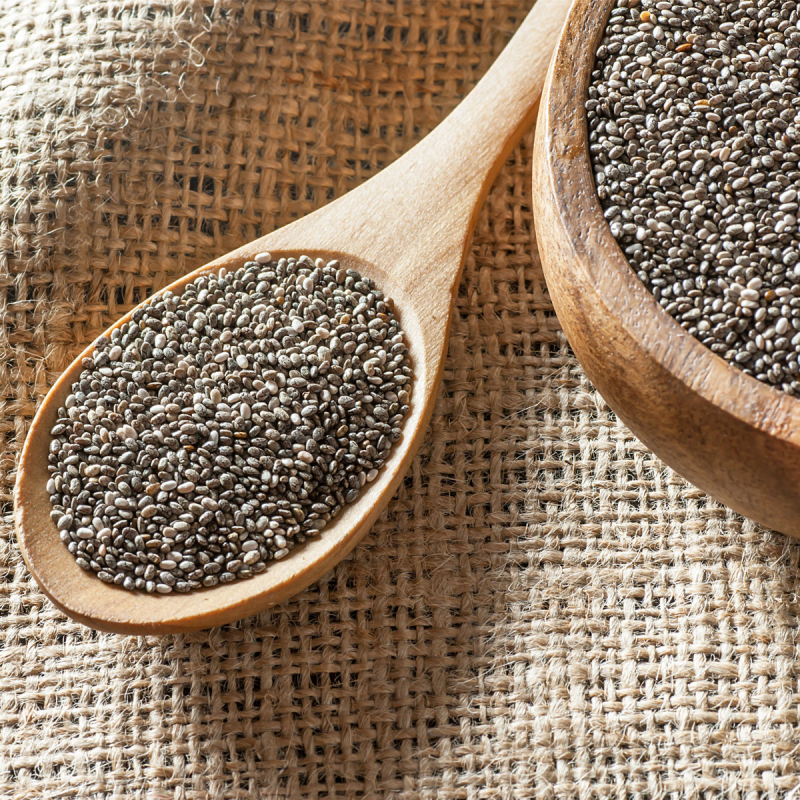 
Chia seeds -
Kale is frequently referred to as a "superfood". It contains compounds including fiber and flavonoid antioxidants that may help lower blood sugar levels. Research involving 42 Japanese people found that eating 7 or 14 grams of kale-containing foods with a high carb meal reduced post-meal blood sugar levels much more than a placebo. The flavonoid antioxidants contained in kale, such as quercetin and kaempferol, have been demonstrated in studies to have potent lowering blood sugar and sensitizing insulin effects.
Antioxidant-rich vegetables like kale and spinach are beneficial to patients with type 2 diabetes. Kale juice has been shown to help with type 2 diabetes management. People with type 2 diabetes benefit from a mixed diet of fresh fruits and vegetables. This is in addition to regular exercise, stress reduction, and good sleep quality.
Kale 
Kale -
Several studies have linked berry consumption to improved blood sugar management. Berries are high in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making them a good choice for those who have trouble controlling their blood sugar. In a 2019 study, eating 2 cups (250 grams) of red raspberries with a high-carb meal lowered post-meal insulin and blood sugar levels in adults with prediabetes considerably more than a control group. Strawberries, blueberries, and blackberries, in addition to raspberries, have been demonstrated in trials to help with blood sugar management by improving insulin sensitivity and glucose clearance from the blood.
Blueberries are considered a diabetic superfood by the American Diabetes Association (ADA). Blueberries are high in vitamins, antioxidants, minerals, and fiber, all of which are beneficial to overall health. They may also aid in disease prevention. Blueberries may aid glucose processing, weight loss, and insulin sensitivity in people with diabetes.

Berries 
Berries -
Avocado is a high-fat food, but it appears as a healthful addition to various diet plans. Avocados, in addition to being creamy and delicious, may have considerable blood sugar-regulating properties. They're high in healthful fats, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and they've been found to lower blood sugar levels when added to meals.
Patients may be advised by a physician or dietitian to consume foods that are low in carbs and sugar. They may also recommend foods that help control blood sugar spikes. Both of these requirements are satisfied by an avocado. Avocados have been discovered to lower blood sugar levels and protect against the development of metabolic syndrome, a group of diseases that includes high blood pressure and high blood sugar and increases the risk of chronic disease.
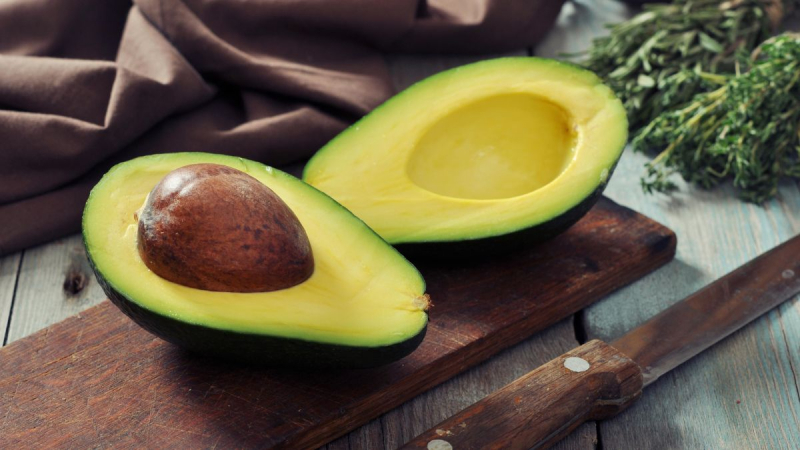

Avocados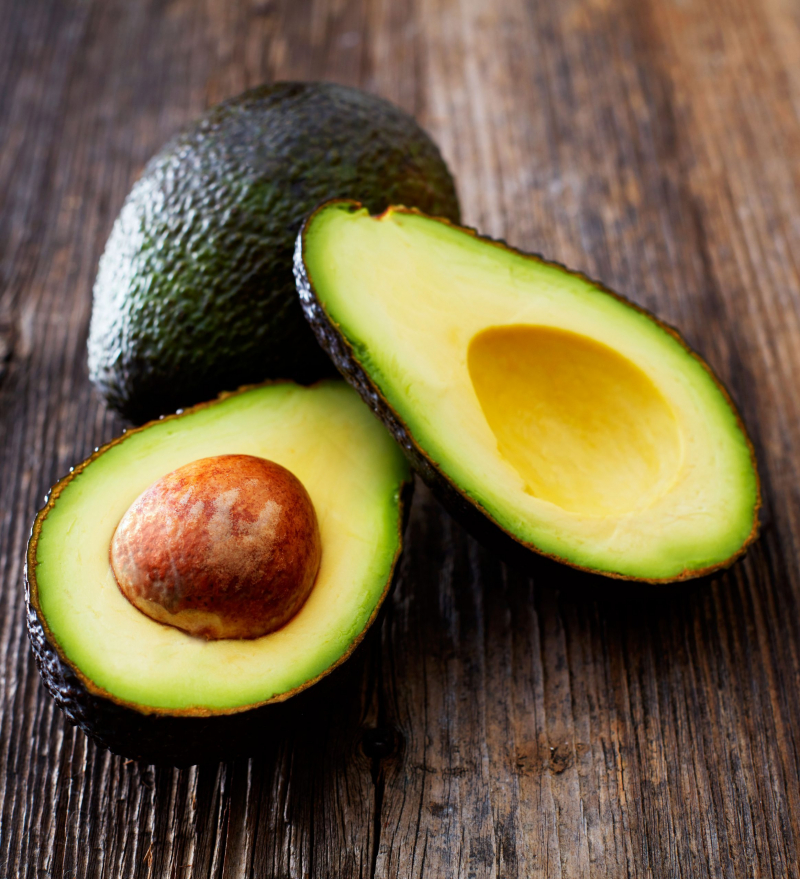 
Avocados -
Due to its high content of soluble fiber, which has been demonstrated to have substantial blood sugar-lowering properties, including oats and oat bran in your diet may help improve your blood sugar levels.
Oats have a GI score of 55 or lower, making them less likely to cause spikes and dips in blood sugar levels. Oats also contain β-glucan, which can reduce glucose and insulin responses after meals, and improve insulin sensitivity. When compared to control meals, oat intake significantly lowered HbA1c and fasting blood sugar levels, according to a review of 16 studies. Furthermore, one small research of ten persons discovered that drinking 7 ounces (200 mL) of water combined with 1 ounce (27.3 grams) of oat bran before eating white bread decreased post-meal blood sugar levels much more than drinking plain water.
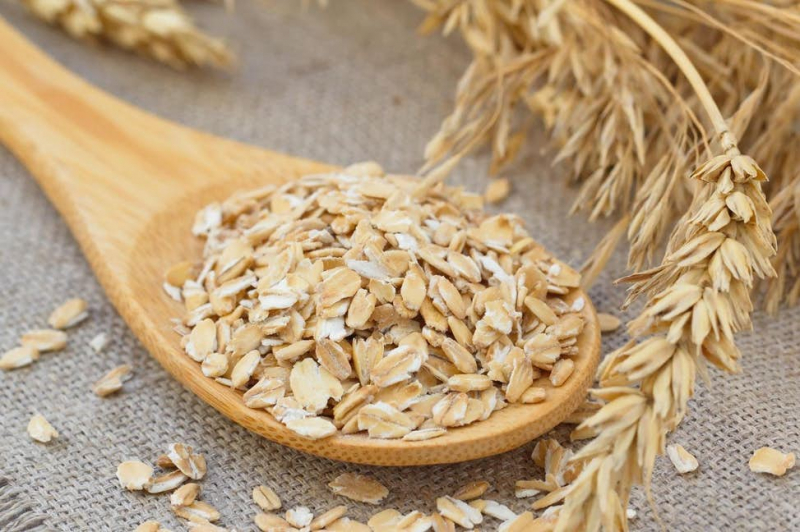

Oats and oat bran 
Oats and oat bran -
Citrus fruits are high in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, all of which contribute to their nutritional value. Citrus fruit is absolutely good for diabetics when consumed in moderation.
Despite the sweetness of many citrus fruits, research suggests that they may help lower blood sugar levels. Citrus fruits are low glycemic, indicating they don't raise blood sugar levels as much as other fruits like watermelon and pineapple. Because they have a low GI, they trigger a slow rise in your blood sugar levels, making them more favorable for people with diabetes. Oranges and grapefruit are high in fiber and include plant compounds such as naringenin, a polyphenol with powerful anti-diabetic benefits. Consumption of whole citrus fruits may improve insulin sensitivity, lower HbA1c, and protect against diabetes.

Citrus fruits 
Citrus fruits -
Fermented dairy products like kefir and yogurt can help control blood sugar levels. Kefir and yogurt intake has been related to improved blood sugar management in research.
Kefir may have a variety of health benefits for people with diabetes and obesity. It might affect diabetes-related markers. For example, 8-week research on 60 people with type 2 diabetes found that drinking 20 ounces (600 mL) of probiotic-rich kefir per day lowered fasting blood sugar and HbA1c substantially more than drinking kefir without probiotics. Yogurt may also help with blood sugar control. A four-week trial of 32 people found that daily consumption of 5 ounces (150 grams) of yogurt reduced post-meal insulin and blood sugar levels as compared to baseline.

Kefir and yogurt 
Kefir and yogurt