Top 9 Best Herbs for Liver Health
Cirrhosis, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), alcoholic liver disease, liver cancer, liver failure, and hepatitis are all illnesses that afflict many ... read more...people around the world. Heavy alcohol consumption, high blood sugar levels, obesity, high blood pressure, infections, excessive triglyceride and cholesterol levels, and other risk factors all contribute to liver damage. Medication, dietary therapy, immunotherapy, lifestyle changes, surgical resection, and even liver transplantation are among the options for treating liver disease. Here are the greatest herbs for liver health that have been studied.
-
Silymarin, often known as milk thistle, is a collection of chemicals derived from the seeds of milk thistle (Silybum marianum), including silybin, silychristin, and silydianin. Milk thistle has been used to treat bile duct and liver disorders for over 2,000 years, and research indicates that it may have liver-protective characteristics. It has been proposed that silymarin has strong antioxidant properties, which may aid in liver cell regeneration, reduce inflammation, and benefit patients suffering from liver disease. Human investigations, on the other hand, have yielded conflicting outcomes.
For instance, some studies have revealed that taking a silymarin supplement may aid in preventing the progression of liver disease, lengthen the lifespan of those with alcoholic cirrhosis, and improve the general quality of life for those with liver disease. The need for more research is highlighted by other studies that show silymarin is no more beneficial than placebo therapies. Even when used in high quantities, silymarin is thought to be safe and has not been linked to any unfavorable side effects.

Milk thistle (silymarin)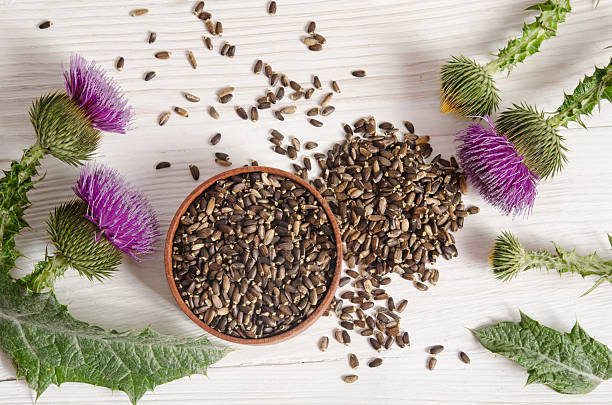 
Milk thistle (silymarin) -
Ginseng is a well-known herbal supplement with anti-inflammatory qualities. A variety of in vitro and animal studies have shown that ginseng has antioxidant properties and may help protect the liver from damage caused by viruses, toxins, and alcohol. Furthermore, it may promote liver cell regeneration following a surgery. Furthermore, human studies have indicated that ginseng medication may improve liver function, as well as reduce fatigue and inflammation in persons with liver illness and malfunction. In a 2020 research of 51 males with increased levels of alanine transaminase (ALT), a marker for liver impairment, those who took 3 grams of ginseng extract per day for 12 weeks saw significant reductions in ALT when compared to a placebo group.
Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) levels, another indicator of liver injury, were also markedly decreased. Despite the fact that these findings are encouraging, more analysis of ginseng's effects on liver function is required. Ginseng is regarded to be somewhat safe for liver health when taken alone. However, ginseng may interact with drugs, which could result in liver damage and other potentially harmful side effects.

Ginseng 
Ginseng -
Green tea and its primary polyphenol ingredient, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), are frequently included in literature reviews focused on herbal therapies for liver disorders, despite the fact that it is not officially a herb. Green tea extract supplementation may help treat liver illness, according to certain research. A study of 80 persons with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) discovered that taking 500 mg of green tea extract daily for 90 days lowered the liver damage markers ALT and aspartate aminotransferase (AST).
Although the AST and ALT levels decreased in the placebo group as well, they did not differ significantly. Another 12-week research in 80 NAFLD patients found that, compared to a placebo, individuals who took 500 mg of green tea extract daily saw significant improvements in their levels of AST, ALT, and inflammatory markers. The medication also lessened fatty liver abnormalities. Consuming green tea has also been proven to be protective against a number of liver diseases, such as chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, fatty liver, and liver cancer. Although most people believe that drinking green tea is safe, green tea extract supplements have on occasion been associated with acute liver damage.

Green tea 
Green tea -
Although chewy candy is commonly associated with licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra), it is actually a herb with great therapeutic effects. Scientific research has demonstrated that licorice root contains anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and liver-protective properties. The saponin compound glycyrrhizin, which is frequently used in traditional Chinese and Japanese medicine to cure a variety of diseases, including liver disease, is the principal active component in licorice root. Some studies have shown that licorice extract treatment may benefit people with certain liver diseases.
In comparison to a placebo, supplementing with 2 grams of licorice root extract daily for two months significantly decreased ALT and AST in 66 patients with fatty liver disease. In another tiny trial, 6 healthy participants drank vodka just at night for 12 days whereas the other 6 participants took a glycyrrhizin supplement before doing so. Liver damage indicators like ALT, AST, and GGT dramatically increased in the vodka-only group. These markers did not significantly rise in the glycyrrhizin group, indicating that the compound may help guard against alcohol-related liver damage.

Licorice 
Licorice -
Turmeric and its key ingredient curcumin have been linked to a slew of outstanding health benefits. Turmeric has potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer effects, making it a popular choice for patients suffering from liver disease. A study in persons with NAFLD found that daily treatment with 500 mg of a curcumin product for 8 weeks lowered liver fat content and levels of AST and ALT considerably more than a placebo group. Another study of 70 persons with NAFLD found that supplementing with 500 mg of curcumin and 5 mg of piperine per day for 12 weeks reduced ALT, AST, LDL (bad) cholesterol, and inflammatory markers significantly more than a placebo group.
Black pepper contains a substance called piperine that improves the absorption of curcumin. Additionally, it was found that the curcumin treatment considerably reduced the severity of NAFLD when compared to the placebo group. Turmeric and curcumin supplements are usually regarded as safe. However, certain instances of severe liver damage have been documented. Uncertainty persists regarding whether these incidents were brought on by tainted curcumin products or the items themselves.

Turmeric 
Turmeric -
Although garlic is botanically classified as a vegetable, it is a common ingredient in many herbal treatments. It's high in antioxidant and anti-inflammatory plant chemicals like allicin, alliin, and ajoene, which may benefit liver function. A 2020 study of 98 persons with NAFLD found that using 800 mg of garlic powder each day for 15 weeks reduced ALT, AST, LDL (bad) cholesterol, and triglyceride levels significantly more than a placebo group. Furthermore, 51% of participants in the garlic group improved the severity of liver fat accumulation, compared to only 16% in the control group.
Men who took raw garlic more than seven times per week had up to a 29% lower chance of developing fatty liver disease, according to another study including more than 24,000 adults. Although consumption of raw garlic was negatively correlated with NAFLD in men, this correlation was not present in women. Furthermore, a study connected eating raw garlic with a lower risk of liver cancer. Compared to eating raw garlic less than twice a week, eating it twice or more a week was linked to a 23% lower risk of liver cancer. Although raw garlic is typically regarded as healthy, some people may have liver damage with concentrated garlic supplements.

Garlic 
Garlic -
Ginger root is a popular culinary ingredient as well as a popular therapeutic remedy for a variety of health concerns, including liver illness. In a 12-week study of 46 persons with NAFLD, supplementing with 1,500 mg of ginger powder per day significantly lowered ALT, total and LDL (bad) cholesterol, fasting blood sugar, and the inflammatory marker C-reactive protein (CRP) compared to placebo. Another study found comparable outcomes. When compared to a placebo group, people with NAFLD who took 2 grams of ginger for 12 weeks saw significant reductions in ALT, GGT, inflammatory markers, and fat accumulation in the liver.
Strong substances found in ginger root, such as gingerols and shogaols, aid to reduce inflammation and guard against cellular damage, which may improve liver function. Additionally, ginger may shield your liver from poisons like alcohol. Ginger is typically regarded as harmless, even for people with liver diseases. To be safe, you should always consult your doctor before taking high-dose ginger supplements.

Ginger 
Ginger -
Danshen is a chemical found in traditional Chinese medicine. The dried roots of the herb Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge are used. Danshen has been demonstrated in human and animal research to be beneficial to liver health. Danshen may help guard against alcohol-related liver illness and promote liver tissue regeneration in animal studies, and danshen injections may help treat liver fibrosis in humans when used in conjunction with other herbal therapies.
Popular herbal supplement ginkgo biloba has been connected to better liver health. Injections of ginkgo biloba, for instance, were found to prevent liver fibrosis and improve liver function in mouse research. Ginkgo biloba has been connected to modest negative side effects, although it hasn't been directly linked to liver damage.

Ginkgo biloba 
Danshen -
Astragalus is a popular edible herb in traditional Chinese medicine. It is rich in medicinal components such as saponins, isoflavonoids, and polysaccharides, all of which have potent therapeutic qualities.
It is generally regarded as safe and has not been linked to liver damage. It may, however, interact with certain drugs. When administered alone or in conjunction with other herbs, rodent studies show that astragalus may help protect against fibrosis and high-fat diet-induced fatty liver. Because many herbs can cause liver damage and interact with common medications, you should always check with your healthcare provider before taking any herbal supplement, especially if you have a condition that affects the liver.

Astragalus 
Astragalus