Top 10 Stress-Related Health Problems
According to studies, numerous health problems have been linked to stress. Conditions including obesity, heart disease, Alzheimer's disease, diabetes, ... read more...depression, gastrointestinal issues, and asthma tend to get worse or have a higher chance of developing due to stress. Let's take a look at common stress-related health problems below!
-
Your muscles tense up, your breathing quickens, your hands start to sweat profusely, and your heart rate increases when you're under extreme stress. The hormones cortisol and adrenaline, which are released by your body in reaction to stress, are what cause your body's natural fight-or-flight response.
The effects stress has on your heart include:
- Chronic stress and heart disease: The link has not yet been scientifically confirmed, but initial studies suggest that chronic stress and an unhealthy level of stress hormones may contribute to heart disease.
- Inflammation of the heart muscle: Chronic stress may be a factor in circulatory system inflammation, especially in coronary arteries. The buildup and rupture of plaque in artery walls, as well as subsequent heart attacks, are all primarily caused by inflammation in the arteries.
- Blood pressure spike: Your body produces an excess of hormones when you are under stress, which makes your blood vessels narrow and your heart beat more quickly. Your blood pressure temporarily rises as a result of this. Your heart, kidneys, and blood vessels are harmed if this happens regularly.
- Other risk factors for heart disease: You could feel the want to overeat, smoke, or skip exercise while you're under stress, all of which are risk factors for heart disease.
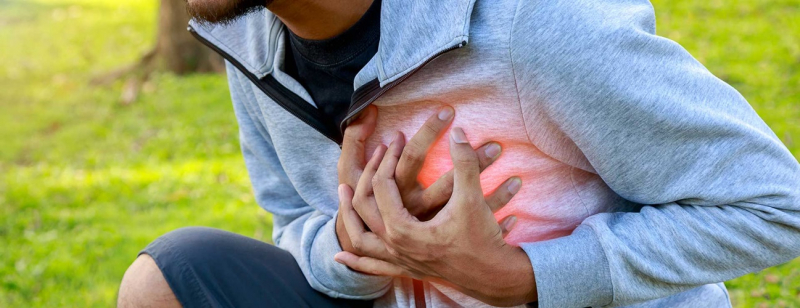
Heart disease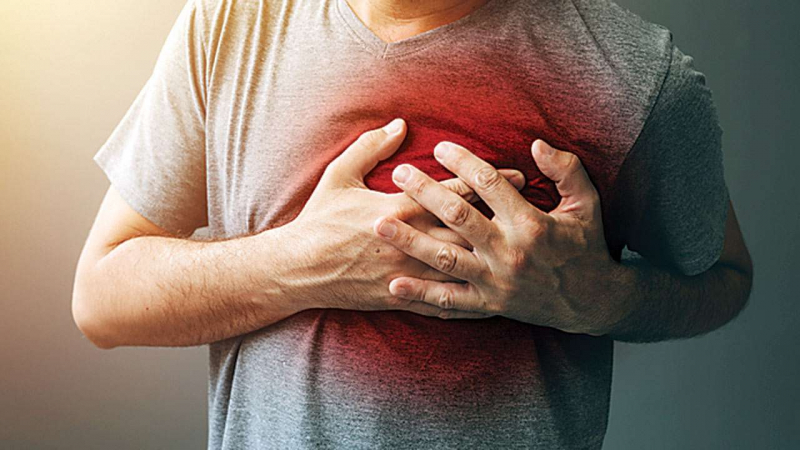 
Heart disease -
IBS is a prevalent chronic condition that affects the large intestine and can result in diarrhea, constipation, bloating, cramping, and pain. Stress is one among the numerous things that can trigger flare-ups, according to many people with the condition.
In fact, a psychological condition like anxiety or depression is prevalent in roughly 60% of IBS patients. People with IBS typically have mood disorders including anxiety or depression. Some mood disorders may also develop as a result of poorly controlled IBS symptoms. Intestinal movement and sensitivity have been associated with stress. External stressors might cause unpleasant bowel symptoms because the pain pathways in the central nervous systems are connected to the gut processes. Additionally, there is evidence that stress and mood disorders might impact the gut microbiome and immune system, both of which are crucial for healthy gut function.
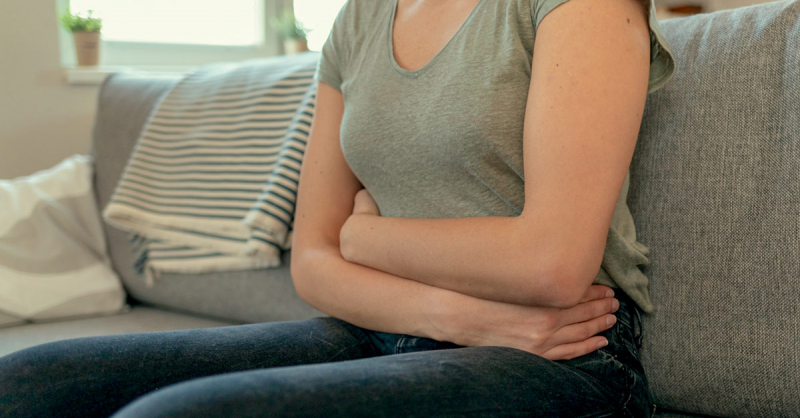

Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)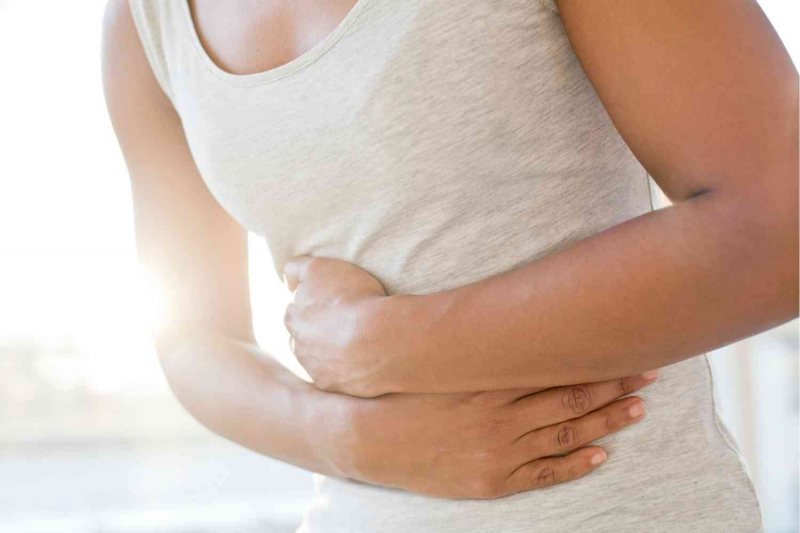 
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) -
A tension headache is the most common type of headache. Your head, neck, and behind your eyes may have mild, moderate, or severe discomfort as a result. A forehead-tightening band may be how a stress headache feels. This is a recognizable symptom of a tension headache.
If you experience chronic stress, you may also get chronic tension headaches. Stress makes headaches more likely to occur. Stress can cause headaches of any kind, including migraine and tension headaches, and it can exacerbate current headaches. An occasional tension headache is often brought on by a single stressful event. A major source of stress is this cycle of pain, which can exacerbate the pressures of daily life.
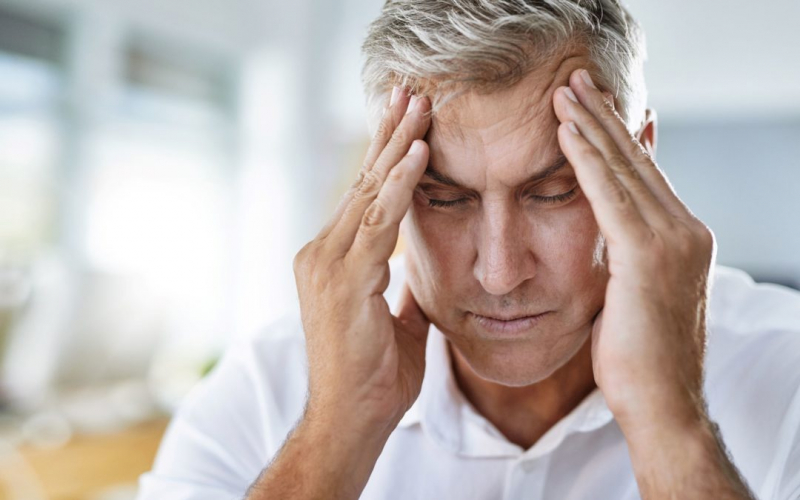

Tension headaches 
Tension headaches -
Your body strives to make sure you have the energy to handle the stressor while you're feeling stressed. As a result, your liver releases more glucagon, adrenaline, and glucose. Your body becomes less responsive to the insulin you do have when insulin levels drop and growth hormone and cortisol levels rise.
Stress and high blood sugar levels combined indicate that you have higher blood sugar levels because more glucose is available in your bloodstream. Your health might suffer as a result of consistently high blood sugar levels with symptoms including increased thirst and urination, blurred vision, light-headedness, flushed skin and restlessness. Extreme stress may raise your risk of developing diabetes, according to some research. According to one study, men who experience feelings of stress are 45% more likely to develop the condition.
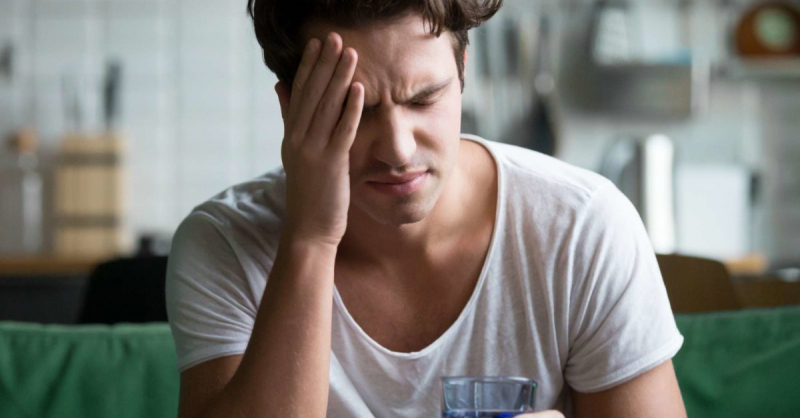

High blood sugar 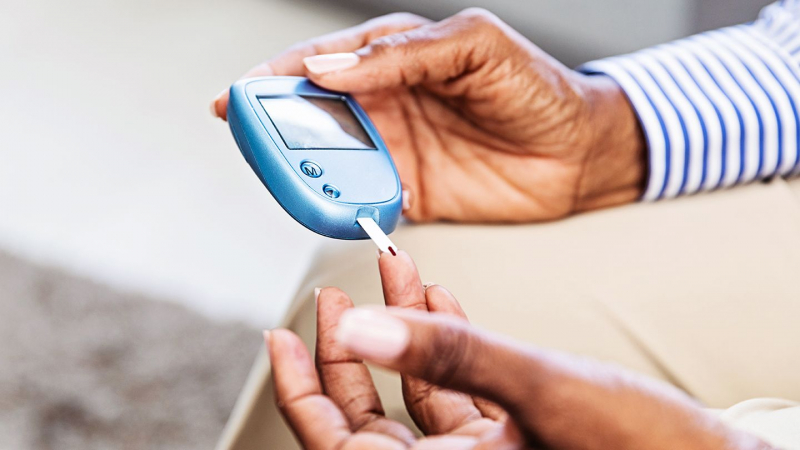
High blood sugar -
Although doctors have not yet proven a link between stress and Alzheimer's disease, stress is considered to produce inflammation of the brain, increasing the risk of various health problems.
According to researchers, one of the elements contributing to the development of Alzheimer's disease may be chronic stress. They claim that chronic stress can have an impact on the brain's immune system, which could result in dementia symptoms. Depression, which is known to increase the chance of developing Alzheimer's, is also linked to stress. In addition, one study discovered that stressful life events (eg. losing a job, going bankrupt, losing a loved one, or facing a financial setback) can age the brain by around 1.5 years, with age obviously being a contributing factor in the onset of the condition.
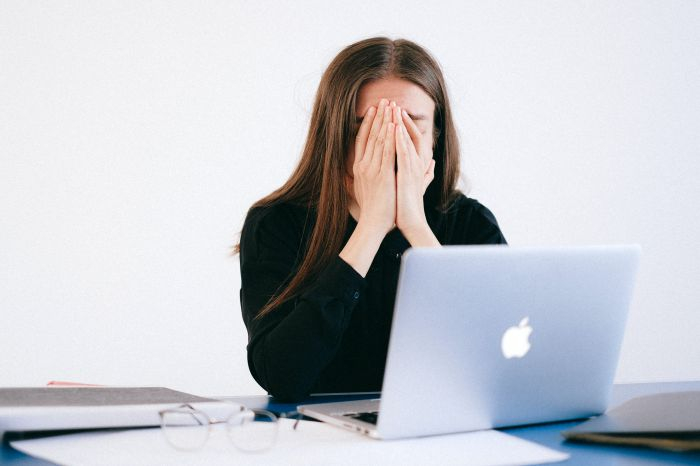

Alzheimer’s disease 
Alzheimer’s disease -
Stress and immunity are inversely correlated, which typically means that the more stressed you are, the less efficient your immune system will be. This is true for stress that is more intense or long-lasting.
The immune system can be affected by stress, which might change its ability to fight against diseases. The immune system's changes may also cause the release of substances linked to inflammation. These changes increase the possibility of getting the flu. Reduced immunity makes you more susceptible to diseases like colds and more serious health problems, so if you're under a lot of stress, you could get sick more often. When exposed to a virus, people who are under severe, prolonged stress (lasting more than a month) are more likely to get the flu than people who are under milder stress.

Common cold 
Common cold -
Public health is significantly impacted by the pandemic of obesity, which is growing quickly. In recent years, there has been many research showing that stress, and in particular, an increase in the glucocorticoid stress hormone cortisol, contributes to the development of obesity.
When under stress, people often turn to "comfort eating", eating foods that are high in fat and sugar in an effort to feel better. The tendency to overeat under pressure increases the likelihood that someone may become obese. Additionally, studies have revealed that those with chronically high cortisol levels were overweight, had higher body mass index (BMI), and had larger waistlines than people with low levels of the hormone.

Obesity 
Obesity -
Chronic or long-term stress can have negative effects, typically it can also worsen depression, a mood disorder that makes you feel down and disinterested in things you find enjoyable. Your sleep patterns, concentration, and appetite can all be affected by depression.
Excessive stress can result in major depression in people who are susceptible to the condition. Chronic stress may wear you down and make you feel overwhelmed when you struggle to handle challenging life situations. This is a result of fluctuating hormone levels, including cortisol, dopamine, and serotonin, which cause a prolonged stress response that can cause depression. Stress-related neglect of a healthy lifestyle, such as excessive drinking and lack of exercise, can also raise the risk of serious depression.

Depression 
Depression -
Stress may cause some types of sleep disorders:
- Insomnia: Insomnia is a problem getting to sleep, staying asleep, or having a good night's sleep in general. Despite having a comfy bed and enough time to sleep, this still happens. Chronic pressures including family issues, work-related issues, the death of a loved one, and severe illness can all cause insomnia. Stressors that last for a short while might also cause symptoms of insomnia. Once the stressful circumstance is passed, these symptoms will often go away. But for some people, a vicious cycle of daytime sleep anxiety and nighttime sleep loss can lead to chronic insomnia.
- Sleep apnoea: Sleep apnoea is a disorder where there is a recurring collapse of the upper airway during sleep. Along with excessive daytime sleepiness and other daytime impairments, this results in loud snoring, choking episodes, and other symptoms. Chronic stress can result in diseases including hypertension, heart disease, obesity, and diabetes, all of which increase one's chance of developing apnea.

Sleep dysfunction 
Sleep dysfunction -
The body becomes ready to respond to stress when a person is under stress. Physical changes in the body may result from this reaction. According to studies, muscle pains discomfort, which often affects the shoulders and neck, can be caused by excessive levels of emotional or psychological stress.
Stress has numerous effects on the shoulders and neck, including:
- Increases the size of the blood vessels in the large muscle groups to facilitate a more rapid oxygen supply.
- Causes the neck, jaw, and shoulders to clench and tighten.
- Increases tension in the muscles that run across the back of your back.
- Limits the mobility of the neck and shoulders.
- Increases your perception of pain and exacerbates any current discomfort.

Neck and shoulder pain 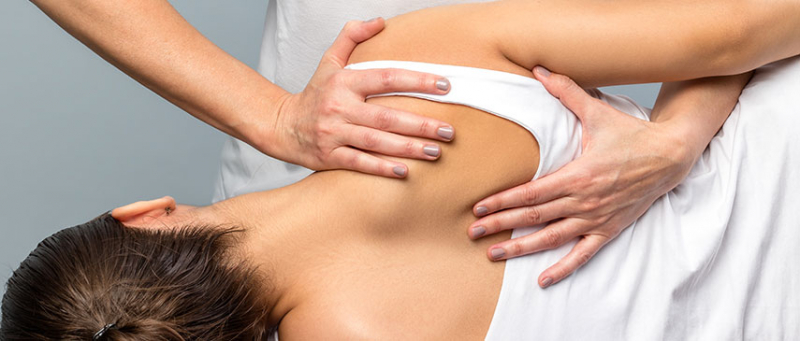
Neck and shoulder pain































